Shoulder Examination Practical Clinical Examination Skills

Shoulder Examination Practical Clinical Examination Skills Youtube This video shows you how to conduct a clinical examination of the shoulder and to identify common causes of pain.this video clip is part of the fifa diploma. The examiner must support the arm of the patient at the level of the elbow so that the upper extremity can be as much relaxed as possible. then the examiner has to internally rotate the shoulder while at the same time perform a cross body adduction of the arm. the test is positive if pain is elicited.

Shoulder Examination Step 1 Inspection Step 2 Palpation Physical Shoulder examination challenges caveats much clinical overlap between pathologies a myriad of examination skills, often given eponyms for their creators, most of which have limited diagnostic accuracy maneuvers are taught as if they are pathognomonic they are not! no single maneuver can be relied upon for the diagnosis. The scarf test assesses the function of the acromioclavicular joint. 1. passively flex the shoulder joint to 90° and ask the patient to place the hand on the side you are examining on to the contralateral shoulder. 2. apply resistance to the elbow in the direction of the contralateral shoulder. Read chapter 15 of practical guide to history taking, physical exam, and functioning in the hospital and clinic online now, exclusively on accessmedicine. accessmedicine is a subscription based resource from mcgraw hill that features trusted medical content from the best minds in medicine. Stabilize the scapula, and slide the humeral head anteriorly and posteriorly within the glenoid fossa to evaluate the stability of the joint. note the axial load being applied to the elbow. position the patient sitting. internally rotate the arm with the thumb facing downward, and abduct and forward flex the arm.
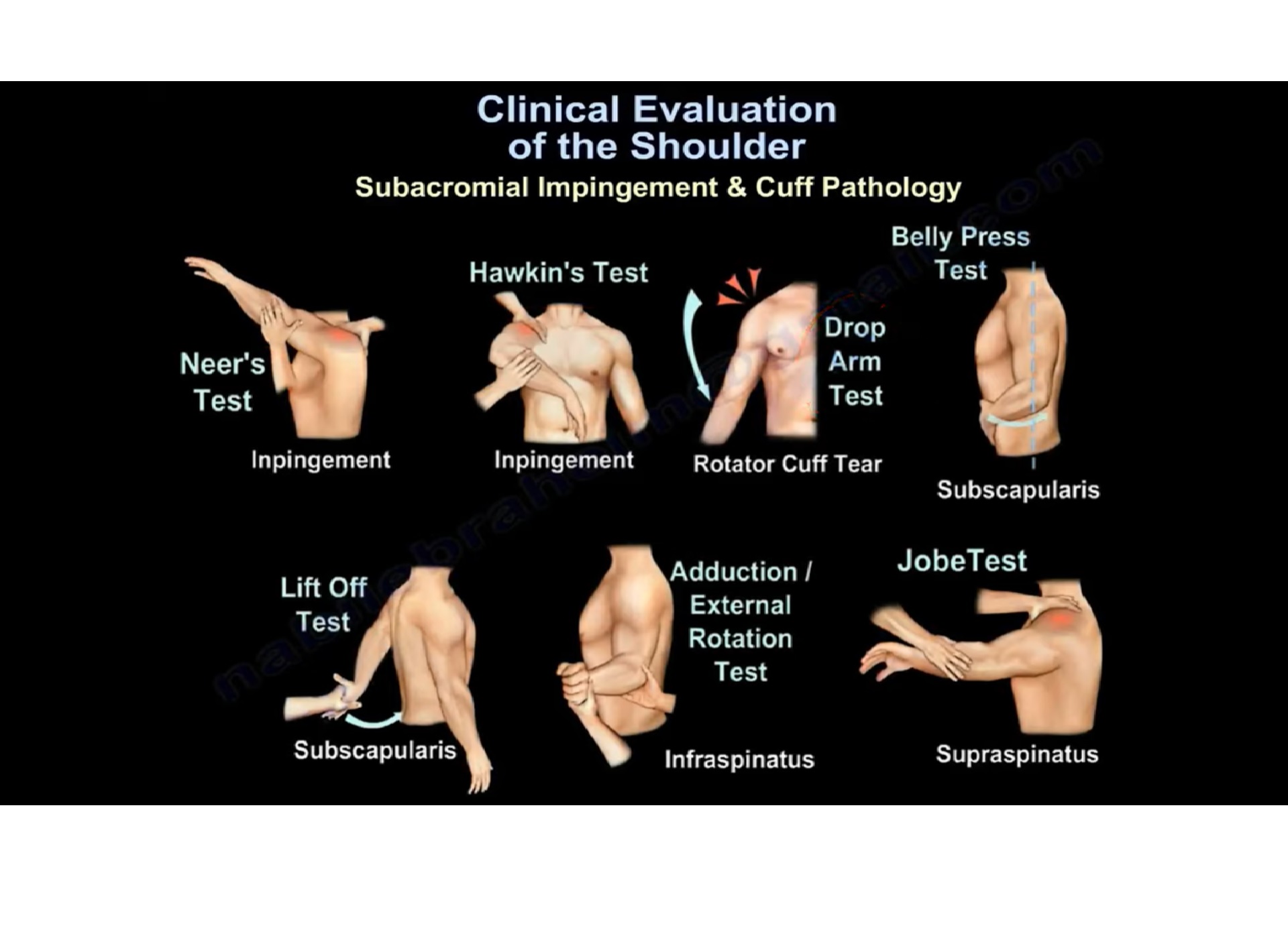
Clinical Evaluation Of The Shoulder Orthopaedicprinciples Read chapter 15 of practical guide to history taking, physical exam, and functioning in the hospital and clinic online now, exclusively on accessmedicine. accessmedicine is a subscription based resource from mcgraw hill that features trusted medical content from the best minds in medicine. Stabilize the scapula, and slide the humeral head anteriorly and posteriorly within the glenoid fossa to evaluate the stability of the joint. note the axial load being applied to the elbow. position the patient sitting. internally rotate the arm with the thumb facing downward, and abduct and forward flex the arm. A. clinical examination 1. vital to successful treatment of shoulder patients 2. must be thorough and systematic a. rule out & rule in 3. main purpose is to establish underlying cause of symptoms 4. also determines where to start with patient a. tolerance level ßà aggressiveness of program b. components of clinical exam 1. subjective history 2. Introduction to pe, vitals and skin screening pe. eye exam. head and neck exam. lung, thorax and spine exams. examination of the heart. abdominal exam. neuro exam. review of cranial nerves. musculoskeletal examination: general principles and detailed evaluation of the knee and shoulder.

Shoulder Examination Osce Guide Latest Ukmla Cpsa Youtube A. clinical examination 1. vital to successful treatment of shoulder patients 2. must be thorough and systematic a. rule out & rule in 3. main purpose is to establish underlying cause of symptoms 4. also determines where to start with patient a. tolerance level ßà aggressiveness of program b. components of clinical exam 1. subjective history 2. Introduction to pe, vitals and skin screening pe. eye exam. head and neck exam. lung, thorax and spine exams. examination of the heart. abdominal exam. neuro exam. review of cranial nerves. musculoskeletal examination: general principles and detailed evaluation of the knee and shoulder.

Shoulder Examination Orthopaedics Oxford Medical Education

Comments are closed.