Representative Image Of The Pelvic Floor Ligaments And Their Relative

Representative Image Of The Pelvic Floor Ligaments And Their Relative Representative image of the pelvic floor ligaments and their relative anatomical positions in a female model full size image the pelvic diaphragm is located deep to the endopelvic fascia and consists of four muscles: ischiococcygeus, iliococcygeus, pubococcygeus, and puborectalis (the last three forming the levator ani muscle). Download scientific diagram | representative image of the pelvic floor ligaments and their relative anatomical positions in a female model from publication: dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of.
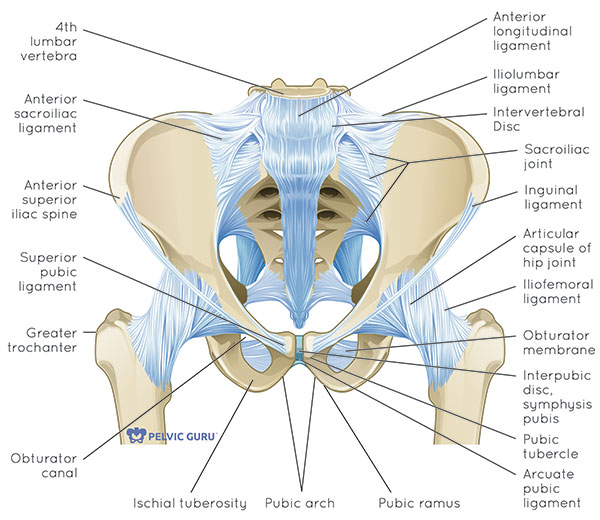
What Is The Pelvic Floor Your Pace Yoga Fig. 3 representative image of the pelvic floor ligaments and their relative anatomical positions in a female model fig. 2 pelvic compartments. sagittal midline t2 tse image. Disorders of the pelvic floor generally refer to the problems of urinary incontinence, fecal incontinence, and pelvic organ prolapse and affect an estimated 23.7% of women in the united states [1]. approximately 10–20% of these patients are symptomatic and by the age of 70 years, an estimated 1 in 10 undergo pelvic floor surgical repair. Pelvic organs are suspended by muscles, connective tissue and ligaments [1]. during a female’s lifetime, pelvic floor muscles and ligaments undergo birth related and age dependent structural alterations. pregnancy and childbirth are key situations in which excessive intra abdominal pressure strains the pelvic support structures. when these structures fail pelvic organ sagging, prolapse and. The pelvic floor is composed of a network of muscles, ligaments, and fasciae, which provide active and passive support for the pelvic organs. impairment of these pelvic floor elements can result in a variety of functional abnormalities and single or multicompartment organ prolapse. knowledge of normal pelvic floor anatomy can aid the radiologist in understanding the complex nature of pelvic.

Pelvic Bone Ligaments Pelvic organs are suspended by muscles, connective tissue and ligaments [1]. during a female’s lifetime, pelvic floor muscles and ligaments undergo birth related and age dependent structural alterations. pregnancy and childbirth are key situations in which excessive intra abdominal pressure strains the pelvic support structures. when these structures fail pelvic organ sagging, prolapse and. The pelvic floor is composed of a network of muscles, ligaments, and fasciae, which provide active and passive support for the pelvic organs. impairment of these pelvic floor elements can result in a variety of functional abnormalities and single or multicompartment organ prolapse. knowledge of normal pelvic floor anatomy can aid the radiologist in understanding the complex nature of pelvic. Axial mr slices at 5 mm intervals arranged caudal to cephalad starting from the image in the upper left. slice location relative to the arcuate pubic ligament (e.g. −0.5) are shown in the lower right corner of each images. deep uterosacral ligament tracings were made in dashed outline. The cardinal and uterosacral ligaments change their length and angle in response to the forces applied to the pelvic organs during increases in abdominal pressure. using 3d reconstructions from mr images of women with and without pelvic organ prolapse at rest and during maximal straining, ligament length and orientation have been measured ( fig.

Representative Image Of The Pelvic Floor Ligaments And Their Relative Axial mr slices at 5 mm intervals arranged caudal to cephalad starting from the image in the upper left. slice location relative to the arcuate pubic ligament (e.g. −0.5) are shown in the lower right corner of each images. deep uterosacral ligament tracings were made in dashed outline. The cardinal and uterosacral ligaments change their length and angle in response to the forces applied to the pelvic organs during increases in abdominal pressure. using 3d reconstructions from mr images of women with and without pelvic organ prolapse at rest and during maximal straining, ligament length and orientation have been measured ( fig.

Pelvic Floor Side View

Comments are closed.