Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair Drrekkas
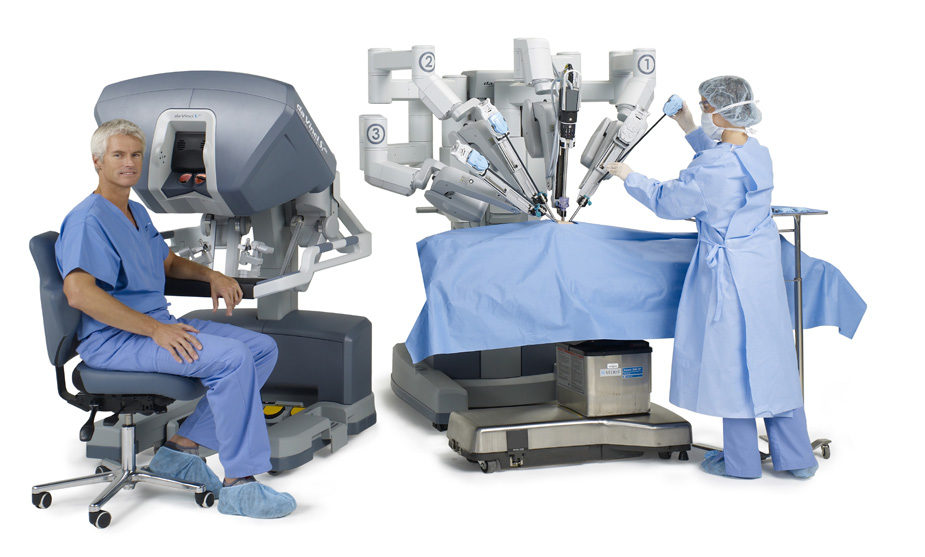
Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair Drrekkas Hernia repair can be performed using traditional open surgery or minimally invasive surgery. with open surgery, doctors make a long incision in the abdomen. the incision must be large enough for the surgeon to fit his her hands and surgical instruments inside the abdomen. open surgery allows doctors to see and touch your organs and tissue while. Purpose of review robotic inguinal hernia repair (rihr) is becoming increasingly more common since its initial description. in the last 5 years short and long term patient outcomes, and specific utility in complex cases such as bilateral hernias, mesh extraction, multiple recurrence, and prior urologic pelvic procedures have become key topics of discussion. this article will serve to review.

Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair Anatomy What is robotic hernia surgery (robotic hernia repair surgery)? robotic hernia surgery is a type of surgery that uses small cuts to treat hernias. a hernia is when an organ pushes through the muscle or tissue wall that contains it. robotic hernia surgery puts the herniated organ back where it belongs and closes the muscles where the organs are. This type of hernia repair creates small incisions, which means less post operative pain and a smaller risk of wound infections. da vinci robot used for minimally invasive surgery at university of utah health. depending on the size, location, and complexity of the hernia, this operation can be as short as 30 minutes, while others may last. By comparing the overall complication rates between laparoscopic and robotic inguinal hernia repair, healthcare providers can determine which approach is associated with better patient outcomes and fewer adverse events . surgical site infections (ssi) are a common and potentially serious complication following hernia repair surgery. A total of 510 patients were identified who underwent inguinal hernia repair between 2012 and 2016. robotic assist was used in 13.8% (n = 69) of repairs, laparoscopic approach in 48.1% (n = 241), and open approach in 38.1% (n = 191). there were no demographic differences between the groups in terms of sex, race, bmi, hospital status (inpatient.

Right Robotic Inguinal Hernia Repair By Jonathan Carter Md Case By comparing the overall complication rates between laparoscopic and robotic inguinal hernia repair, healthcare providers can determine which approach is associated with better patient outcomes and fewer adverse events . surgical site infections (ssi) are a common and potentially serious complication following hernia repair surgery. A total of 510 patients were identified who underwent inguinal hernia repair between 2012 and 2016. robotic assist was used in 13.8% (n = 69) of repairs, laparoscopic approach in 48.1% (n = 241), and open approach in 38.1% (n = 191). there were no demographic differences between the groups in terms of sex, race, bmi, hospital status (inpatient. Benefits of robotic hernia repair compared to laparoscopic repair include: dexterity to reach previously inaccessible areas of the body. improved range of motion; the robot’s arms can rotate 360 degrees and are much more flexible than the human hand or wrist. high definition, magnified 3d images allow for improved visibility and accuracy. A systematic literature search was performed in pubmed, embase, and scopus for studies published between january 1st, 2010, and july 29th, 2021. search terms used were robotic inguinal hernia repair. titles, abstracts and full text articles were screened and selected by two authors (ls and gr) independently based on eligibility criteria.

Robotic Inguinal Hernia Full Length Hd Youtube Benefits of robotic hernia repair compared to laparoscopic repair include: dexterity to reach previously inaccessible areas of the body. improved range of motion; the robot’s arms can rotate 360 degrees and are much more flexible than the human hand or wrist. high definition, magnified 3d images allow for improved visibility and accuracy. A systematic literature search was performed in pubmed, embase, and scopus for studies published between january 1st, 2010, and july 29th, 2021. search terms used were robotic inguinal hernia repair. titles, abstracts and full text articles were screened and selected by two authors (ls and gr) independently based on eligibility criteria.

Comments are closed.