Red Eye Differential Diagnosis 教育 健
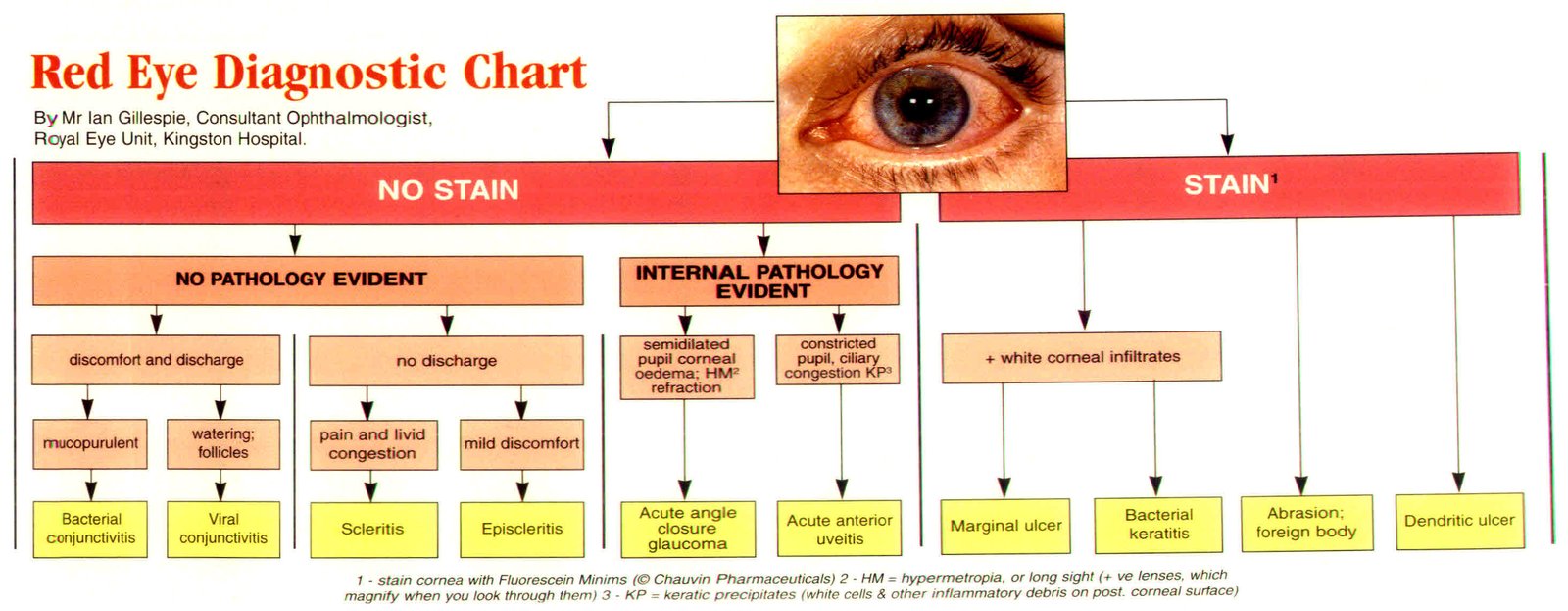
Red Eye Differential Diagnosis Chart Conjunctivitis is the most common cause of red eye and is one of the leading indications for antibiotics. 1 causes of conjunctivitis may be infectious (e.g., viral, bacterial, chlamydial) or. Red eye is a catch all term for the inflamed or injected external appearance of the eye, for which there are many causes. i like jeff mann’s approach to the red eye — he breaks the causes down into 3 groups: extra ocular causes (e.g. orbital cellulitis, cavernous sinus thrombosis, carotid cavernous fistula, cluster headache).
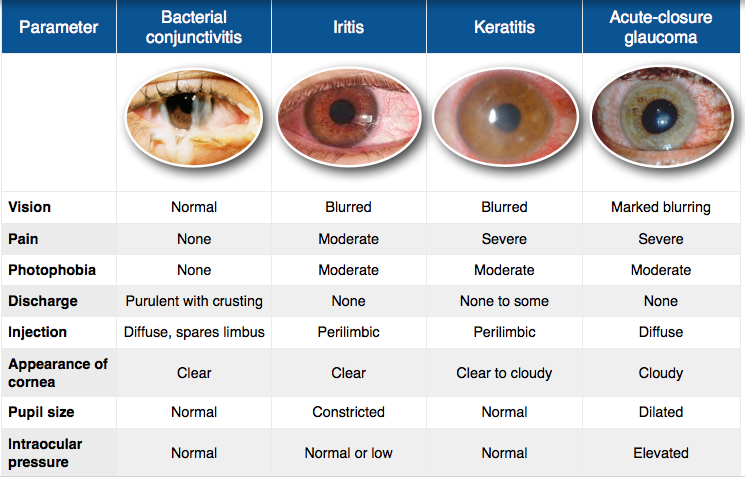
Red Eye Differential Diagnosis Medizzy Introduction "red eye" is a common presenting complaint in ambulatory practice. this topic presents an approach for distinguishing patients with red eye who must be referred to an ophthalmologist, such as those with angle closure glaucoma, from patients who can be managed by the primary care clinician, such as those with allergic conjunctivitis (table 1 and table 2). Usha chakravarthy, mbbs, frcs, phd. acute red eye is a common presenting complaint to primary care physicians. a detailed history of the presenting symptoms and previous ophthalmological and medical history can narrow the differential diagnosis and aid in the interpretation of key examination findings. Diagnosis of the underlying cause of red eye note: blepharitis, hordeolum, and chalazion are associated with a localized red, swol len, tender eyelid; other symptoms are rare. Definition: infection of soft tissues of the eye socket, difficult to distinguish from periorbital cellulitis. risk factors: ethmoid sinusitis, recent orbital trauma, endophthalmitis, or infections from teeth middle ear. symptoms: pain, swelling, and redness of eye and surrounding tissue. may note proptosis.

Red Eye Differential Diagnosis Chart Diagnosis of the underlying cause of red eye note: blepharitis, hordeolum, and chalazion are associated with a localized red, swol len, tender eyelid; other symptoms are rare. Definition: infection of soft tissues of the eye socket, difficult to distinguish from periorbital cellulitis. risk factors: ethmoid sinusitis, recent orbital trauma, endophthalmitis, or infections from teeth middle ear. symptoms: pain, swelling, and redness of eye and surrounding tissue. may note proptosis. Differential diagnosis of red eye 2,3,4,7,13,15 iop, intraocular pressure click table for larger version. blunt trauma, injury, or persistent pain are beyond the scope of this article and warrant. A red eye signifies ocular inflammation. the differential diagnosis includes both benign and sight threatening conditions. the pattern of redness; presence absence of eye pain or photophobia, vision loss, or eye discharge; involvement of cornea; and visual acuity are helpful in differentiating among causes (see table 25 1). although most red.
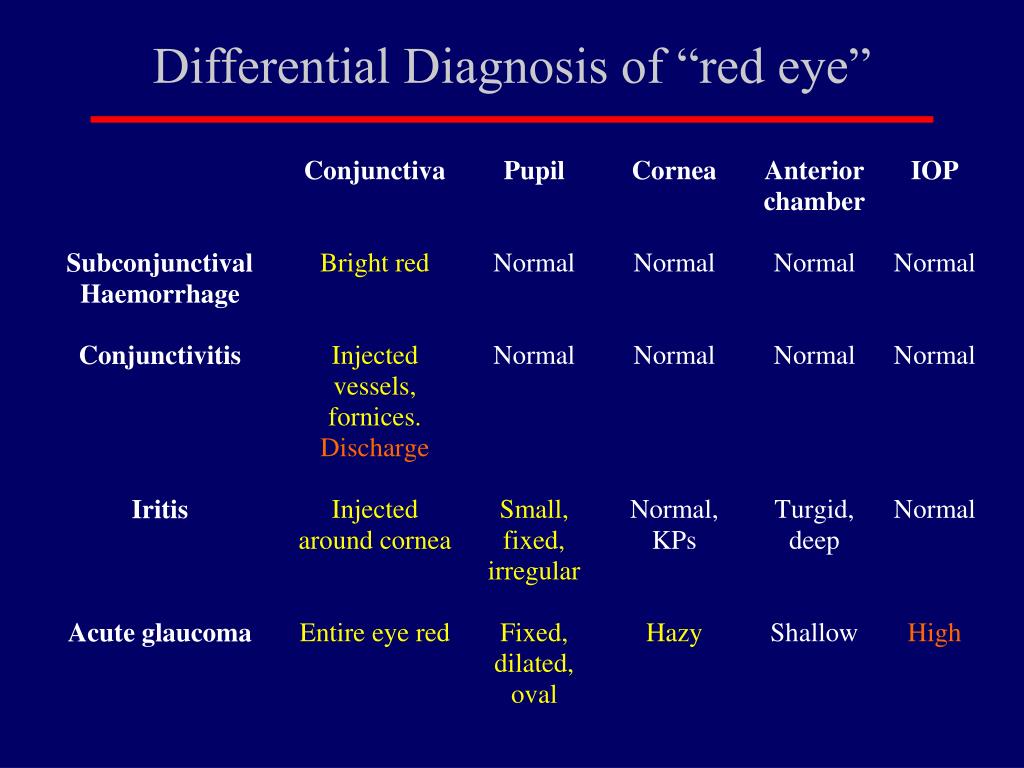
Ppt The Red Eye Differential Diagnosis Powerpoint Presentation Free Differential diagnosis of red eye 2,3,4,7,13,15 iop, intraocular pressure click table for larger version. blunt trauma, injury, or persistent pain are beyond the scope of this article and warrant. A red eye signifies ocular inflammation. the differential diagnosis includes both benign and sight threatening conditions. the pattern of redness; presence absence of eye pain or photophobia, vision loss, or eye discharge; involvement of cornea; and visual acuity are helpful in differentiating among causes (see table 25 1). although most red.

Comments are closed.