Section 3 2 Energy Flow Kha S Biology Portfolio
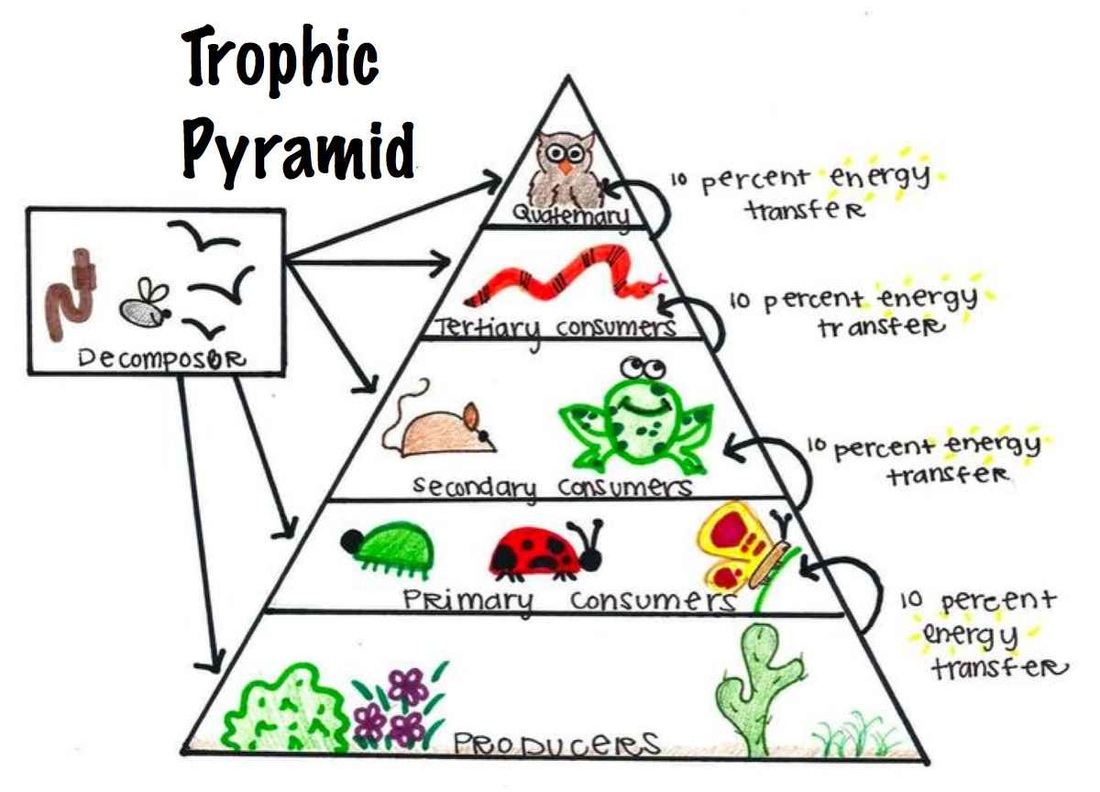
Section 3 2 Energy Flow Kha S Biology Portfolio 3.2 energy flow. sunlight is the main energy source for life on earth. some types of organisms rely on the energy stored in inorganic chemical compounds. autotrophs can capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use that energy to produce food. autotrophs can also be called producers due to them being able to make their own food. Carinvore. heterotroph that eats animals. ex.lion, tiger. omnivore. eats plants and animals. ex.humans,bears. study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like what is at the core of every organisms interaction with the environment?, what source of energy do organisms use that don't use the suns energy?, what are autotrophs? and.
Section 3 2 Energy Flow Kha S Biology Portfolio Energy flow section 3 2. flashcards. learn. test. match. flashcards. learn. test. match. created by. jaileen106. terms in this set (15) autotroph. organism that uses. Section 3 2 energy flow. 5.0 (1 review) term. 1 16. autotrophs. click the card to flip 👆. definition. 1 16. organisms that can capture energy from sunlight or chemicles and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds; also called a producer. 3.3 cycles of matter unlike the one way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. element , chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed form one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another through biogeochemical cycles . A biome is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities. scientist use three basic approaches for ecological research: observing, experimenting, and modeling. observing is when ecologists ask questions and develop an hypothesis. experimenting can be use to test a hypothesis. modeling is when ecologists make.

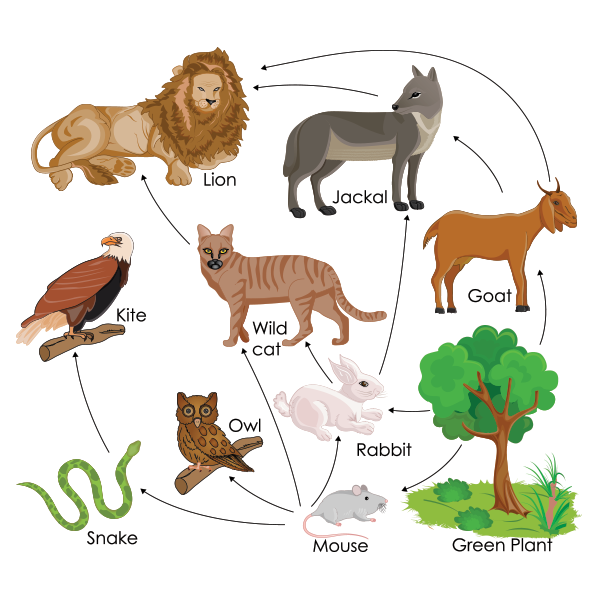
Ppt Chapter 3 Section 2 Energy Flow Powerpoint Presentation Free 3.3 cycles of matter unlike the one way flow of energy, matter is recycled within and between ecosystems. element , chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed form one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another through biogeochemical cycles . A biome is a group of ecosystems that have the same climate and similar dominant communities. scientist use three basic approaches for ecological research: observing, experimenting, and modeling. observing is when ecologists ask questions and develop an hypothesis. experimenting can be use to test a hypothesis. modeling is when ecologists make. Section 3–2 energy flow (pages 67–73) this section explains where the energy for life processes comes from. it also describes how energy flows through living systems and how efficient the transfer of energy is among organisms in an ecosystem. introduction (page 67) 1. what is at the core of every organism’s interaction with the environment?. Course: high school biology (deprecated) > unit 9. lesson 5: trophic levels. flow of energy and matter through ecosystems. food chains & food webs. example identifying roles in a food web. energy flow and primary productivity. trophic levels review. trophic levels.

Chapter 3 Section 2 Energy Flow Section 3–2 energy flow (pages 67–73) this section explains where the energy for life processes comes from. it also describes how energy flows through living systems and how efficient the transfer of energy is among organisms in an ecosystem. introduction (page 67) 1. what is at the core of every organism’s interaction with the environment?. Course: high school biology (deprecated) > unit 9. lesson 5: trophic levels. flow of energy and matter through ecosystems. food chains & food webs. example identifying roles in a food web. energy flow and primary productivity. trophic levels review. trophic levels.

3 2 Energy Flow Objectives Ppt Download

Ppt Energy Flow Section 3 2 Powerpoint Presentation Free Download

Comments are closed.