Sensory Processes Bio103 Human Biology

Sensory Systems Biology Of Humans Systems Biology Sensory System Senses provide information about the body and its environment. humans have five special senses: olfaction (smell), gustation (taste), equilibrium (balance and body position), vision, and hearing. additionally, we possess general senses, also called somatosensation, which respond to stimuli like temperature, pain, pressure, and vibration. Chapter 7 the skeletal system. introduction to the skeletal system. classify bones according to their shapes. human skeletal system. the axial skeleton general features and functions of the skull. axial skeleton the vertebral column and the thoracic cage. human appendicular skeleton. joints and skeletal movements.

Sensory Processes Bio103 Human Biology This process is called sensory transduction. there are two broad types of cellular systems that perform sensory transduction. in one, a neuron works with a sensory receptor, a cell, or cell process that is specialized to engage with and detect a specific stimulus. stimulation of the sensory receptor activates the associated afferent neuron. Senses provide information about the body and its environment. humans have five special senses: olfaction (smell), gustation (taste), equilibrium (balance and body position), vision, and hearing. additionally, we possess general senses, also called somatosensation, which respond to stimuli like temperature, pain, pressure, and vibration. When the sensory signal exits the thalamus, it is conducted to the specific area of the cortex dedicated to processing that particular sense. figure 36.2.1 36.2. 1: sensation processing: the brain has dedicated areas to the processing of stimuli, including: (a) thalamus and (b) the auditory, visual and somatosensory processing regions. Spinal nerves transmit sensory and motor information between the spinal cord and the rest of the body. each of the 31 spinal nerves contains both sensory and motor axons. the sensory neuron cell bodies are grouped in structures called dorsal root ganglia and are shown in figure 4. each sensory neuron has one projection—with a sensory receptor.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/brain_senses-56ccf48f5f9b5879cc5ba0e6.jpg)
The Five Senses And How They Work When the sensory signal exits the thalamus, it is conducted to the specific area of the cortex dedicated to processing that particular sense. figure 36.2.1 36.2. 1: sensation processing: the brain has dedicated areas to the processing of stimuli, including: (a) thalamus and (b) the auditory, visual and somatosensory processing regions. Spinal nerves transmit sensory and motor information between the spinal cord and the rest of the body. each of the 31 spinal nerves contains both sensory and motor axons. the sensory neuron cell bodies are grouped in structures called dorsal root ganglia and are shown in figure 4. each sensory neuron has one projection—with a sensory receptor. Senses provide information about the body and its environment. humans have five special senses: olfaction (smell), gustation (taste), equilibrium (balance and body position), vision, and hearing. additionally, we possess general senses, also called somatosensation, which respond to stimuli like temperature, pain, pressure, and vibration. Key points. reception is the process of activating a sensory receptor by a stimuli. sensory transduction is the process of converting that sensory signal to an electrical signal in the sensory neuron. the process of reception is dependent on the stimuli itself, the type of receptor, receptor specificity, and the receptive field, which can vary.
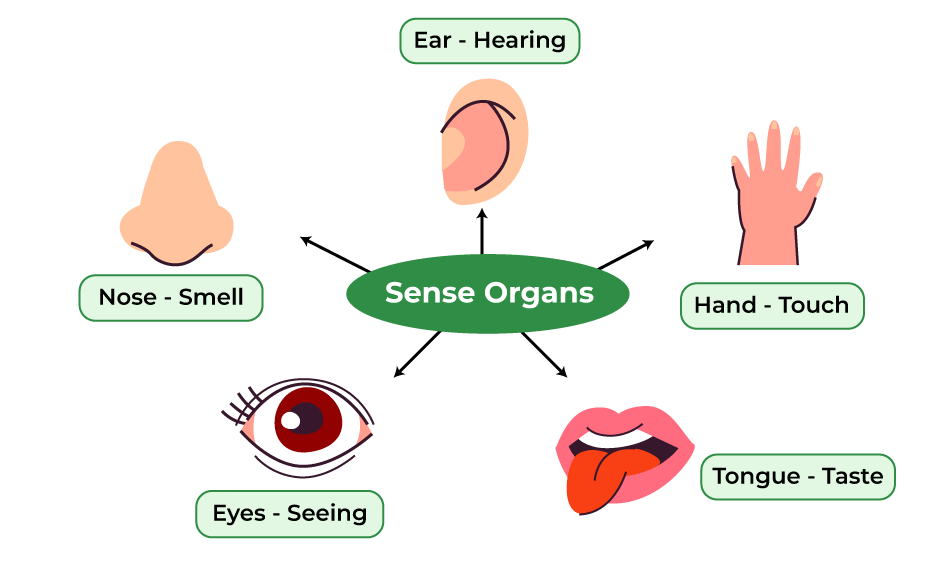
List Of Five Sense Organs Eyes Nose Ears Tongue And Skin Senses provide information about the body and its environment. humans have five special senses: olfaction (smell), gustation (taste), equilibrium (balance and body position), vision, and hearing. additionally, we possess general senses, also called somatosensation, which respond to stimuli like temperature, pain, pressure, and vibration. Key points. reception is the process of activating a sensory receptor by a stimuli. sensory transduction is the process of converting that sensory signal to an electrical signal in the sensory neuron. the process of reception is dependent on the stimuli itself, the type of receptor, receptor specificity, and the receptive field, which can vary.

Sensory Processes Bio103 Human Biology
Sensory Processes Biological Bases Of Behavior Online Notes Nepal

Comments are closed.