Sensory Neuron Diagram Labeled
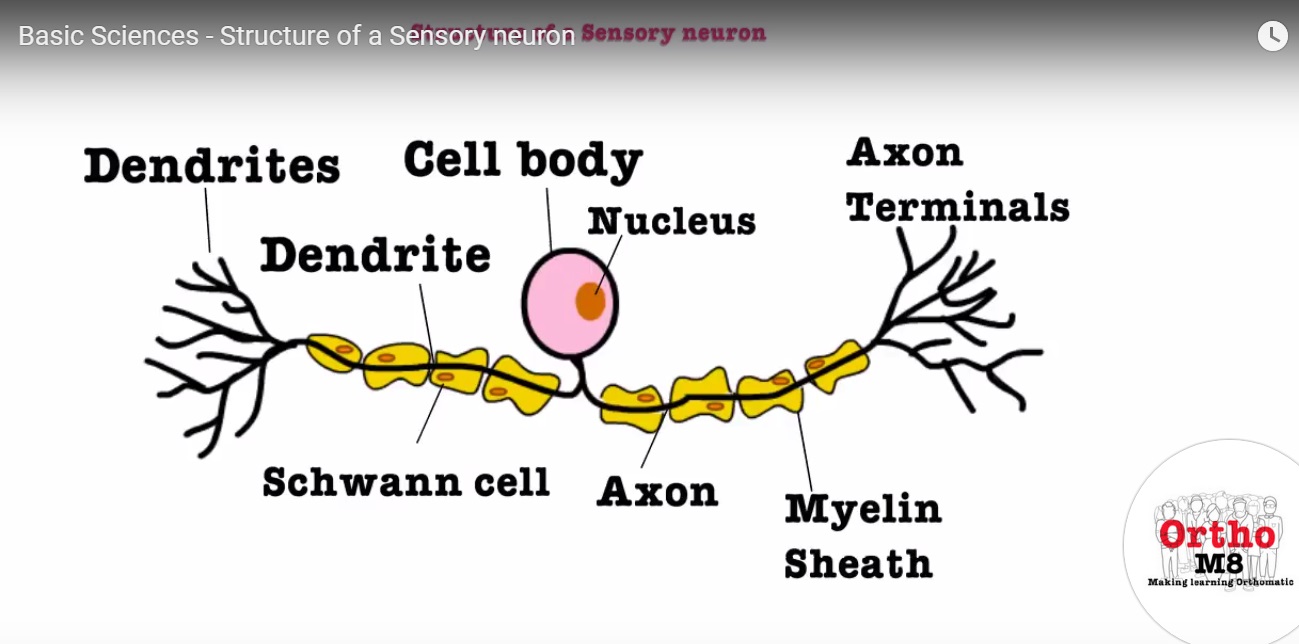
Structure Of A Sensory Neuron Orthopaedicprinciples A sensory neuron (sometimes referred to as an afferent neuron) is a nerve cell that detects and responds to external signals. sensory neurons receive information via their receptors, which are part of the peripheral nervous system, and convert this information into electrical impulses. these impulses act as signals and are passed on to the. A neuron is a nerve cell that processes and transmits information through electrical and chemical signals in the nervous system. neurons consist of a cell body, dendrites (which receive signals), and an axon (which sends signals). synaptic connections allow communication between neurons, facilitating the relay of information throughout the body.
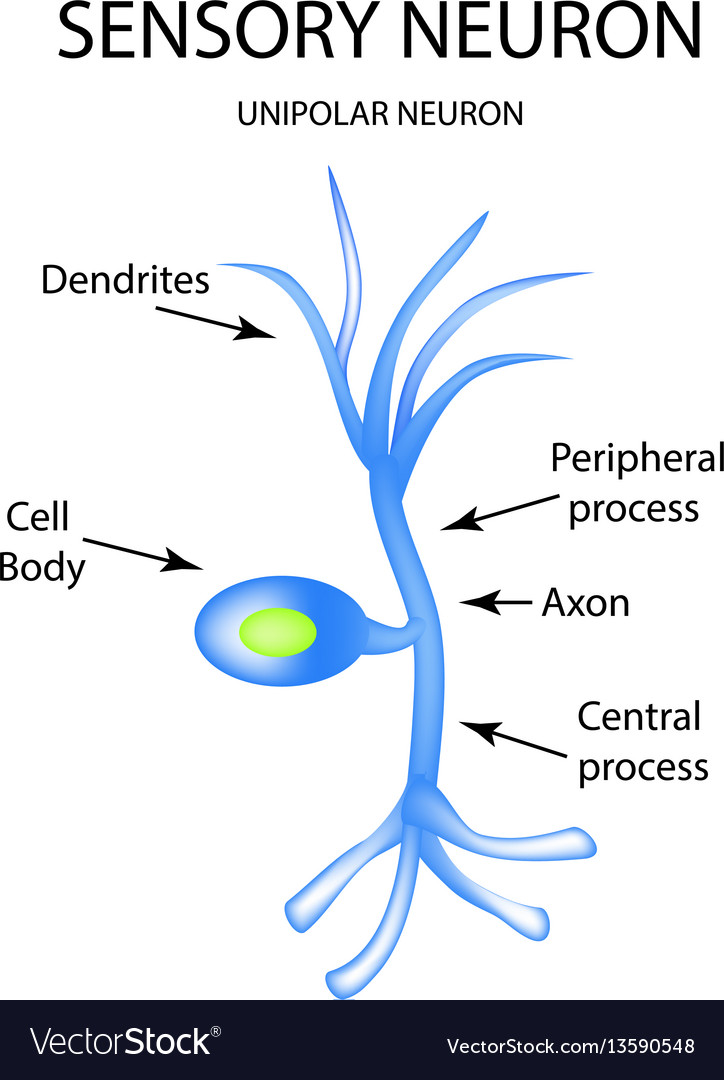
The Structure Of The Sensory Neuron Infographics Vector Image Lesson 2: the neuron and nervous system. anatomy of a neuron. overview of neuron structure and function. the membrane potential. electrotonic and action potentials. Surround inhibition. receptor potential. (show more) sensory neuron, nerve cell that carries information about changes in external and internal environments to the central nervous system (cns). such neurons are part of the peripheral nervous system, which lies outside the brain and spinal cord. they collect information from so called sensory. Neuron structure. figure \(\pageindex{2}\) shows the structure of a typical neuron. the main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. figure \(\pageindex{2}\): somatic motor neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of the bulbs, and other associated. Four types of sensory neuron. sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded receptor potentials. [1] this process is called sensory transduction. the cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal.
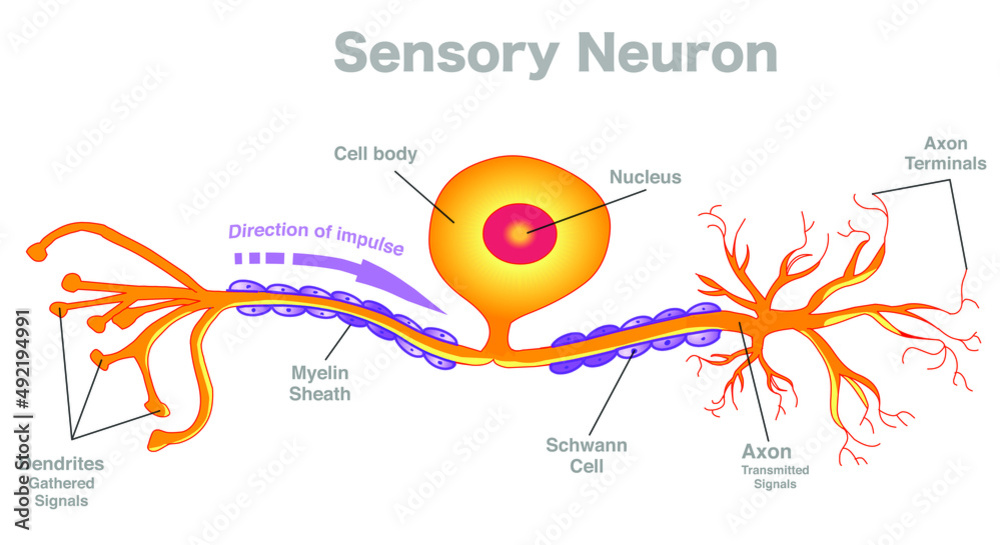
Sensory Neuron Anatomy Structure Parts Pseudounipolar Afferent Neuron structure. figure \(\pageindex{2}\) shows the structure of a typical neuron. the main parts of a neuron are labeled in the figure and described below. figure \(\pageindex{2}\): somatic motor neuron with cell body, axon, axon, myelin sheath, nodes of ranvier, axon terminal, dendrites, synaptic end of the bulbs, and other associated. Four types of sensory neuron. sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are neurons in the nervous system, that convert a specific type of stimulus, via their receptors, into action potentials or graded receptor potentials. [1] this process is called sensory transduction. the cell bodies of the sensory neurons are located in the dorsal. While they have the common features of a typical cell, they are structurally and functionally unique from other cells in many ways. all neurons have three main parts: 1) dendrites, 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. besides the three major parts, there is the presence of axon terminal and synapse at the end of the neuron. Neuron anatomy. nerve cell: dendrites receive messages from other neurons. the message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. from there the message can move to the next neuron. neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal.

An Easy Guide To Neuron Anatomy With Diagrams An Tâm While they have the common features of a typical cell, they are structurally and functionally unique from other cells in many ways. all neurons have three main parts: 1) dendrites, 2) cell body or soma, and 3) axons. besides the three major parts, there is the presence of axon terminal and synapse at the end of the neuron. Neuron anatomy. nerve cell: dendrites receive messages from other neurons. the message then moves through the axon to the other end of the neuron, then to the tips of the axon and then into the space between neurons. from there the message can move to the next neuron. neurons pass messages to each other using a special type of electrical signal.

Comments are closed.