Shifts In Market Demand Tutor2u Economics

Shifts In Market Demand Economics Tutor2u This study note looks at the causes of shifts in market demand. understanding market demand revision video. key summary. give me 5 reasons why demand may increase (i.e. the demand curve shifts to the right) increasing income (for normal goods) decreasing income (for inferior goods) rising price of substitutes. falling price of complements. Availability of credit and the cost of credit (loan interest rates) rising relative prices of substitutes. falling prices of complementary goods and services. changing consumer tastes and preferences (impacted by advertising) speculative demand – such as for financial assets and commodities. the price mechanism explaining shifts in market.
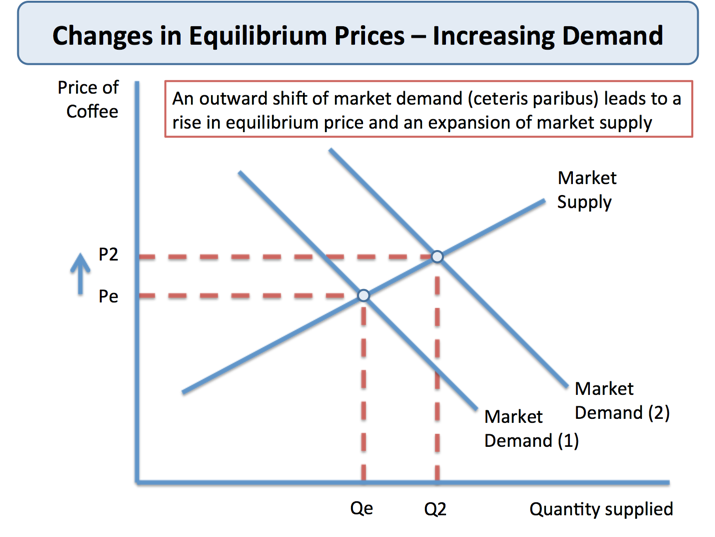
Changes In Market Equilibrium Price Tutor2u Economics Understanding market demand. level: as. board: aqa, edexcel, ocr, ib, eduqas, wjec. last updated 21 mar 2021. share : this topic video looks at the theory of demand including movements along the demand curve, shifts in demand and seasonal, social, emotional and network factors affecting demand for goods and services. market demand. Shift in the demand curve. a shift in the demand curve occurs when the whole demand curve moves to the right or left. for example, an increase in income would mean people can afford to buy more widgets even at the same price. the demand curve could shift to the right for the following reasons: the price of a substitute good increased. Ntity of q3 is demanded. this is a contraction of demand. only changes i. ments along the demand curve.shifting the d. mand curve:price changes do not shift the demand curve. a shift from d1 to d2 is an inward shift in demand, so a lowe. quantity of goods is demanded at the market price o. p1. a shift from d1 to d3 is an outward shift in. The demand for a good depends on several factors, such as price of the good, perceived quality, advertising, income, confidence of consumers and changes in taste and fashion. we can look at either an individual demand curve or the total demand in the economy. the individual demand curve illustrates the price people are willing to pay for a.

The Price Mechanism Explaining Shifts In Market Demand Reference Ntity of q3 is demanded. this is a contraction of demand. only changes i. ments along the demand curve.shifting the d. mand curve:price changes do not shift the demand curve. a shift from d1 to d2 is an inward shift in demand, so a lowe. quantity of goods is demanded at the market price o. p1. a shift from d1 to d3 is an outward shift in. The demand for a good depends on several factors, such as price of the good, perceived quality, advertising, income, confidence of consumers and changes in taste and fashion. we can look at either an individual demand curve or the total demand in the economy. the individual demand curve illustrates the price people are willing to pay for a. So we first consider (1) rightward shift of the demand curve (i.e., a rise in the demand for a commodity) causes an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity (as is shown by the arrows in fig. 9.3). 2. a fall in demand: next we may consider the effect of a fall in demand. Conceptually, equilibrium means state of rest. it is a stage where the balance between two opposite functions, demand and supply, is achieved. mathematically, market equilibrium is expressed as: qd (p) = qs (p) where, qd (p) is the quantity demanded at price p. qs (p) is the quantity supplied at price p.

Theory Of Demand Tutor2u Economics So we first consider (1) rightward shift of the demand curve (i.e., a rise in the demand for a commodity) causes an increase in the equilibrium price and quantity (as is shown by the arrows in fig. 9.3). 2. a fall in demand: next we may consider the effect of a fall in demand. Conceptually, equilibrium means state of rest. it is a stage where the balance between two opposite functions, demand and supply, is achieved. mathematically, market equilibrium is expressed as: qd (p) = qs (p) where, qd (p) is the quantity demanded at price p. qs (p) is the quantity supplied at price p.

Shifts In Market Supply Tutor2u Economics

Changes In Market Equilibrium Price Tutor2u Economics

Comments are closed.