Skeletal System The Skeletal System Hap Unit 4th The Skeletal System
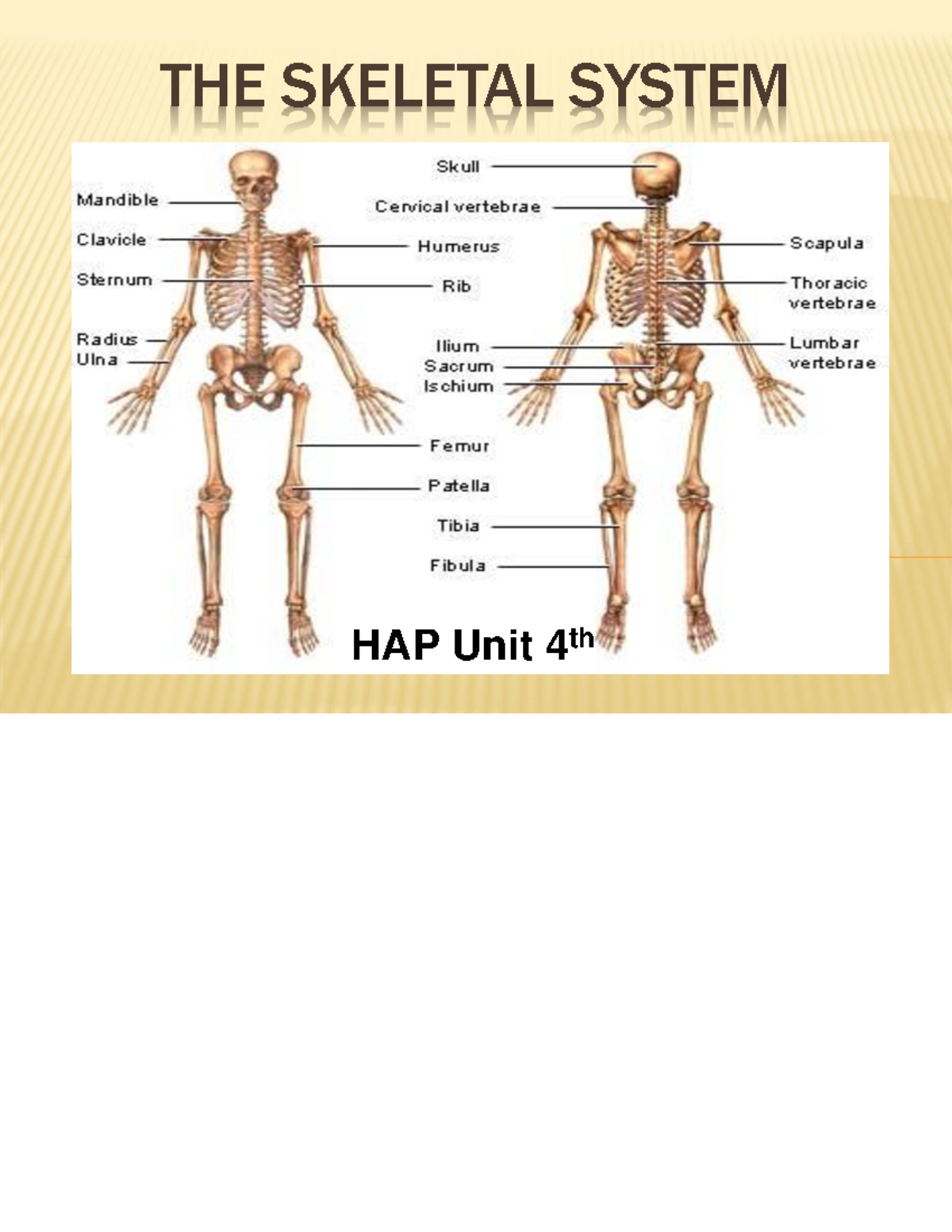
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Hap Unit 4th The Skeletal System Bones and tendons. which of the following is not a function of the skeletal system? 1. promoting the interface of muscles with nerves. 2. serving as a reservoir of calcium. 3. protection of organ structures. 4. facilitating movement. 5. blood cell production. promoting the interface of muscles with nerves. how is skeletal homeostasis related to. Bursitis. inflammation of bursae. dislocation. when a bone is displaced from a joint. scoliosis. a side to side or lateral curvature of the spine. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like list the five functions of bones., name the eight bones that form the cranium, name the twenty six vertebrae. and more.

Your Online Doctor Human Skeletal System The skeletal system hap unit 4th the skeletal system parts of the skeletal system include: bones (skeleton) joints cartilages ligaments divided into two divisions: axial skeleton (skull, ribs and vertebra) appendicular skeleton (pelvis, extremities) bones of the human body the adult skeleton has 206 bones. Terms in this set (134) four main functions of the skeletal system. support and movement, organ protection, storage of calcium and phosphorus salts, and sites for muscular attachment. axial skeleton. skull, vertebral column, sternum, laryngeal skeleton, and thoracic cage. appendicular skeleton. The skeletal system. the skeletal system consists of bones, joints, cartilages, and ligaments. functions of the skeletal system: support of the body; protection of soft organs; movement due to attached skeletal muscles; storage of minerals and fats; blood cell formation; bones of the human body. the adult skeleton has 206 bones. A. bone tissue and the skeletal system. your skeleton is a structure of living tissue that grows, repairs, and renews itself. the bones within it are dynamic and complex organs that serve a number of important functions, including some necessary to maintain homeostasis. the skeletal system forms the rigid internal framework of the body.
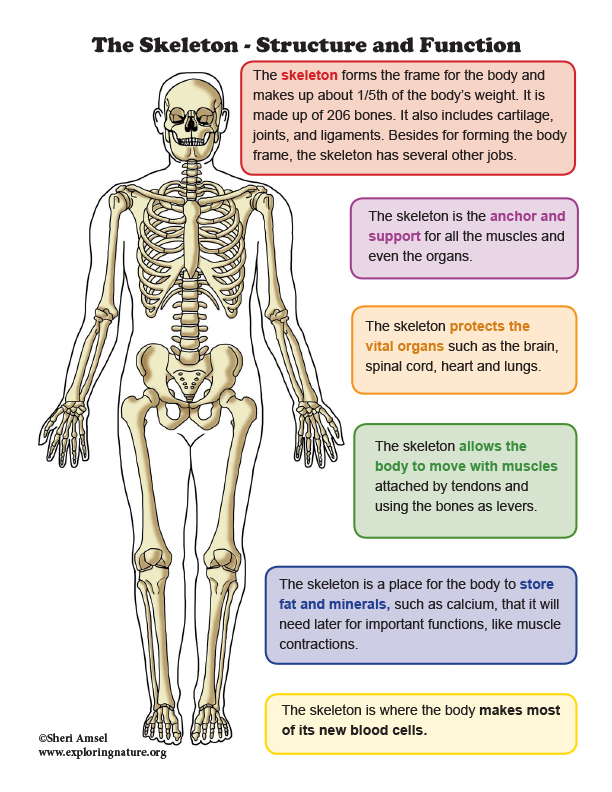
Skeletal System Structure And Function The skeletal system. the skeletal system consists of bones, joints, cartilages, and ligaments. functions of the skeletal system: support of the body; protection of soft organs; movement due to attached skeletal muscles; storage of minerals and fats; blood cell formation; bones of the human body. the adult skeleton has 206 bones. A. bone tissue and the skeletal system. your skeleton is a structure of living tissue that grows, repairs, and renews itself. the bones within it are dynamic and complex organs that serve a number of important functions, including some necessary to maintain homeostasis. the skeletal system forms the rigid internal framework of the body. The skeletal system is divided into the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. the axial skeleton forms the body's central axis and includes the skull, vertebral column, and bony thorax. the skull is composed of two sets of bones the cranium and facial bones. the cranium is made up of eight flat bones: the frontal, parietal, temporal. The skeletal system’s main function is to provide support for the body. for example, the spinal column provides support for the head and torso. the legs, on the other hand, support and bear the.
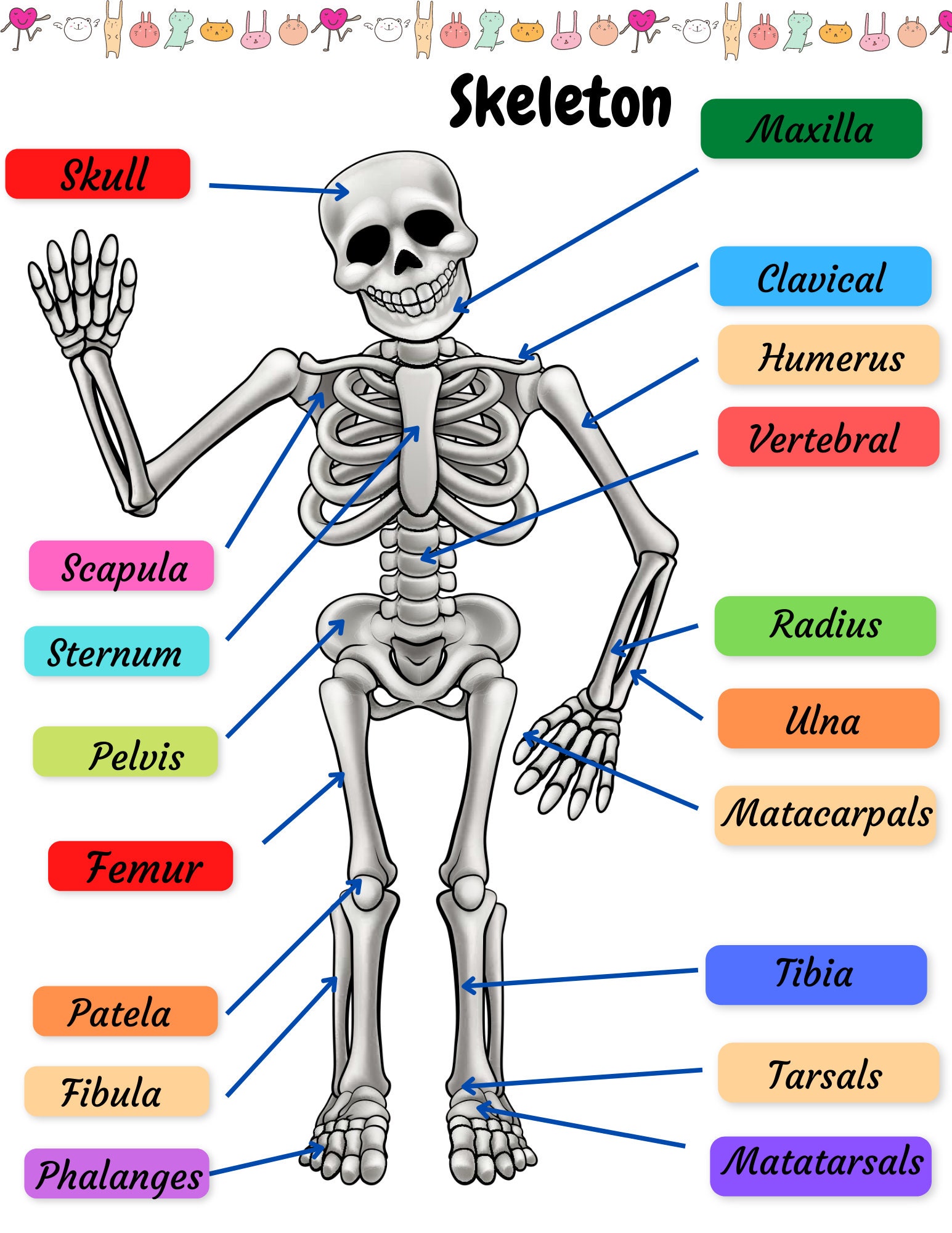
Skeletal System Practice Page Human Bones Activities Sheet Skeleton The skeletal system is divided into the axial skeleton and appendicular skeleton. the axial skeleton forms the body's central axis and includes the skull, vertebral column, and bony thorax. the skull is composed of two sets of bones the cranium and facial bones. the cranium is made up of eight flat bones: the frontal, parietal, temporal. The skeletal system’s main function is to provide support for the body. for example, the spinal column provides support for the head and torso. the legs, on the other hand, support and bear the.

Comments are closed.