Shifts In Demand
What Is Shift In Demand Curve Examples Factors Shift in demand. a shift in demand means that at any price (and at every price), the quantity demanded will be different than it was before. following is an example of a shift in demand due to an income increase. step 1. draw the graph of a demand curve for a normal good like pizza. pick a price (like p 0). identify the corresponding q 0. Learn how factors other than price affect demand and supply curves, and how to graph demand shifts and supply shifts. understand the ceteris paribus assumption and its implications for economic analysis.

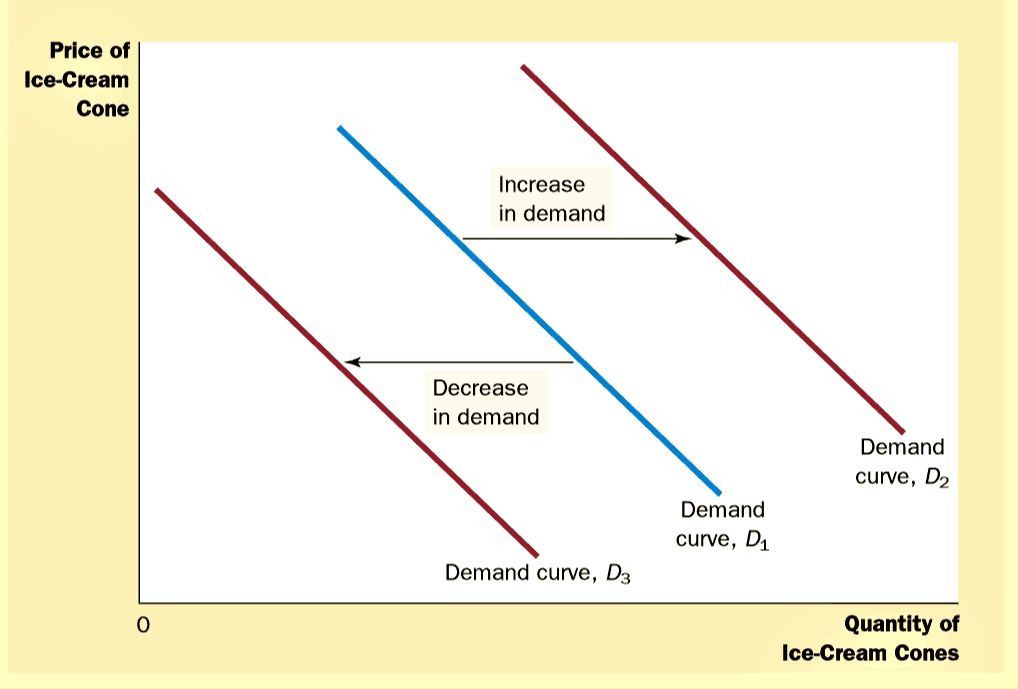
Shift In Demand And Movement Along Demand Curve Economics Help Learn the difference between a shift in demand and a movement along the demand curve, and how they affect the quantity demanded at a given price. see diagrams and examples of factors that can cause a shift in demand, such as income, price of substitutes or complements, and seasonality. Shifts in demand key takeaways. shift in demand is a representation of a change in the quantity of a good or service demanded at every price level due to various economic factors. if the quantity demanded at each price level increases, the new points of quantity will move rightward on the graph to reflect an increase. An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right, as shown in panel (a) of figure 3.17 “changes in demand and supply”. the equilibrium price rises to $7 per pound. as the price rises to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. An increase in income shifts the demand curve for fresh fruit (a normal good) to the right; it shifts the demand curve for canned fruit (an inferior good) to the left. demographic characteristics the number of buyers affects the total quantity of a good or service that will be bought; in general, the greater the population, the greater the demand.

Shift In Demand Graph An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right, as shown in panel (a) of figure 3.17 “changes in demand and supply”. the equilibrium price rises to $7 per pound. as the price rises to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. An increase in income shifts the demand curve for fresh fruit (a normal good) to the right; it shifts the demand curve for canned fruit (an inferior good) to the left. demographic characteristics the number of buyers affects the total quantity of a good or service that will be bought; in general, the greater the population, the greater the demand. A change in demand represents a shift in consumer desire to purchase a particular good or service, irrespective of a variation in its price. the change could be triggered by a shift in income. Factors that shift demand curves. (a) a list of factors that can cause an increase in demand from d 0 to d 1. (b) the same factors, if their direction is reversed, can cause a decrease in demand from d 0 to d 1. when a demand curve shifts, it will then intersect with a given supply curve at a different equilibrium price and quantity.
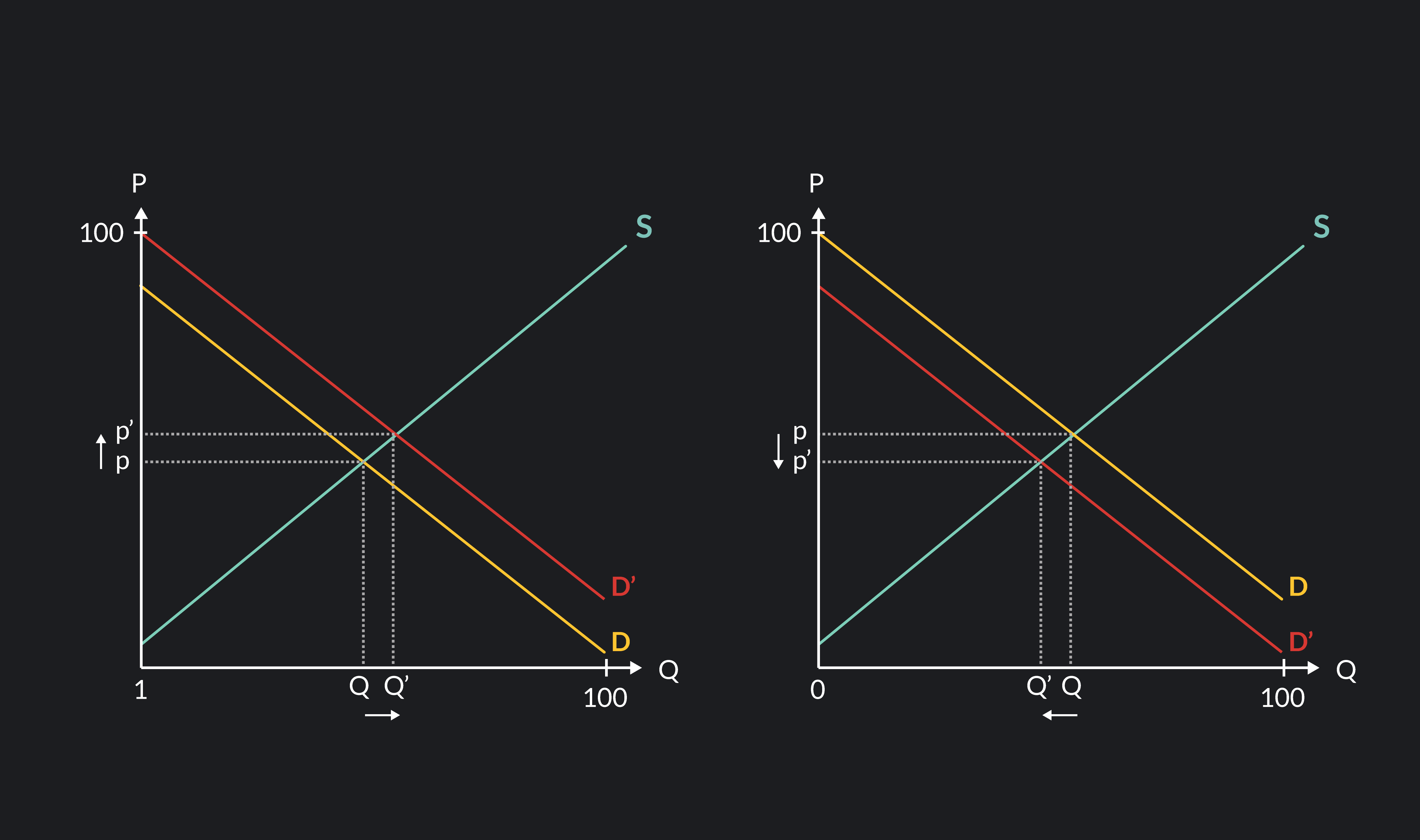
5 Things That Can Shift A Demand Curve Outlier A change in demand represents a shift in consumer desire to purchase a particular good or service, irrespective of a variation in its price. the change could be triggered by a shift in income. Factors that shift demand curves. (a) a list of factors that can cause an increase in demand from d 0 to d 1. (b) the same factors, if their direction is reversed, can cause a decrease in demand from d 0 to d 1. when a demand curve shifts, it will then intersect with a given supply curve at a different equilibrium price and quantity.
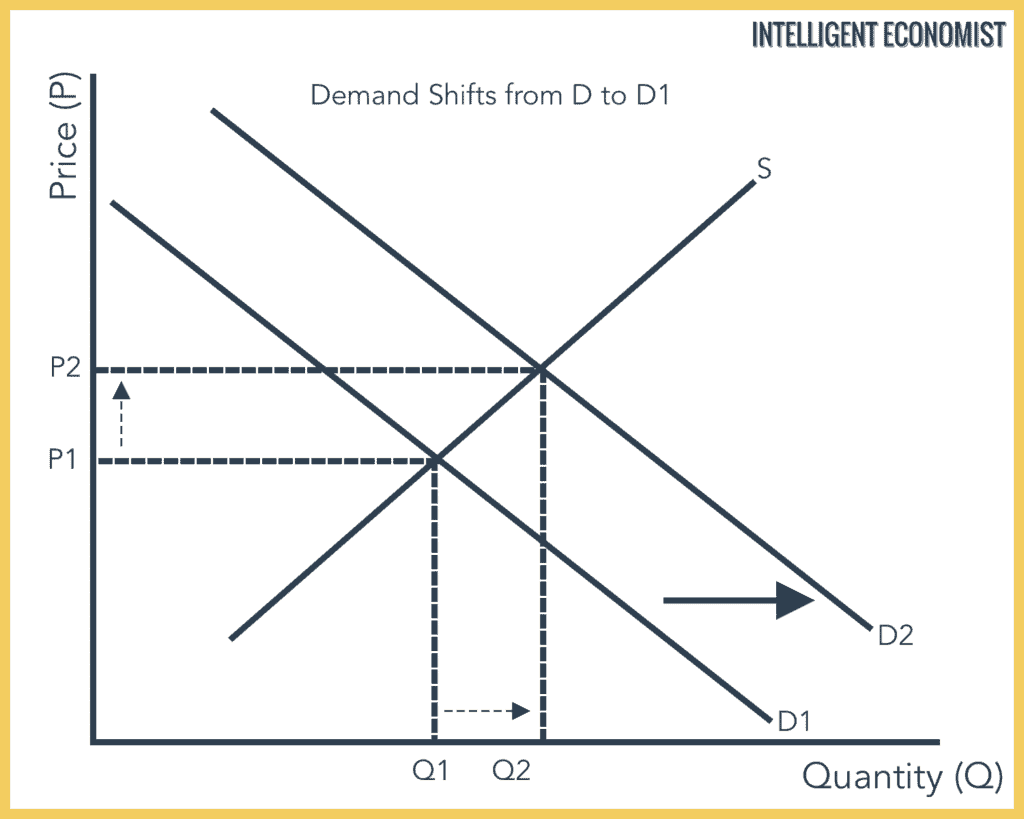
Introduction To Demand Intelligent Economist

Comments are closed.