Skeletal System Anaphy Online Review Guide For Anatomy And Physiology
Skeletal System Anaphy Online Review Guide For Anatomy And Physiology Learn anatomy faster andremember everything you learn. a free website study guide review that uses interactive animations to help you learn online about anatomy and physiology, human anatomy, and the human body systems. start learning now!. 2 the brain : can you name the main anatomical areas of the brain? 3 the cell : learn the anatomy of a typical human cell. 4 the skull : do you know the bones of the skull? 5 the axial skeleton : how about the bones of the axial skeleton? 6 the heart : name the parts of the human heart.
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs Classification of bones. the adult skeleton is composed of 206 bones and there are two basic types of osseous, or bone, tissue: compact bone and spongy bone, and are classified into four groups according to shape: long, short, flat, and irregular. compact bone. compact bone is dense and looks smooth and homogeneous. Essentials of human anatomy and physiology anatomy skeletal system. 59 terms. autumn7536. preview. ch 16 pt 1. 36 terms. s6028. preview. study guide for tomorrow. Skeletal system. protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. made up of bones and joints. skeleton. derived from the greek word, meaning dried. joint. it is an area where two bones come together. functions of skeletal system. support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell production. Resumen. the skeletal system is made up of bones, cartilage, and other connective tissues that provide support and structure to the body. the primary functions of the skeletal system are to protect internal organs, provide support for the body, allow for movement, produce blood cells, and store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus.
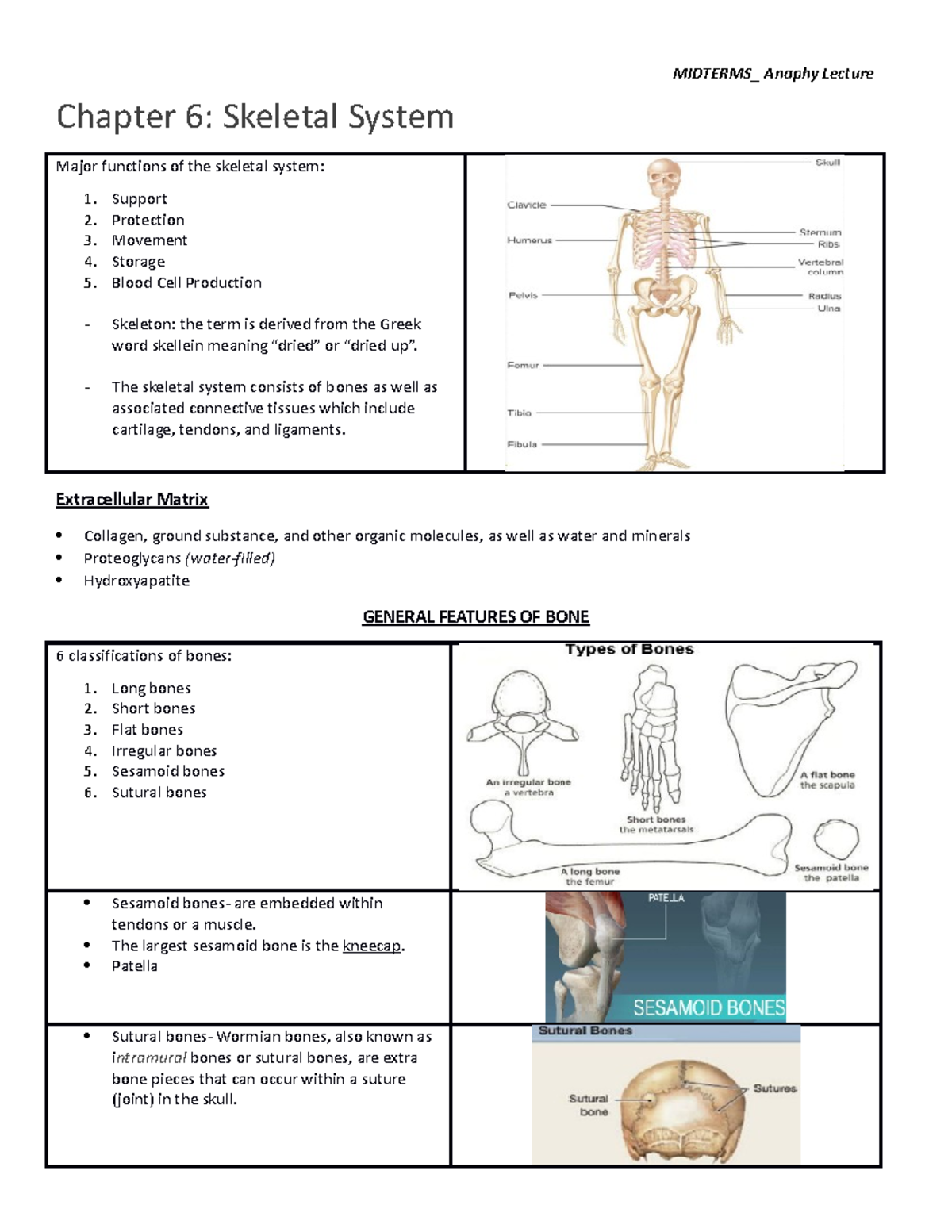
Chap 6 Anaphy Chapter 6 Skeletal System Major Skeletal system. protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. made up of bones and joints. skeleton. derived from the greek word, meaning dried. joint. it is an area where two bones come together. functions of skeletal system. support, protection, movement, storage, blood cell production. Resumen. the skeletal system is made up of bones, cartilage, and other connective tissues that provide support and structure to the body. the primary functions of the skeletal system are to protect internal organs, provide support for the body, allow for movement, produce blood cells, and store minerals such as calcium and phosphorus. 25.0 introduction. 25.1 internal and external anatomy of the kidney. 25.2 microscopic anatomy of the kidney: anatomy of the nephron. 25.3 physiology of urine formation: overview. 25.4 physiology of urine formation: glomerular filtration. 25.5 physiology of urine formation: tubular reabsorption and secretion. The 5 major functions of the skeletal system include: support, protection, movement, storage, and blood cell production. for support (major function of the skeletal system) provides firm yet flexible support within certain structures, such as the nose, external ear, thoracic cage, and trachea. cartilage.
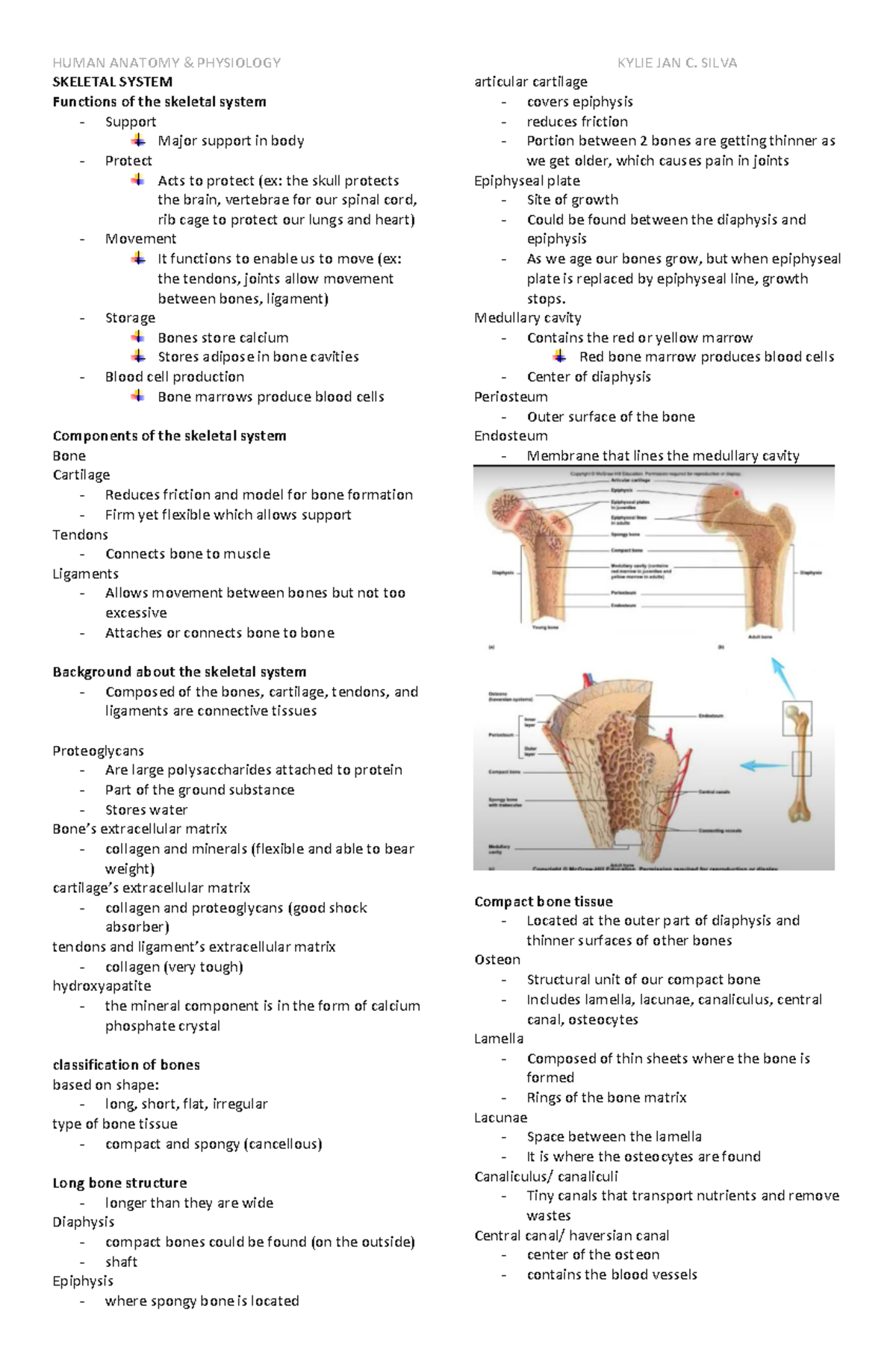
Anaphy Chapter 6 Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions Of The 25.0 introduction. 25.1 internal and external anatomy of the kidney. 25.2 microscopic anatomy of the kidney: anatomy of the nephron. 25.3 physiology of urine formation: overview. 25.4 physiology of urine formation: glomerular filtration. 25.5 physiology of urine formation: tubular reabsorption and secretion. The 5 major functions of the skeletal system include: support, protection, movement, storage, and blood cell production. for support (major function of the skeletal system) provides firm yet flexible support within certain structures, such as the nose, external ear, thoracic cage, and trachea. cartilage.
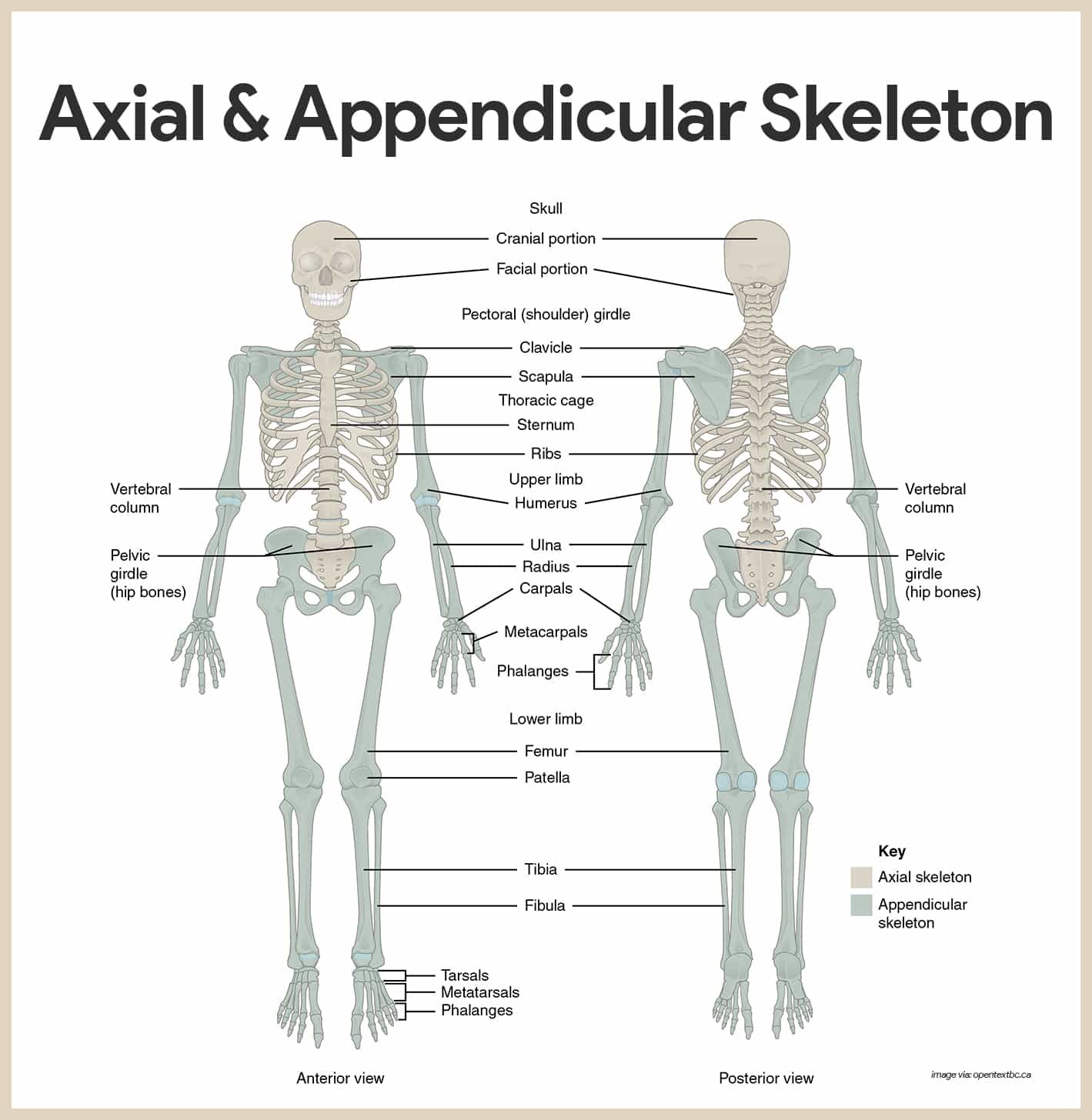
Skeletal System Anatomy And Physiology Nurseslabs

Comments are closed.