Short Circuit Faults Else
Types Of Short Circuit Faults In Power Systems Explained In a balanced three phase system, a three phase short circuit occurs when all three phases are shorted together, either directly or through a low impedance. this type of fault results in the maximum fault current because all three phases contribute to the fault. it is usually considered the worst case scenario because it leads to the highest. A short circuit is a significant electrical anomaly and much more than just an inconvenience; it's an emergency for any electrical system. let's break down what it means and the potential consequences it holds. a short circuit occurs when electricity strays from its intended path, flowing through a shorter, unintended path with little to no.
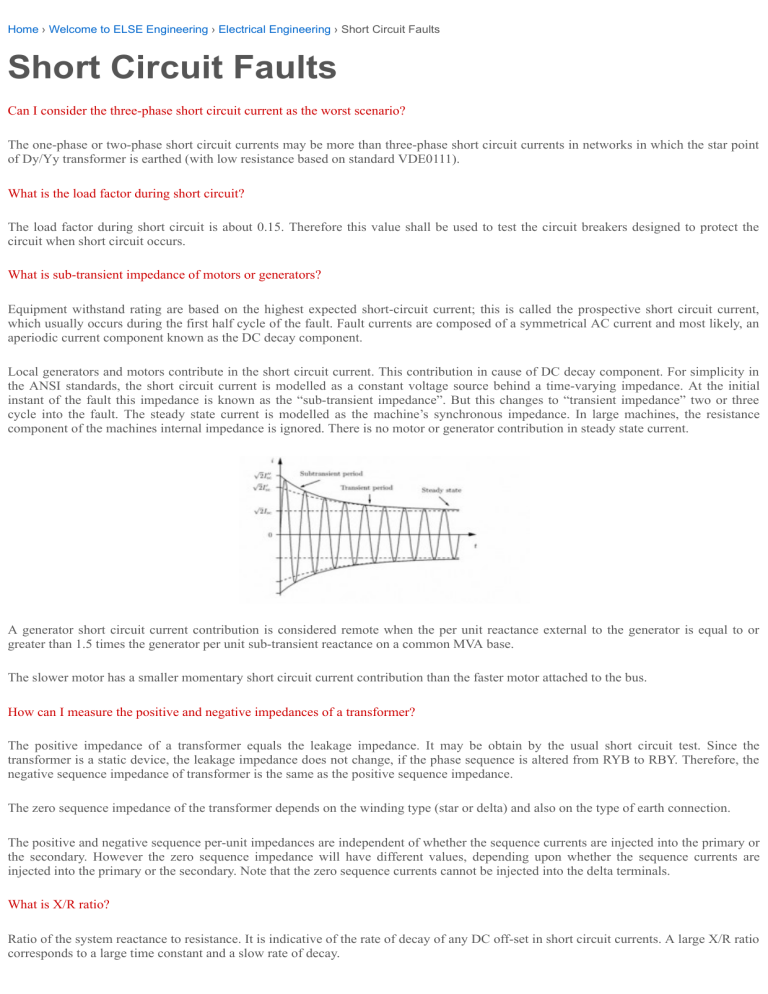
Short Circuit Faults Else Types of short circuits. the two types of electrical short circuits are: 1. normal short circuit. the normal short circuit occurs when a hot wire carrying current hits a neutral wire. as a result, the resistance will decrease immediately, and a significant amount of current will flow in a different direction. 2. What causes short circuits. short circuits can be caused by: vermin or pests chewing through wires. water or other fluids coming into contact with electrical wiring. loose connections in an electrical box. old or damaged outlets, switches, lights, appliances, or other electrical devices. nails or screws piercing through walls and coming in. In a three phase system various types of short circuit can occur. for example, short circuit current can be phase to earth (80% of faults), phase to phase (15% of faults — this type of fault often degenerates into a three phase fault) and three phase (only 5% of initial faults). these different short circuit currents are shown in figure 4. To identify a blown fuse, one should inspect for an overloaded circuit, breaker issues such as tripping, and signs of a short circuit or ground fault such as arc marks. unusual sounds and smells while most of us associate electricity with silence, the presence of unusual sounds can be a telltale sign of a short circuit.

Short Circuit Faults Download Scientific Diagram In a three phase system various types of short circuit can occur. for example, short circuit current can be phase to earth (80% of faults), phase to phase (15% of faults — this type of fault often degenerates into a three phase fault) and three phase (only 5% of initial faults). these different short circuit currents are shown in figure 4. To identify a blown fuse, one should inspect for an overloaded circuit, breaker issues such as tripping, and signs of a short circuit or ground fault such as arc marks. unusual sounds and smells while most of us associate electricity with silence, the presence of unusual sounds can be a telltale sign of a short circuit. An electrical short circuit, often referred to simply as a “short circuit,” is a situation in an electrical circuit where an unintended low resistance path forms between two or more conductive elements. this low resistance path allows electrical current to flow along an unintended route, bypassing the normal load or components in the circuit. Each of these types of faults can result in different magnitudes of fault current. in all types, however, there is a common element: an abnormally low impedance path or shorted path for current to flow, hence the name short circuit current. such a condition can lead to extremely high currents. by ohm’s law, voltage equals current times.
Types Of Short Circuit Faults In Power Systems Explained An electrical short circuit, often referred to simply as a “short circuit,” is a situation in an electrical circuit where an unintended low resistance path forms between two or more conductive elements. this low resistance path allows electrical current to flow along an unintended route, bypassing the normal load or components in the circuit. Each of these types of faults can result in different magnitudes of fault current. in all types, however, there is a common element: an abnormally low impedance path or shorted path for current to flow, hence the name short circuit current. such a condition can lead to extremely high currents. by ohm’s law, voltage equals current times.
Types Of Short Circuit Faults In Power Systems Explained

Comments are closed.