Root Cause Analysis Tools In Lean Six Sigma

Lean Six Sigma Root Cause Analysis Rca Vative Root cause analysis (rca) is a key tool in continuous improvement, acting as a systematic approach to identify and tackle the underlying issues behind problems. rca aims not only to provide a temporary fix but to offer long lasting solutions by addressing the root causes. rca, such as the fishbone diagram, the 5 whys, and fmea. A root cause analysis (rca) is a problem solving method to identify the root causes of faults or problems. a factor is considered a root cause if removal from the problem fault sequence prevents the final undesirable event from recurring. short term actions are not profitable for the organization; thus, rca helps permanently eliminate the issues.

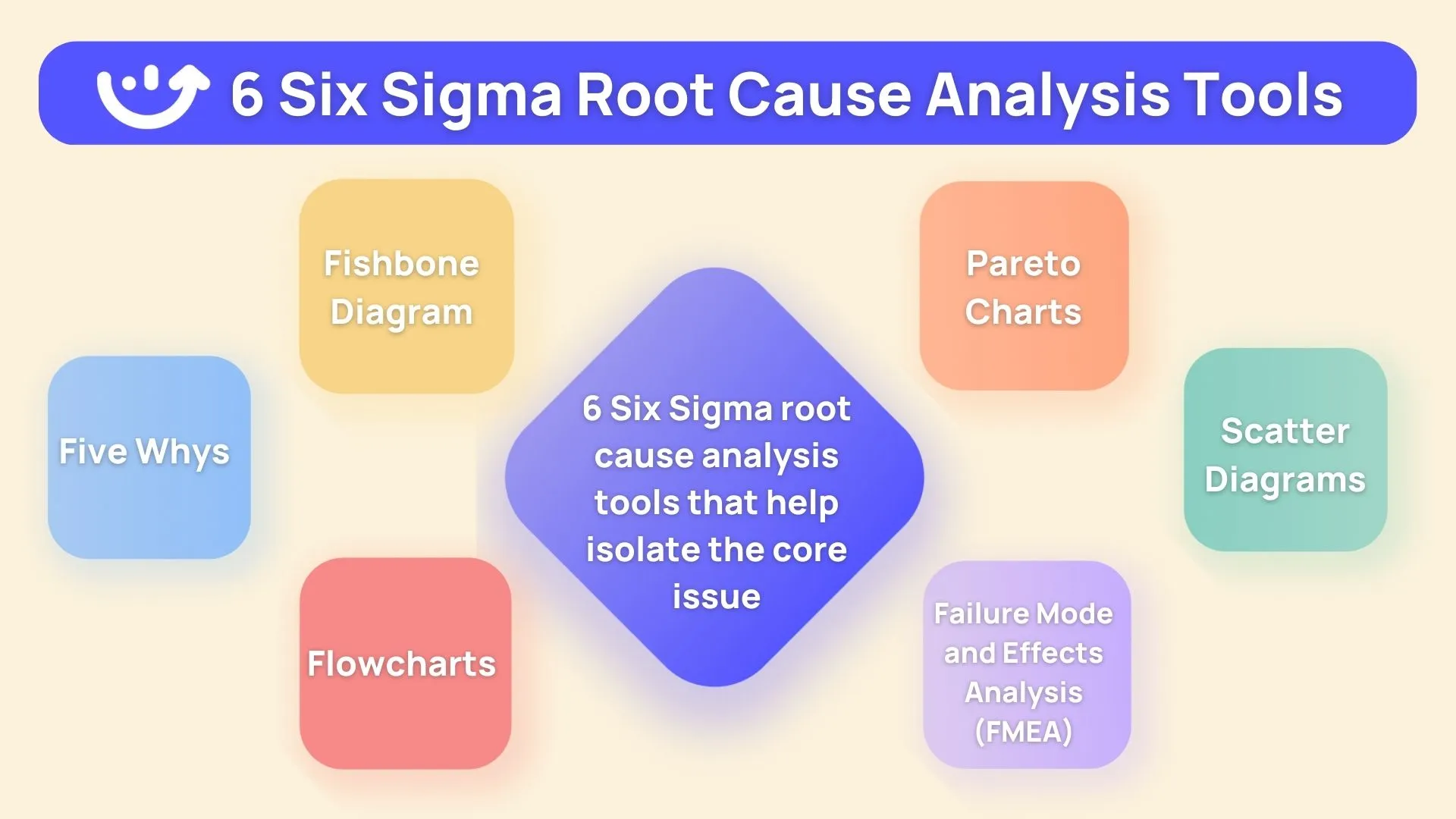
Root Cause Analysis Tools In Lean Six Sigma Root cause analysis is a range of tools and techniques used to address a problem in a business, we define a problem as the difference between what is happening vs what should be happening (an abnormal occurrence) e.g., product defects, late deliveries, processes not running at correct speed etc. the tools and techniques used in root cause. Root cause analysis is an important part of six sigma methodology, as it is a key component of the analysis phase of dmaic – define, measure, analyze, improve, and control. there are six major tools of root cause analysis, which are used through the process of identifying the root causes of a problem. pareto chart. the 5 whys. The "root cause analysis toolbox" from sologic is another invaluable resource. it offers a variety of tools for different rca tasks, covering methods like the 5 whys, ishikawa fishbone, incident timeline, and sologic rca methods. it provides a comprehensive guide for tackling rca from multiple perspectives. Root cause analysis seamlessly integrates into lean six sigma cultures demonstrating infrastructure capabilities enabling reliable prevention. however, any organization in search of elevating standards, systematizing enhancements, or diagnosing tricky recurring issues can benefit from instituting rca capabilities.
A Complete Guide To A Six Sigma Root Cause Analysis The "root cause analysis toolbox" from sologic is another invaluable resource. it offers a variety of tools for different rca tasks, covering methods like the 5 whys, ishikawa fishbone, incident timeline, and sologic rca methods. it provides a comprehensive guide for tackling rca from multiple perspectives. Root cause analysis seamlessly integrates into lean six sigma cultures demonstrating infrastructure capabilities enabling reliable prevention. however, any organization in search of elevating standards, systematizing enhancements, or diagnosing tricky recurring issues can benefit from instituting rca capabilities. The 6ms refer to six key inputs that contribute to process variation: machinery, manpower, materials, methods, measurement, and mother nature. categorizing causal factors into the 6ms provides an intuitive framework for structured brainstorming and analysis. the approach helps identify root causes by mapping relationships in an ishikawa. The goal of rca is to detect and resolve the root cause of a problem, thereby preventing the issue from recurring. in the context of lean six sigma, rca is used as a problem solving method to address inefficiencies and defects in a manufacturing process. it forms an integral part of the ‘analyze’ phase of the dmaic (define, measure, analyze.

Root Cause Analysis Tools In Lean Six Sigma The 6ms refer to six key inputs that contribute to process variation: machinery, manpower, materials, methods, measurement, and mother nature. categorizing causal factors into the 6ms provides an intuitive framework for structured brainstorming and analysis. the approach helps identify root causes by mapping relationships in an ishikawa. The goal of rca is to detect and resolve the root cause of a problem, thereby preventing the issue from recurring. in the context of lean six sigma, rca is used as a problem solving method to address inefficiencies and defects in a manufacturing process. it forms an integral part of the ‘analyze’ phase of the dmaic (define, measure, analyze.

Comments are closed.