Small Cell Basics 4g 5g
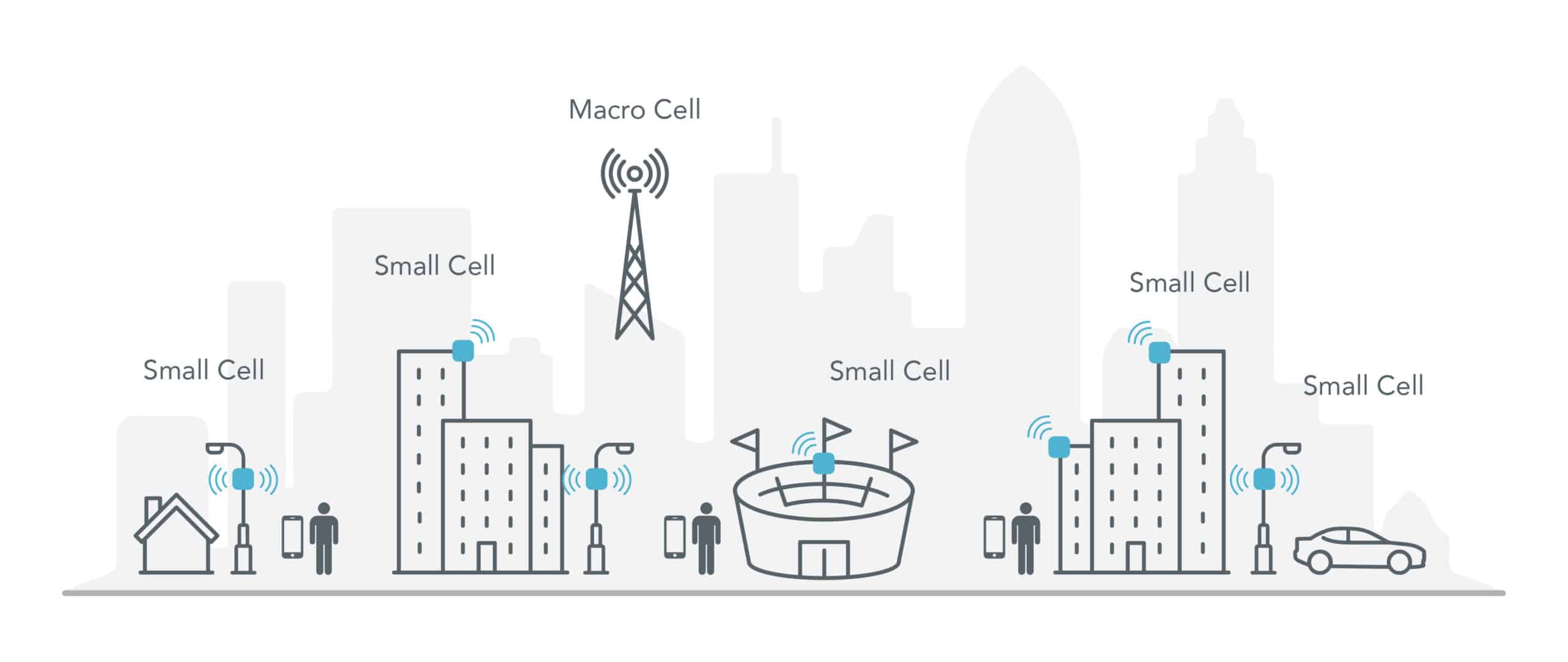
An Introduction To The 5g Small Cell Litepoint A review of how small cells became so popular, how they differ from odas and why they are so important to 5g networks. 5g small cell networks. there are different types of 5g small cells; femtocells, picocells, and microcells, all providing different coverage limits. broadly speaking, femtocells reach 10 meters, picocells 200 meters, and microcells around two kilometers. and the term small cell is a catch all that describes all the above mobile base stations.
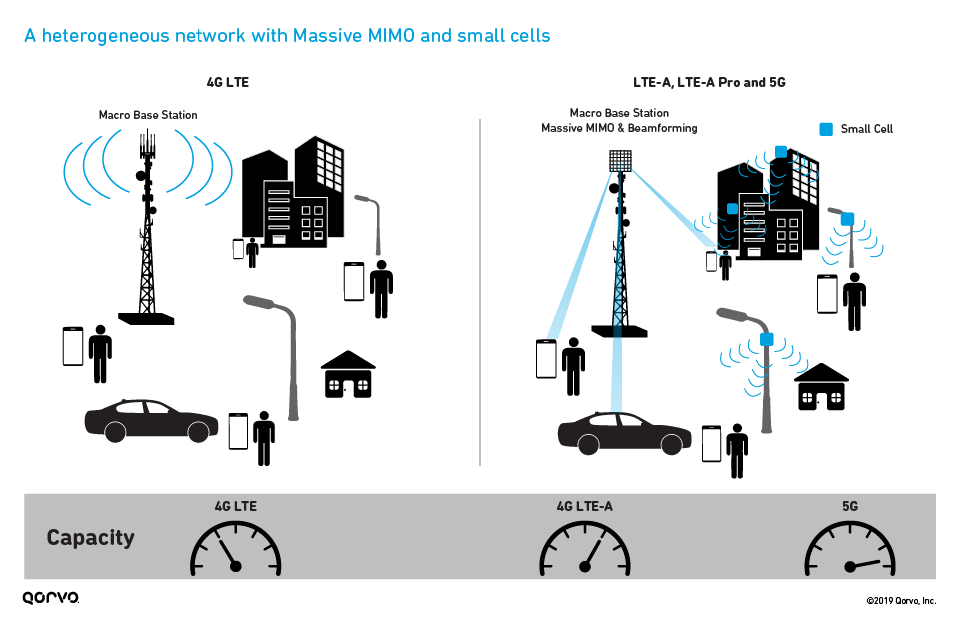
Tips And Trends Small Cell 5g Systems Qorvo One difference is how small cells and femtocells connect back to the network. a small cell connects on a dedicated link. a femtocell connects back on the internet. another difference is a femtocell is private, while a small cell is a public network. femtocells are also smaller than small cells around the size of a paperback book or smaller. Small cells will help companies build denser 5g networks that can reuse bandwidth more efficiently. today’s mobile users want faster data speeds and more reliable service. the next generation of. In fact, 4g small cells operate in sub 3 ghz frequencies and some 5g small cells operate in frequencies lower than the 30 ghz to 300 ghz of millimeter wave (mmwave). what makes a small cell a small cell, then, according to the federal communications commission (fcc), is its height and volume — perhaps not too surprising given its name. more. A small cell is a low cost radio access point with low radio frequency (rf) power output, footprint and range. it can be deployed indoors or outdoors, and in licensed, shared or unlicensed spectrum. small cells deliver high quality, secure cellular coverage indoors and out, complementing the macro network to improve coverage, add targeted.

5g Small Cells Basics 5g Small Cell Types Advantages Manufacturers In fact, 4g small cells operate in sub 3 ghz frequencies and some 5g small cells operate in frequencies lower than the 30 ghz to 300 ghz of millimeter wave (mmwave). what makes a small cell a small cell, then, according to the federal communications commission (fcc), is its height and volume — perhaps not too surprising given its name. more. A small cell is a low cost radio access point with low radio frequency (rf) power output, footprint and range. it can be deployed indoors or outdoors, and in licensed, shared or unlicensed spectrum. small cells deliver high quality, secure cellular coverage indoors and out, complementing the macro network to improve coverage, add targeted. Small cell networks and the evolution of 5g (part 1) may 17, 2017. this is the first blog post in a 2 part series looking at small cell base stations. part 1 covers the basics of small cells and how they fit into the evolution of 4g and 5g. part 2 will look at the latest trends and design challenges in the small cell market. Thus the need for coverage indoors and in large venues like stadiums is prevalent, where capacity is a significant issue – that’s where small cell systems play as the leading solution. under the 5g small cell umbrella, one will find the following cell types: 1. femtocells – 0.001 0.25 (w) output power & 0.010 0.1 (km) cell radius. 2.

Comments are closed.