Secondary Consumers Characteristics And Examples Science 2024

Secondary Consumers Characteristics And Examples Science 2024 Spiders, snakes, and seals are all examples of carnivorous secondary consumers. omnivores are the other type of secondary consumer. they eat both plant and animal materials for energy. bears and skunks are examples of omnivorous secondary consumers that both hunt prey and eat plants. however, some omnivores are simply scavengers. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.

Secondary Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in a typical food chain. they are organisms that feed on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. while primary consumers are always herbivores; organisms that only feed on autotrophic plants, secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat only animals, but omnivores eat. Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. Published jul 18, 2024. secondary consumers are pivotal in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. they play a crucial role by regulating populations of primary consumers, thus ensuring that plant life is not overexploited. understanding their impact helps us appreciate the complexity and interdependence within food webs. A food chain is a visual depiction of a one way flow of energy within an ecosystem. this is in contrast to a food web, which includes many organisms and many potential paths connecting them to.
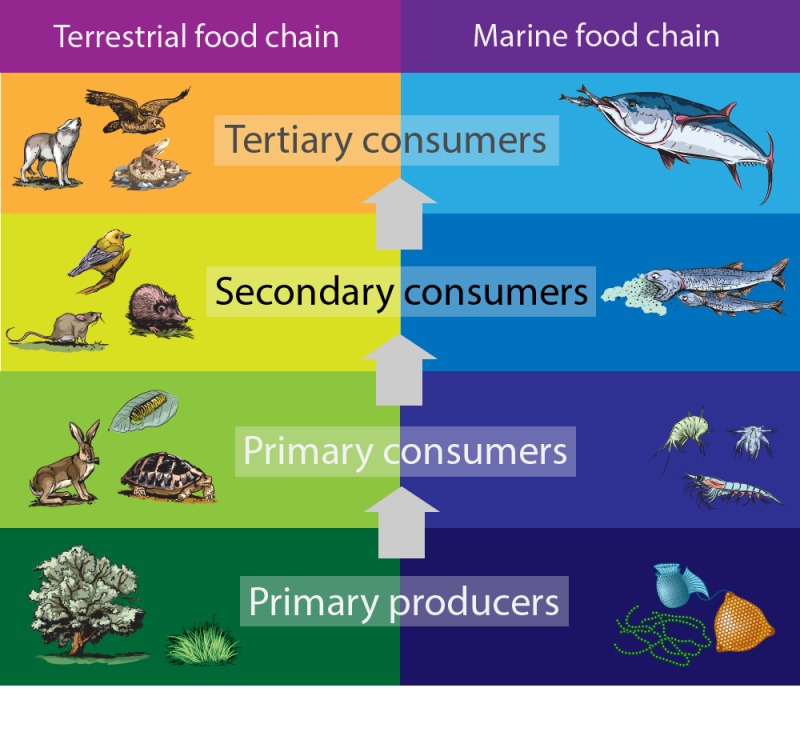
Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples Published jul 18, 2024. secondary consumers are pivotal in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. they play a crucial role by regulating populations of primary consumers, thus ensuring that plant life is not overexploited. understanding their impact helps us appreciate the complexity and interdependence within food webs. A food chain is a visual depiction of a one way flow of energy within an ecosystem. this is in contrast to a food web, which includes many organisms and many potential paths connecting them to. Group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. noun. organism that eats mainly plants and other producers. molecule. Types of consumer. 1. primary consumers. herbivores are the dominant consumers. their food source is the first trophic level in the food web, which consists of plants. plants are also considered autotrophs. autotrophs make their own energy from sunlight and basic nutrients through photosynthesis; the phrases producer and autotroph have the same.

Comments are closed.