Skeleton Hands Anatomy

Skeletal Anatomy Of The Hand Hand Clinics Carpal bones (proximal) – a set of eight irregularly shaped bones. they are located in the area of the wrist. metacarpals – a set of five bones, each one related to a digit. they are located in the area of the palm. phalanges (distal) – the bones of the digits. the thumb has two phalanges, whilst the rest of the fingers have three. Those are flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction of the hand. take this specially designed quiz to test your knowledge about the hand and wrist. it specifically focuses on bones, muscles (including attachments, innervation, functions), arteries, veins, and nerves. custom quiz: wrist anatomy start quiz.

Skeletal Anatomy Of The Hand Trialexhibits Inc Triquetrum. pisiform. trapezium. trapezoid. capitate. hamate. together, these bones connect the lower arm to the hand and fingers as the proximal carpal bones articulate with the radius and ulna to form the wrist joint. these bones articulate with each other, allowing wrist movement so we can perform common daily activities with our hands. Rotation of the radius around the ulna results in the supination and pronation of the hand. these bones also form the flexible wrist joint with the proximal row of the carpals. there are eight small carpal bones in the wrist that are firmly bound in two rows of four bones each. the mass that results from these bones is called the carpus. Capitate: the largest of the wrist bones, this rests between the trapezoid and the hamate behind the middle and ring fingers. hamate: this small bone has a hook on the palmar side. it rests next. Trapezoid. capitate. hamate. your radius (the larger of the two bones in your forearm) forms a joint your scaphoid and lunate bones to form the part of your wrist that helps it move and rotate. the carpal tunnel is a rounded space between your pisiform, hamate, scaphoid and trapezium. this space is a literal tunnel in your wrist that lets nine.
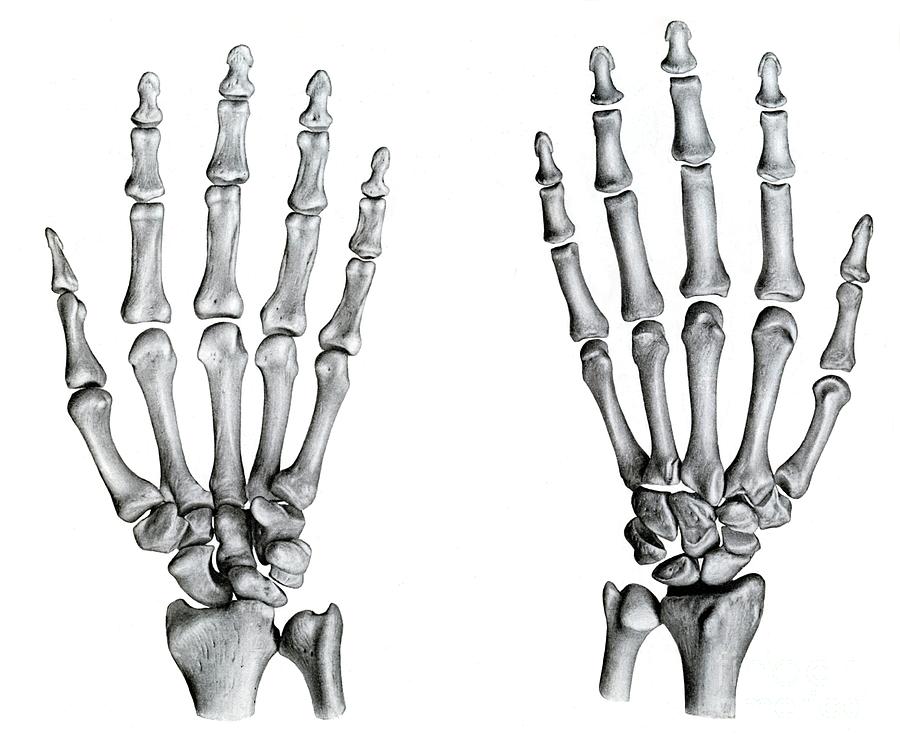
Hand Skeletal Anatomy Capitate: the largest of the wrist bones, this rests between the trapezoid and the hamate behind the middle and ring fingers. hamate: this small bone has a hook on the palmar side. it rests next. Trapezoid. capitate. hamate. your radius (the larger of the two bones in your forearm) forms a joint your scaphoid and lunate bones to form the part of your wrist that helps it move and rotate. the carpal tunnel is a rounded space between your pisiform, hamate, scaphoid and trapezium. this space is a literal tunnel in your wrist that lets nine. Nerves of the hand. the ulnar nerve (c8 t1 nerve roots) arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and supplies all of the intrinsic muscles of the hand with a few exceptions. these are the muscles of the thenar eminence and the radial two lumbricals, which are supplied by the median nerve (c5 t1). 1 8. synonyms: none. the carpal bones (i.e. carpus) are eight irregularly shaped bones located in the wrist region. these bones connect the distal aspects of the long bones of the forearm (radius and ulna) to the proximal aspects of the metacarpal bones. the carpal bones are organized in two rows: proximal and distal.

Hand Definition Anatomy Bones Diagram Facts Britannica Nerves of the hand. the ulnar nerve (c8 t1 nerve roots) arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus and supplies all of the intrinsic muscles of the hand with a few exceptions. these are the muscles of the thenar eminence and the radial two lumbricals, which are supplied by the median nerve (c5 t1). 1 8. synonyms: none. the carpal bones (i.e. carpus) are eight irregularly shaped bones located in the wrist region. these bones connect the distal aspects of the long bones of the forearm (radius and ulna) to the proximal aspects of the metacarpal bones. the carpal bones are organized in two rows: proximal and distal.

Comments are closed.