Rockwood Classification Of Acromioclavicular Joint Injury Aliem

Rockwood Classification Of Acromioclavicular Joint Injury Aliem Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injury. 2020 04 05t03:17:58 07:00. apr 5, 2020 | aliem is your digital connection to the cooperative world of. The rockwood classification system is limited to describing soft tissue injuries and does not assess osseous injuries 8. classification. the rockwood classification takes into account not only the acromioclavicular joint itself but also the coracoclavicular ligament, the deltoid, and trapezius muscles, whilst considering the direction of.

Rockwood Classification Of Acromioclavicular Joint Injuries Download Summary. an acromioclavicular joint injury, otherwise known as a shoulder separation, is a traumatic injury to the acromioclavicular (ac) joint with disruption of the acromioclavicular ligaments and or coracoclavicular (cc) ligaments. diagnosis is made with bilateral focused shoulder radiographs to assess for ac and cc interval widening. Acromioclavicular (ac) joint injury is a frequent diagnosis after acute shoulder trauma and is very common among athletic populations. it accounts for 40% to 50% of shoul der injuries in many contact sports. 1 approximately 9% of shoulder girdle injuries cause damage to the ac joint.1 they are mostly minor sprains and occur five times more. Rockwood's classification of acromioclavicular separations types i to vi is shown. a type i injury is a mild sprain of the ac ligament, type ii is a ruptured ac ligament and sprained cc ligaments, type iii is a superior dislocation of the ac joint with ruptured ac ligament, cc ligament, and joint capsule, type iv is a posterior dislocation of the ac joint with ruptured ac ligament, cc ligament. Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injuries is divided into: type i: normal radiograph. type ii: slightly raised clavicle (cc distance increased <25% that of the contralateral side) type iii: completely displaced clavicle (cc distance <25 mm or increased 25 100% that of the contralateral side) type iv: posterior clavicle dislocation.

Ac Joint Injury Grading Rockwood's classification of acromioclavicular separations types i to vi is shown. a type i injury is a mild sprain of the ac ligament, type ii is a ruptured ac ligament and sprained cc ligaments, type iii is a superior dislocation of the ac joint with ruptured ac ligament, cc ligament, and joint capsule, type iv is a posterior dislocation of the ac joint with ruptured ac ligament, cc ligament. Rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint injuries is divided into: type i: normal radiograph. type ii: slightly raised clavicle (cc distance increased <25% that of the contralateral side) type iii: completely displaced clavicle (cc distance <25 mm or increased 25 100% that of the contralateral side) type iv: posterior clavicle dislocation. Classifications in brief: rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint separations. jacob d. gorbaty md, jason e. hsu md, albert o. gee md. blished online: 16 september 2016 the association of bone and joint surgeons1 2016historyacromioclavicular (ac) joint sepa. ation is a common shoulder injury, representing up to 9% of all shoulder. Acromioclavicular (ac) joint dislocations account for nearly 10% of all shoulder injuries that seek medical attention. 1 the ac joint is particularly at risk in athletes, and it accounts for 40–50% of shoulder injuries in this population. 2 the mechanism of injury is usually a result of either a fall or a collision, 3 and as a result, ac.
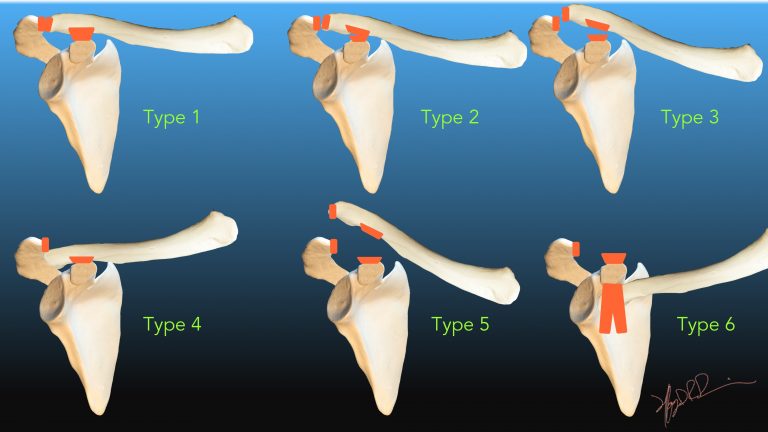
Rockwood Classification Of Acromioclavicular Joint Separation Uw Classifications in brief: rockwood classification of acromioclavicular joint separations. jacob d. gorbaty md, jason e. hsu md, albert o. gee md. blished online: 16 september 2016 the association of bone and joint surgeons1 2016historyacromioclavicular (ac) joint sepa. ation is a common shoulder injury, representing up to 9% of all shoulder. Acromioclavicular (ac) joint dislocations account for nearly 10% of all shoulder injuries that seek medical attention. 1 the ac joint is particularly at risk in athletes, and it accounts for 40–50% of shoulder injuries in this population. 2 the mechanism of injury is usually a result of either a fall or a collision, 3 and as a result, ac.

Rockwood Classification Of Acromioclavicular Injuries Download Table

Rockwood Classification Of Acromioclavicular Joint Injury Image

Comments are closed.