Revolutionizing Pci Imaging And Physiology Take Center Stage For Superior Outcomes Cardiology
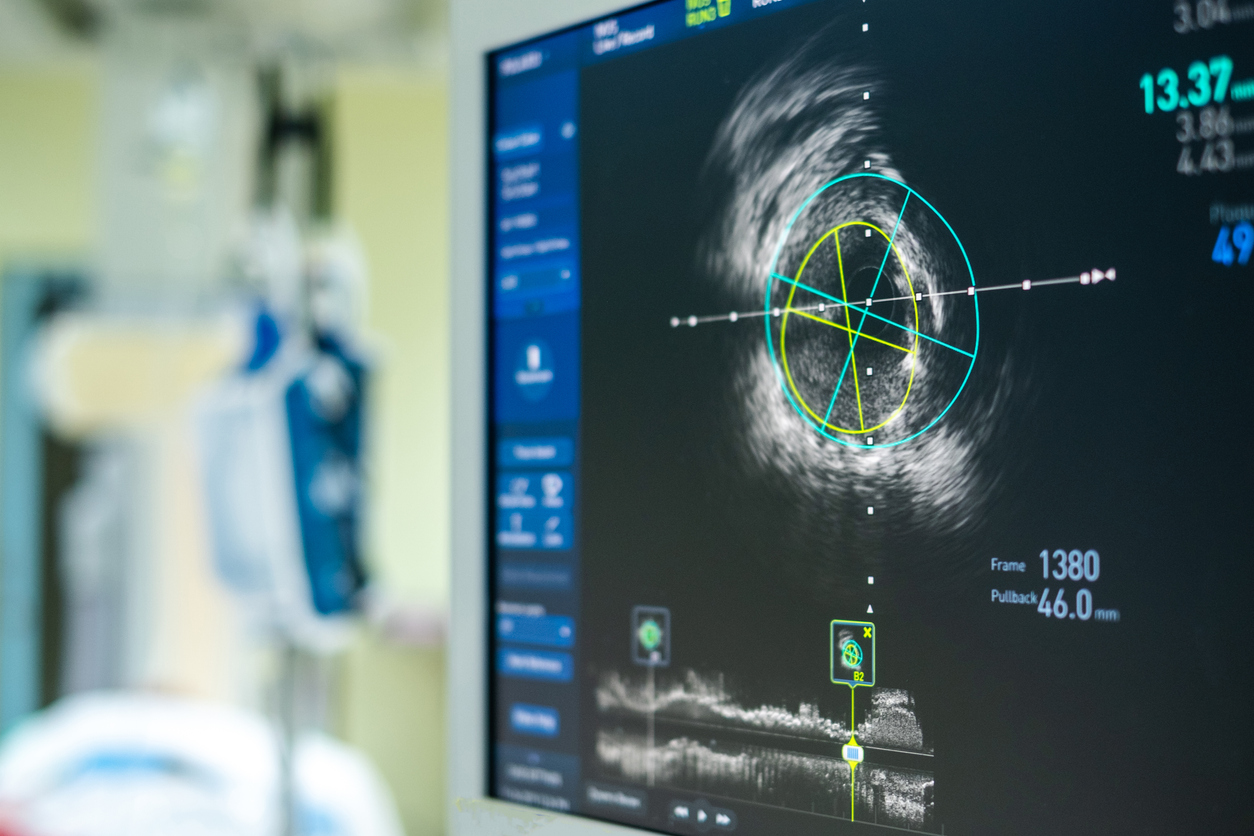
Precision Pci Guided By Physiology And Intracoronary Imaging The ffr search (fractional flow reserve–stent evaluated at rotterdam cardiology hospital) registry showed that 56% of patients treated in routine practice had ≥1 lesion with post pci ffr ≤0.90, a figure that was confirmed in the recently presented target ffr (an evaluation of a physiology guided pci optimisation strategy) study (68%) (71,72). Nevertheless, merely using these modalities is not enough, and to truly improve patient outcomes, optimal intravascular dimensions with minimal vascular injury should be targeted. when assessing post pci results using either type of physiological or imaging technology, a broad spectrum of stent and vessel related anomalies can be expected.
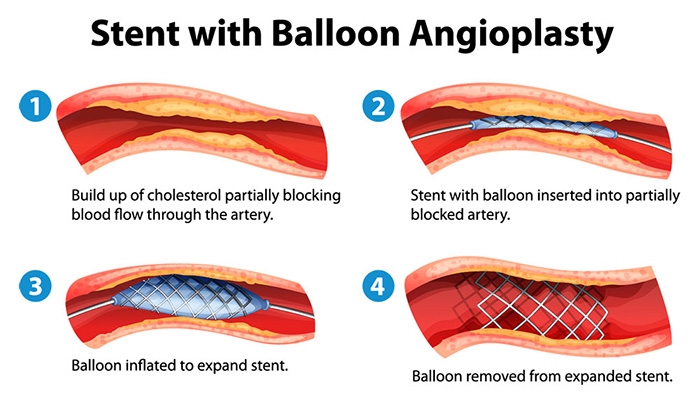
Beaumont Ambulatory Surgery Center Beaumont Heart Vascular Surgery Jacc cardiovasc interv 2021;14:2415 2430. the following are key points to remember from this state of the art review on improving percutaneous coronary intervention (pci) outcomes using postprocedural physiology and intravascular imaging: although clinical outcomes after pci are improving, the long term risk for target vessel failure remains. While intravascular imaging is recommended for planning and optimization of pci, 11 poststent physiological assessment can also independently estimate risk of adverse clinical events after stent implantation. 26,27 nonetheless, head to head comparison of clinical outcomes between physiology and imaging based pci optimization has rarely been. Minimum and mean stent expansion with oct was noninferior to ivus guided pci (but not superior to angiography alone). 41 together, these antecedent data set the stage for the large scale ilumien iv (optical coherence tomography guided coronary stent implantation compared to angiography: a multicenter randomized trial in pci; nct03507777), which. The main purpose of our trial was to evaluate whether intravascular imaging–guided pci would lead to a lower long term risk of target vessel failure for complex coronary lesions than angiography.

Improving Pci Outcomes Using Postprocedural Physiology And Minimum and mean stent expansion with oct was noninferior to ivus guided pci (but not superior to angiography alone). 41 together, these antecedent data set the stage for the large scale ilumien iv (optical coherence tomography guided coronary stent implantation compared to angiography: a multicenter randomized trial in pci; nct03507777), which. The main purpose of our trial was to evaluate whether intravascular imaging–guided pci would lead to a lower long term risk of target vessel failure for complex coronary lesions than angiography. Recent studies have demonstrated that multivessel disease patients with st elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (pci) experience better outcomes with culprit vessel pci followed by staged pci of other diseased vessels. 1 – 3 these findings are reflected in the current american college of cardiology american heart association guidelines for the. Contemporary reports indicate that post pci physiology results might remain below the clinical revascularisation thresholds of ≤0.80 for ffr and 0.90 for nhpr in approximately 24 36% of cases 2 3 71. potential mechanisms of suboptimal post pci physiology results are outlined in figure 4.

Comments are closed.