Shift Of The Demand Supply Curves Vs Movement Along The Demand
Overview Of Movement Vs Shift In The Demand Curve Outlier The simplest way to understand the difference between movement and shift on the demand and supply curves is to understand these two rules. you get a movement along the demand or supply curve, when all factors affecting demand and supply are constant and only the price changes. with regards to a shift, the rule to remember is:. Shift in the demand curve. a shift in the demand curve occurs when the whole demand curve moves to the right or left. for example, an increase in income would mean people can afford to buy more widgets even at the same price. the demand curve could shift to the right for the following reasons: the price of a substitute good increased.

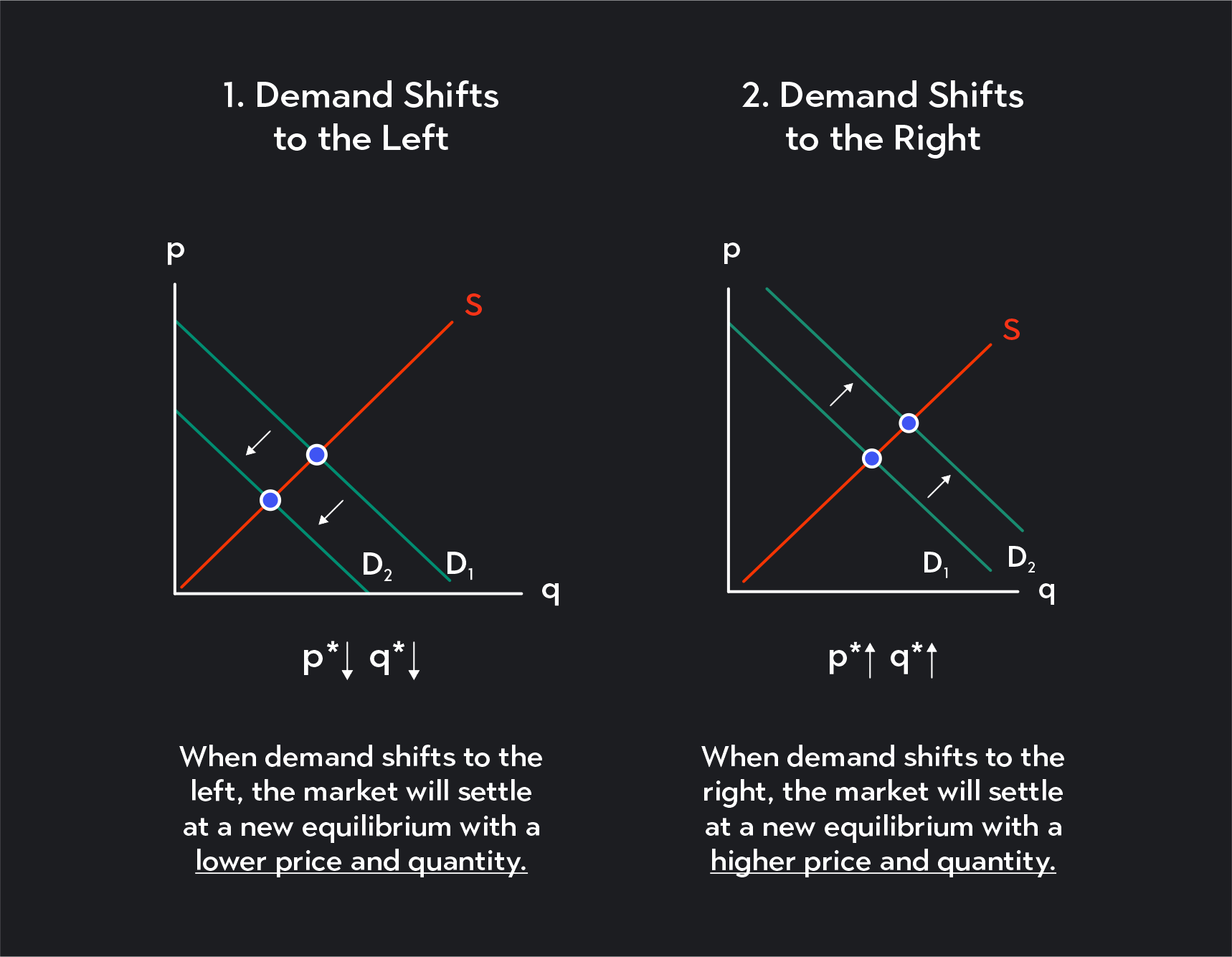
Movement Vs Shift In Demand Curve Difference Between Them With The movement in demand curve occurs due to the change in the price of the commodity whereas the shift in demand curve is because of the change in one or more factors other than the price. the demand curve is downward sloping from left to right, depicting an inverse relationship between the price of the product and quantity demanded. A change in supply means that the entire supply curve shifts either left or right. the initial supply curve s 0 shifts to become either s 1 or s 2. this is caused by production conditions, changes in input prices, advances in technology, or changes in taxes or regulations. a change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the supply. A change in the price of a good or service causes a movement along a specific demand curve, and it typically leads to some change in the quantity demanded, but it does not shift the demand curve. figure 3.9 factors that shift demand curves (a) a list of factors that can cause an increase in demand from d 0 to d 1 . A leftward shift of the demand curve represents an overall decrease in demand. when demand shifts left, the quantities consumers demand will fall at every price. in the figure below, the demand curve has shifted from d o do to d 2 d2. at any given price, the quantity demanded has decreased. for example, at a price of $6, the quantity demanded.
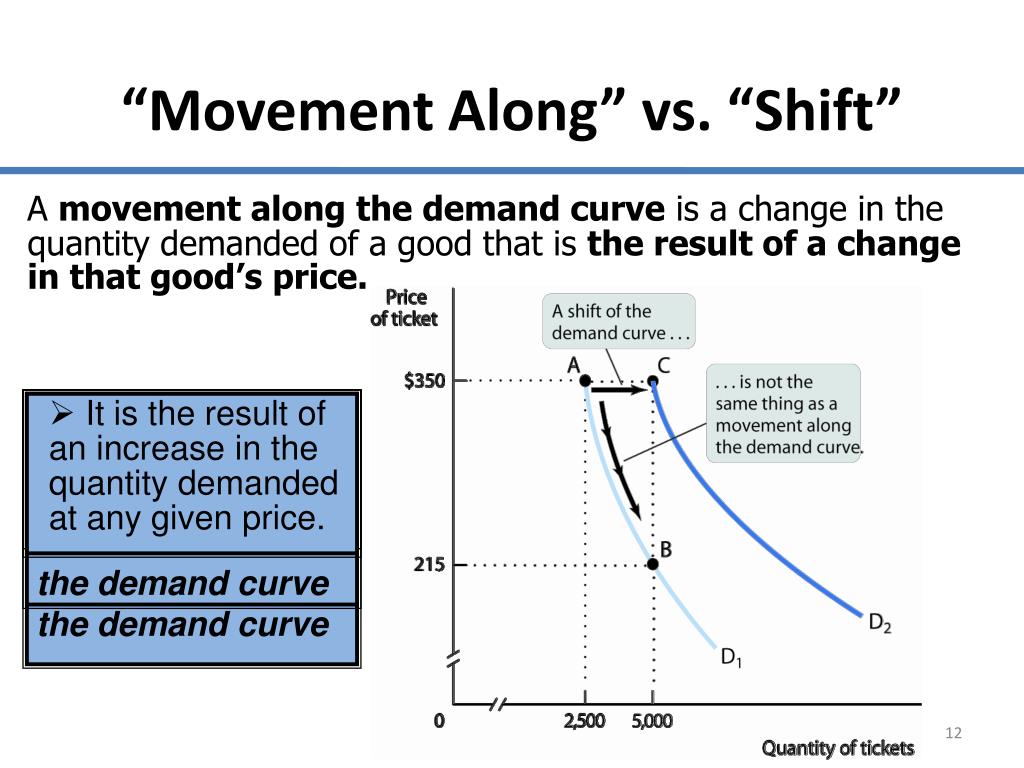
Ppt Chapter 3 Supply Demand Powerpoint Presentation Free Download A change in the price of a good or service causes a movement along a specific demand curve, and it typically leads to some change in the quantity demanded, but it does not shift the demand curve. figure 3.9 factors that shift demand curves (a) a list of factors that can cause an increase in demand from d 0 to d 1 . A leftward shift of the demand curve represents an overall decrease in demand. when demand shifts left, the quantities consumers demand will fall at every price. in the figure below, the demand curve has shifted from d o do to d 2 d2. at any given price, the quantity demanded has decreased. for example, at a price of $6, the quantity demanded. A change in supply means that the entire supply curve shifts either left or right. the initial supply curve s 0 shifts to become either s 1 or s 2. this is caused by production conditions, changes in input prices, advances in technology, or changes in taxes or regulations. a change in quantity supplied refers to a movement along the supply. Conversely, an upward movement along the demand curve indicates that as the price increases, the quantity demanded decreases. movements along the demand curve are influenced solely by changes in price and are described under the assumption of ceteris paribus, meaning that all other relevant factors are held constant.

Comments are closed.