Skeleton Posterior View
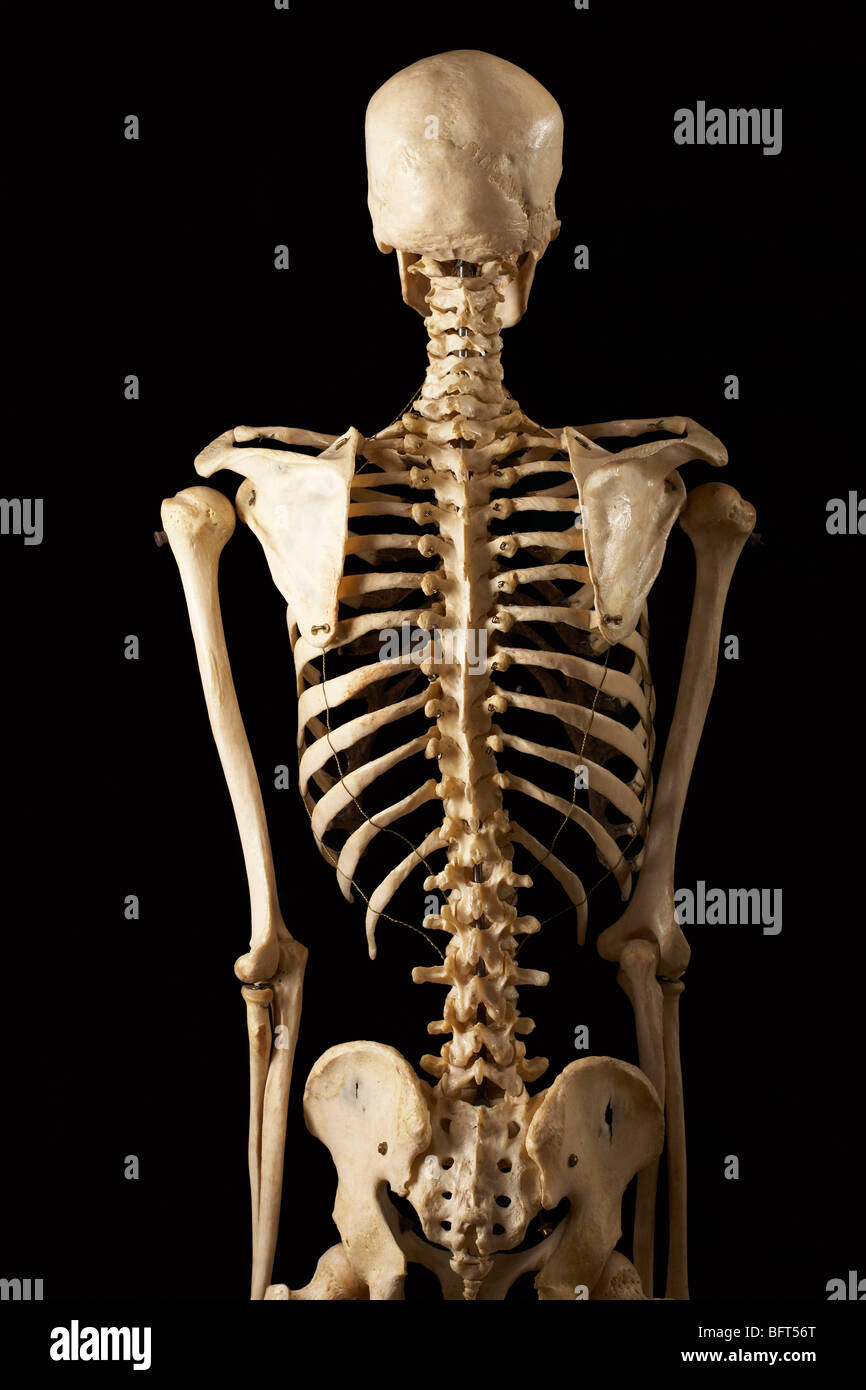
Posterior View Of Skeleton Stock Photo Alamy The skeletal system. explore the skeletal system with our interactive 3d anatomy models. learn about the bones, joints, and skeletal anatomy of the human body. the skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body. each bone is a complex living organ that is made up of many cells, protein fibers, and minerals. Occipital bone. flat skull bone articulating with the parietal bone and atlas (first cervical vertebra), among others; it makes up the largest portion of the base of the skull. lateral view of skull.
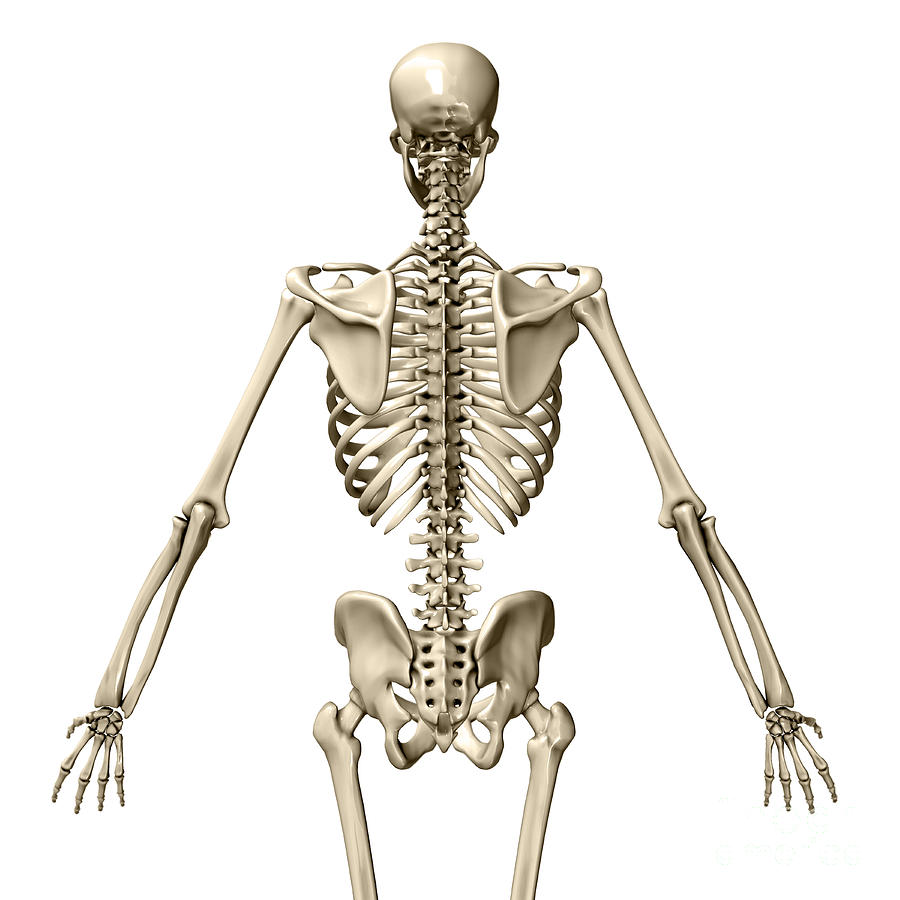
Human Skeleton Posterior View Photograph By Evan Oto Fine Art America Anatomy systems. skeletal system the skeletal system includes all of the bones and joints in the body. muscular system the muscular system is responsible for the movement of the human body. cardiovascular system the cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and the approximately 5 liters of blood that the blood vessels transport. Skeletal system (anterior view) from the moment you open your eyes in the morning until you go to bed, you move around. even during sleep you may fret, twist, and turn. every movement that you do, no matter how inconspicuous, consists of a complex series of events with an equally complex anatomy behind the scenes. The anterior view is the front of the body, and the posterior view is the back of the body. see an illustration of the standard anatomical position of a human body in both anterior and posterior views in figure 2.7. [1] figure 2.7 standardized anatomical view of the human body in (a) anterior view and (b) posterior view. Anatomical terms of location. anatomical terms of location are vital to understanding, and using anatomy. they help to avoid any ambiguity that can arise when describing the location of structures. learning these terms can seem a bit like a foreign language to being with, but they quickly become second nature.
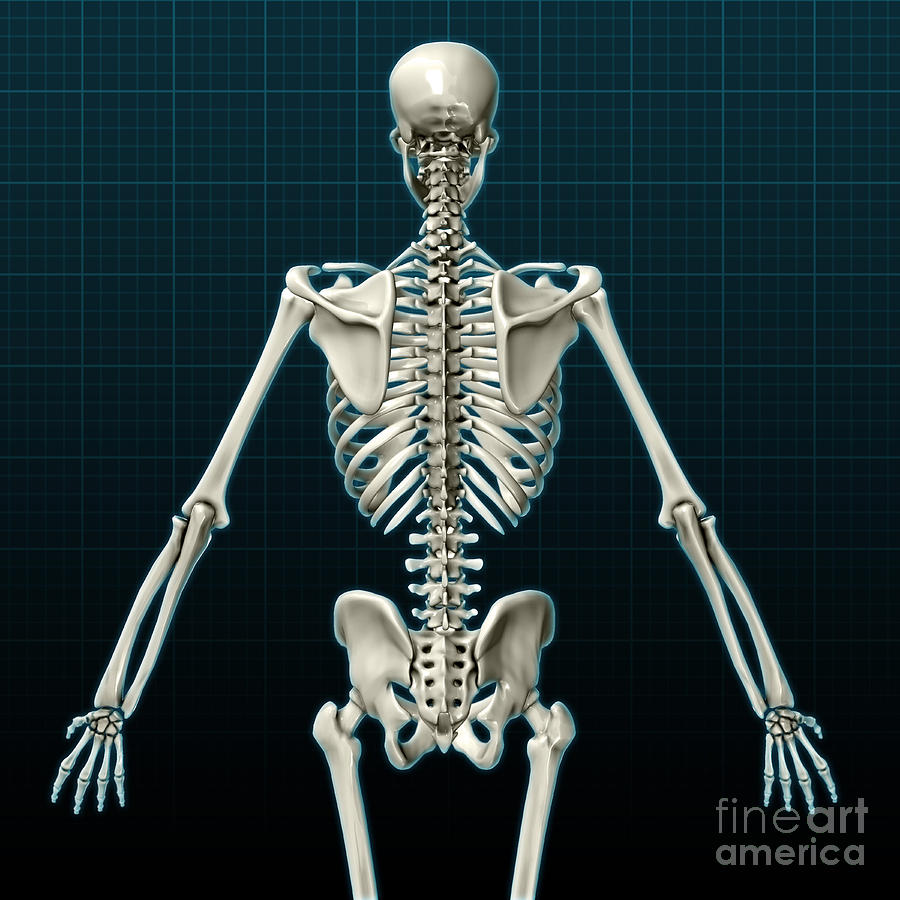
Skeleton Viewer The anterior view is the front of the body, and the posterior view is the back of the body. see an illustration of the standard anatomical position of a human body in both anterior and posterior views in figure 2.7. [1] figure 2.7 standardized anatomical view of the human body in (a) anterior view and (b) posterior view. Anatomical terms of location. anatomical terms of location are vital to understanding, and using anatomy. they help to avoid any ambiguity that can arise when describing the location of structures. learning these terms can seem a bit like a foreign language to being with, but they quickly become second nature. Human skeleton, the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. this framework consists of many individual bones and cartilages. there also are bands of fibrous connective tissue —the ligaments and the tendons —in intimate relationship with the parts of the skeleton. this article is concerned primarily with the gross. 3. the skeleton protects vital organs. the brain is surrounded by bones that form part of the skull. the heart and lungs are located within the thoracic cavity, and the vertebral column provides structure and protection for the spinal cord. 4. interactions between the skeleton, muscles, and nerves move the body.
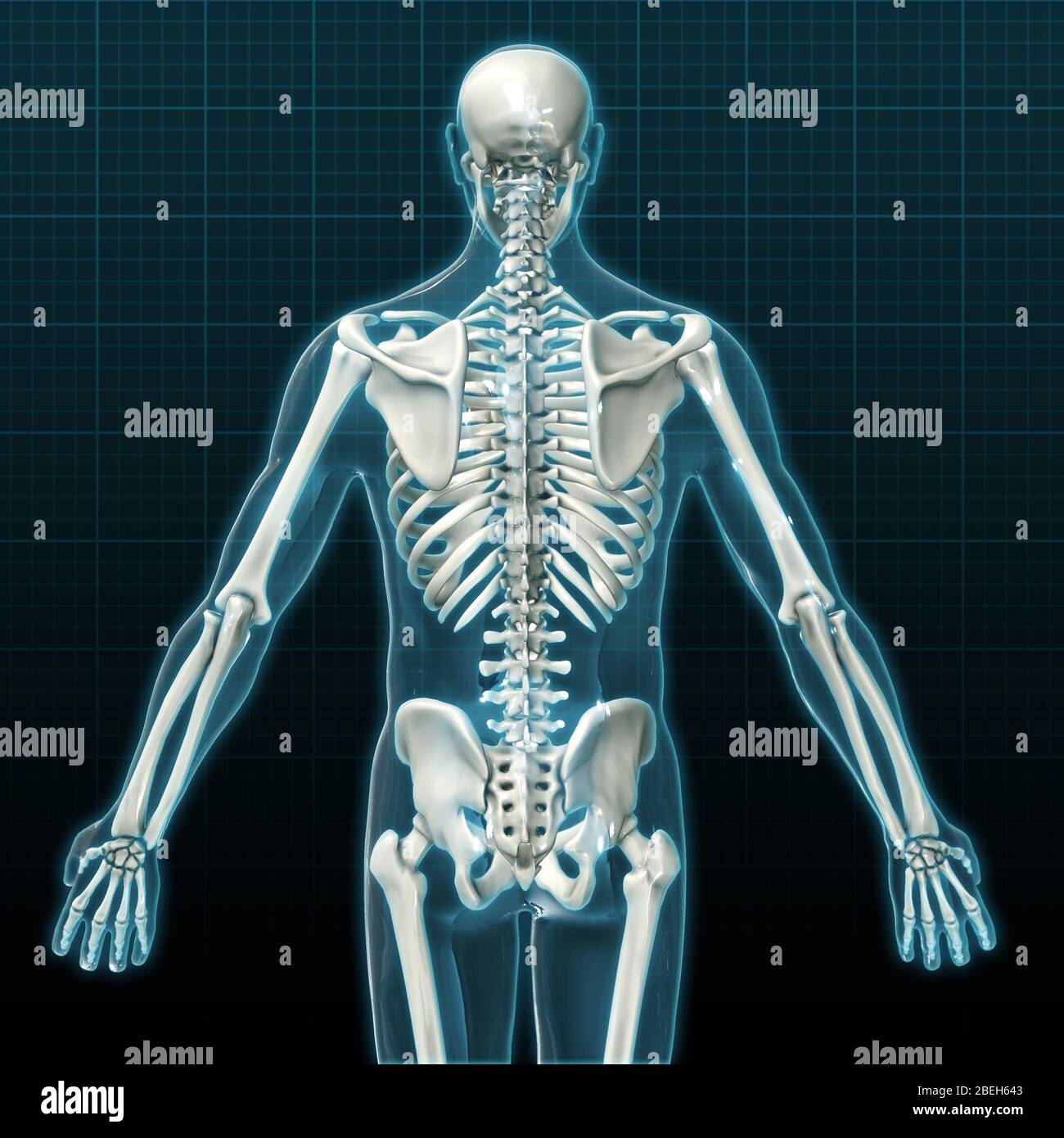
Human Skeleton Posterior View Hi Res Stock Photography And Images Alamy Human skeleton, the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. this framework consists of many individual bones and cartilages. there also are bands of fibrous connective tissue —the ligaments and the tendons —in intimate relationship with the parts of the skeleton. this article is concerned primarily with the gross. 3. the skeleton protects vital organs. the brain is surrounded by bones that form part of the skull. the heart and lungs are located within the thoracic cavity, and the vertebral column provides structure and protection for the spinal cord. 4. interactions between the skeleton, muscles, and nerves move the body.
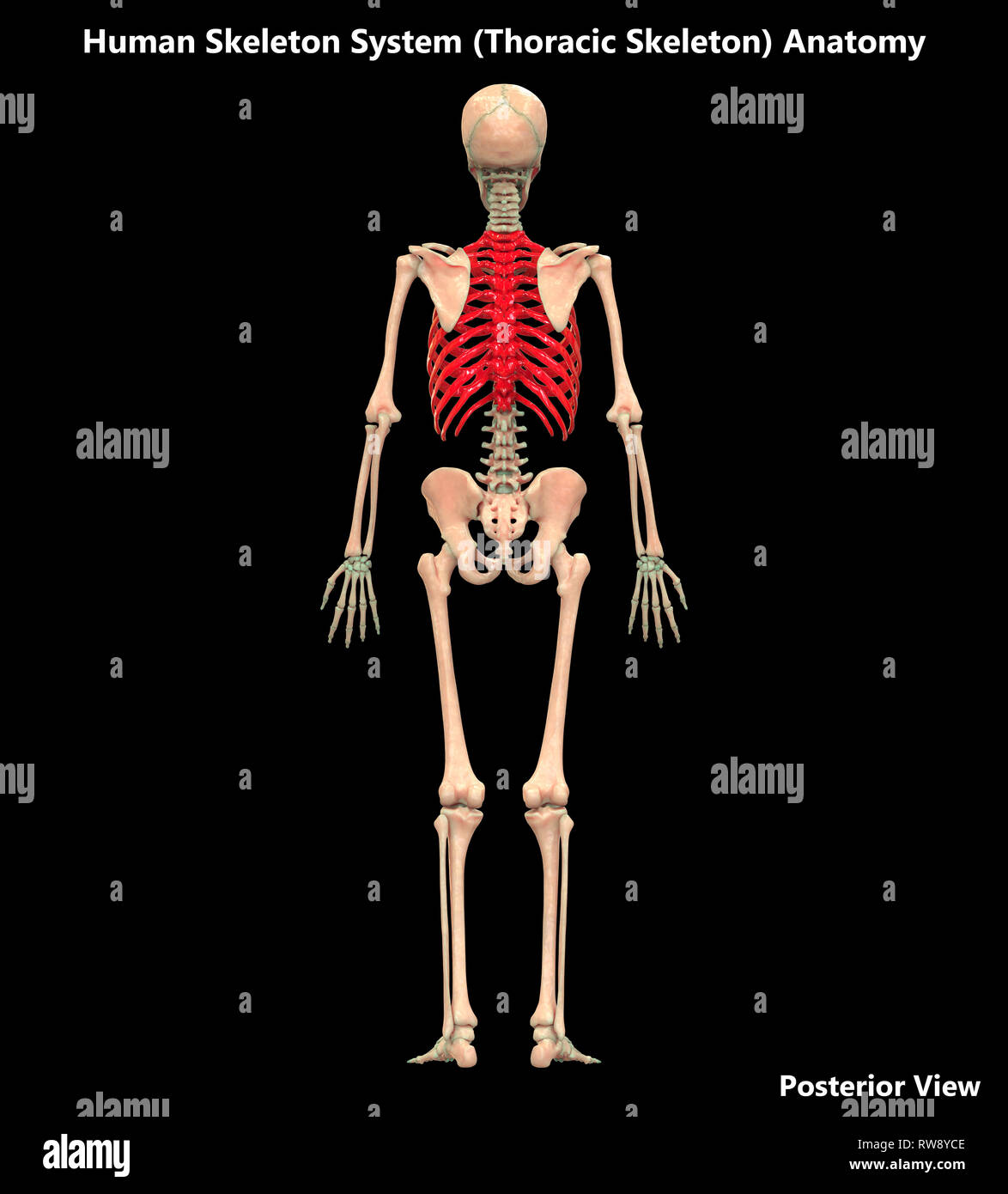
Human Skeleton System Anatomy Posterior View Stock Photo Alamy

Comments are closed.