Short Run Supply Curve In Perfect Competition
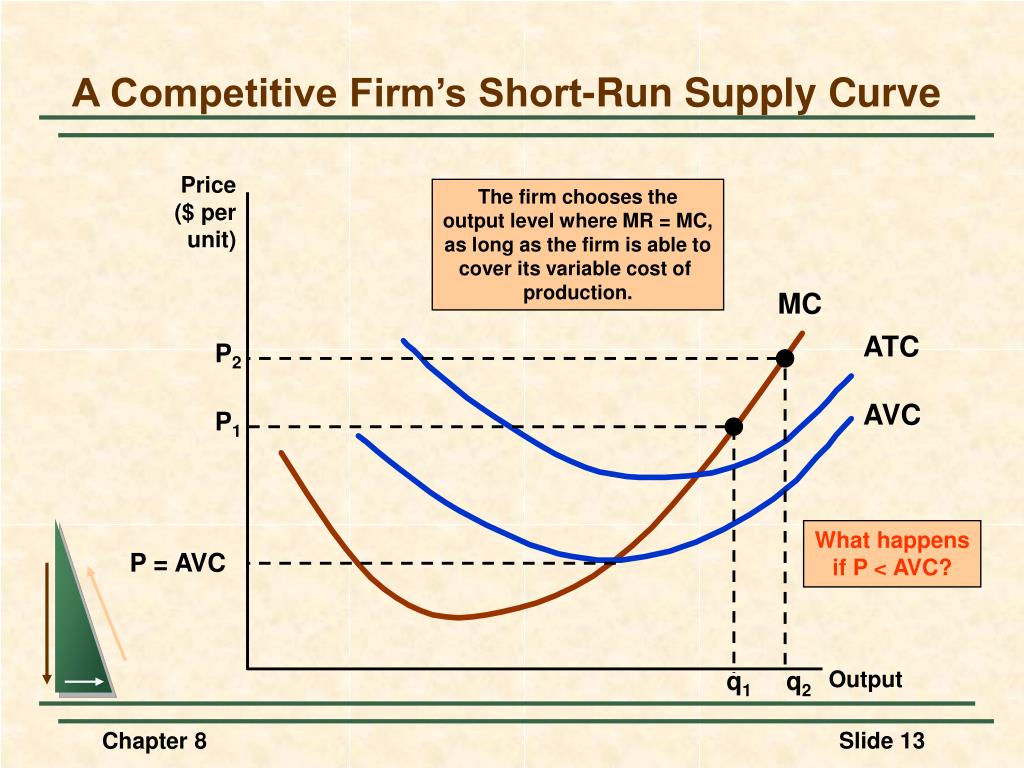
Ppt Perfectly Competitive Markets Powerpoint Presentation Free A deep understanding of how competitive markets work and are formed is the cornerstone to understand why it’s so hard to reach them. in this first learning path on perfect competition, we start by analysing firms’ cost structure, before analysing their interaction in the market. perfect competition. period analysis. short run cost analysis. The price is set by the industry supply and demand. firms are price takers; this means their demand curve is perfectly elastic. if they set a higher price, nobody would buy because of perfect knowledge. therefore firms have an elastic demand curve. in the long run firms in perfect competition will make normal profits. diagram of perfect competition.

Short Run Supply Curve Of A Firm Cases In Short Run Supply Curve Of A Learn how a firm maximizes its profits by choosing the level of output where its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost in a perfectly competitive market. see how the firm's short run supply curve is derived from its marginal cost curve and how it may shut down in the short run if its losses are too high. Learn how the supply curve of a firm and an industry changes in the short run and long run under perfect competition. see diagrams and examples of constant, increasing and decreasing cost industries. Long run equilibrium of the firm: perfect competition. in the long run equilibrium, firms adjust their capacity to produce at the minimum point of lac, given the technology and factor prices. at the equilibrium, smc = lmc = lac = p = mr. in the long run equilibrium, both short run and long run equilibrium conditions coincide. The short run supply curve of firms in perfect competition is the upsloping portion of the marginal cost curve (above the average variable cost intersection). indeed, a firm determines its optimum volume of sales by taking the intersection of marginal revenue and marginal cost.
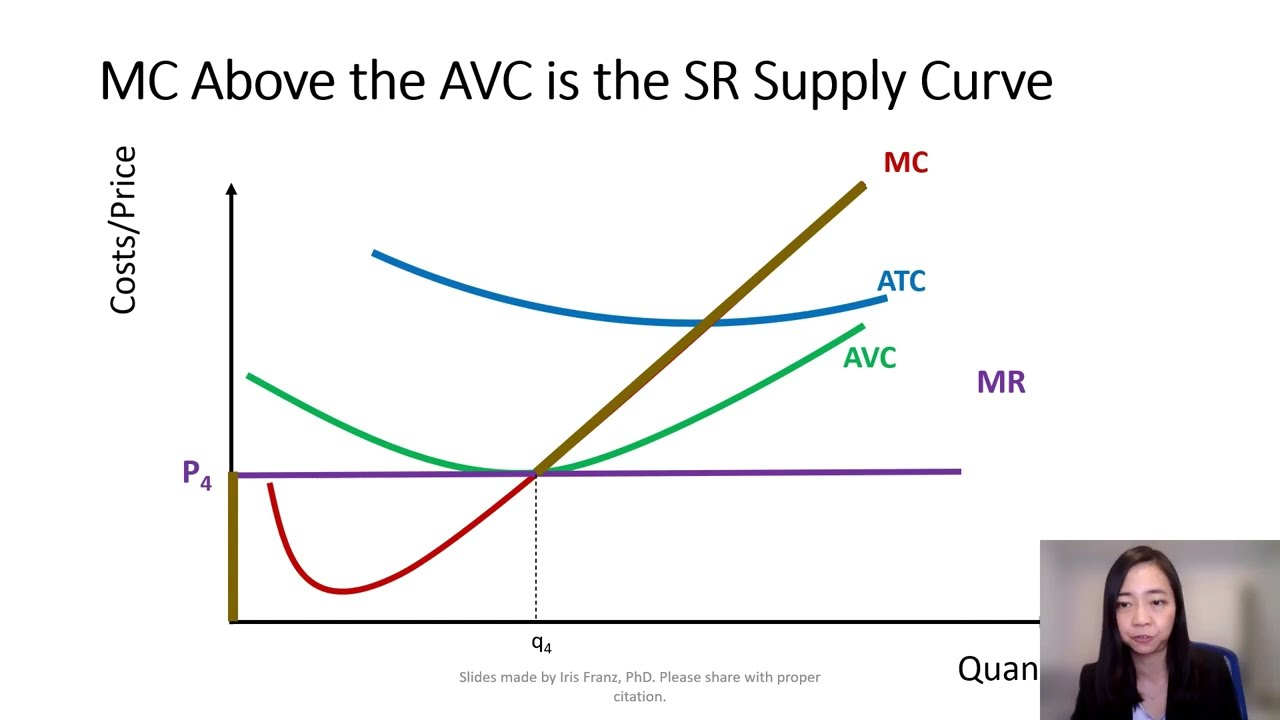
Perfect Competition 8 Short Run Supply Curve Youtube Long run equilibrium of the firm: perfect competition. in the long run equilibrium, firms adjust their capacity to produce at the minimum point of lac, given the technology and factor prices. at the equilibrium, smc = lmc = lac = p = mr. in the long run equilibrium, both short run and long run equilibrium conditions coincide. The short run supply curve of firms in perfect competition is the upsloping portion of the marginal cost curve (above the average variable cost intersection). indeed, a firm determines its optimum volume of sales by taking the intersection of marginal revenue and marginal cost. Learn how firms maximize profit in the short run and long run under perfect competition. the short run supply curve shifts to the right as firms enter the industry, while the long run supply curve is a horizontal line at the minimum point on the average cost curve. Market long run supply curve: the market supply curve is actually a short run supply curve. that is because in the short run, the market can produce more at high prices and less at low prices. the long run supply curve is a perfectly elastic (horizontal) curve at the bottom of the firm’s atc.
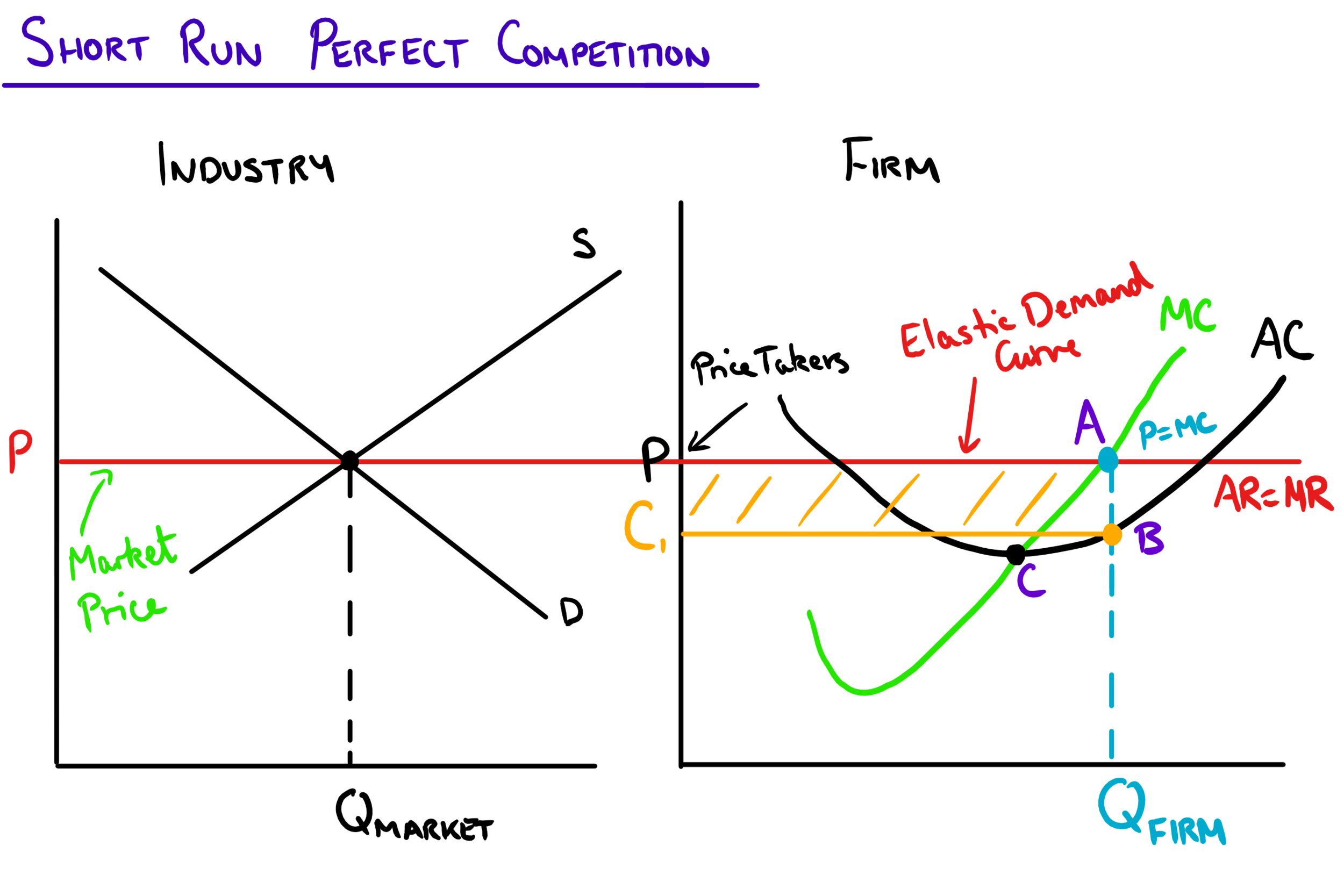
Perfect Competition Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources Tutoring Learn how firms maximize profit in the short run and long run under perfect competition. the short run supply curve shifts to the right as firms enter the industry, while the long run supply curve is a horizontal line at the minimum point on the average cost curve. Market long run supply curve: the market supply curve is actually a short run supply curve. that is because in the short run, the market can produce more at high prices and less at low prices. the long run supply curve is a perfectly elastic (horizontal) curve at the bottom of the firm’s atc.
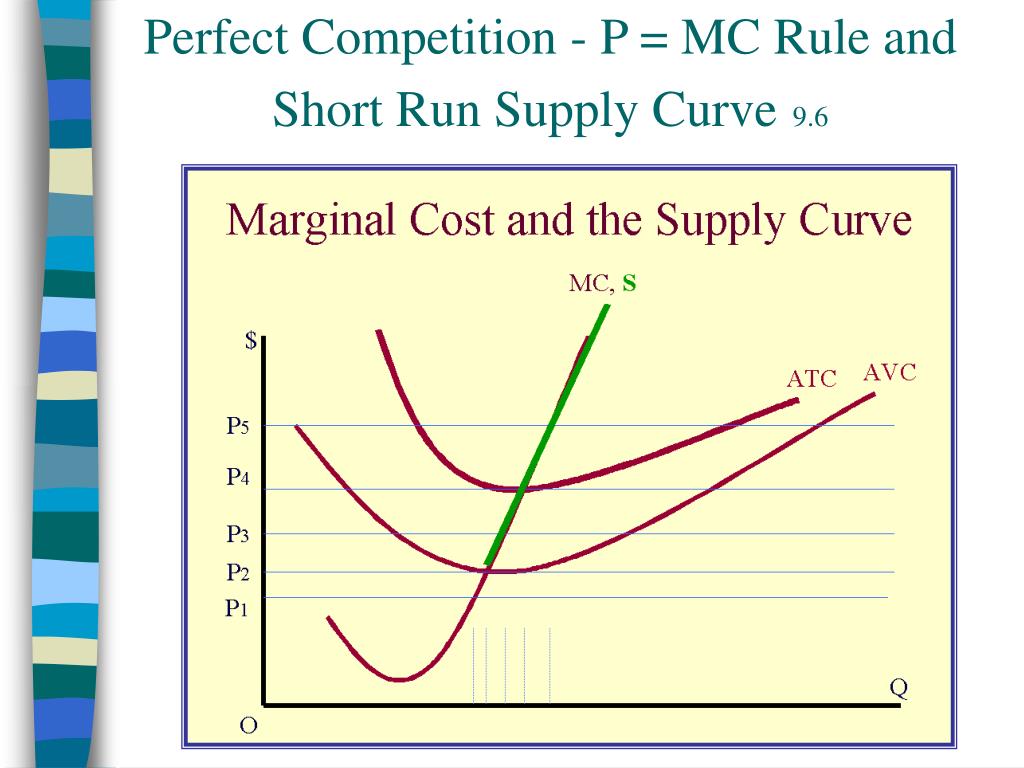
Ppt Key Graphs Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4294287

Comments are closed.