Recreational Volcanology Cross Section Of A Volcano

Recreational Volcanology Cross Section Of A Volcano (b) cross section across an outcropping sequence of lava flows of the mangahouhounui fm, tongariro compound volcano, new zealand, exposed by erosion. note that in both seismic and outcropping examples, the relationship between the strata defines a succession of volcanic events bounded by unconformities, across which younger rocks are deposited. Volcanoes are fascinating and powerful geological features that play a crucial role in shaping the earth's surface. studying the anatomy of volcanoes is essential for understanding their formation, behavior, and the impact they can have on the environment. this introduction will provide a brief overview of the definition of a volcano and highlight the importance of studying these dynamic.
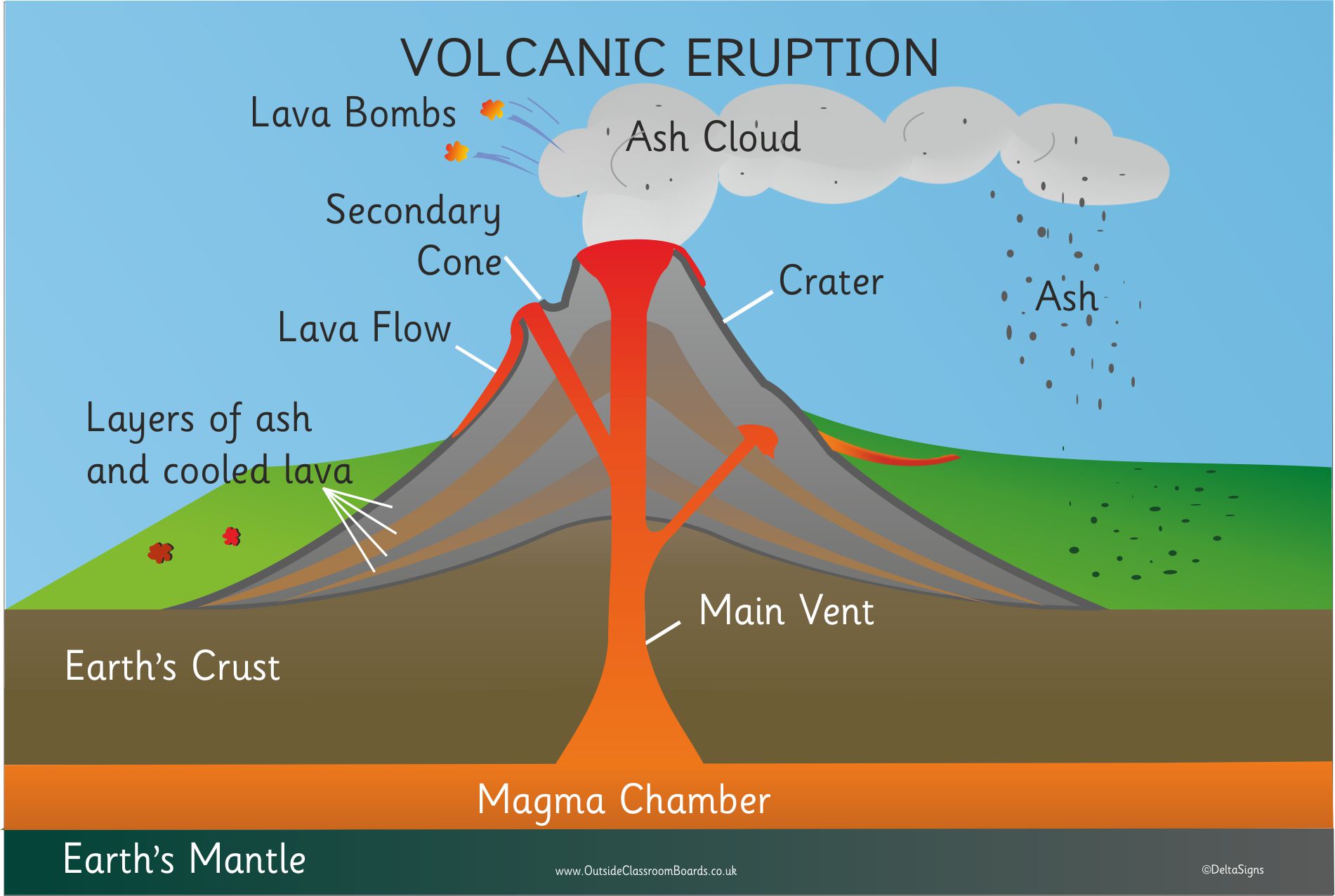
Cross Section Of Volcano Scienceforyou The result is the classic cone shape of composite volcanoes. figure 3. a cross section of a composite volcano reveals alternating layers of rock and ash: (1) magma chamber, (2) bedrock, (3) pipe, (4) ash layers, (5) lava layers, (6) lava flow, (7) vent, (8) lava, (9) ash cloud. frequently there is a large crater at the top from the last eruption. Cross section of a stratovolcano: 1. magma chamber 2. bedrock 3. vent 4. base 5. sill 6. dike 7. layers of ash 8. flank 9. layers of lava 10. throat 11. parasitic cone 12. lava flow 13. vent 14. Cross section of a volcano from enchanted learning. posted by ghost guns at 11:44 am. email this blogthis! share to twitter share to facebook share to pinterest. no. A theoretical cross section of a maar–diatreme volcano (a) and a tuff cone (b).on “a” the left side of the diagram shows the most likely volcanic edifice cross section developed on a “hard substrate” country rock environment, while on the right side of the diagram the typical features expected in the cross section of a maar–diatreme formed over “soft substrate” are shown.

Cross Section Of A Volcano Printable Cross section of a volcano from enchanted learning. posted by ghost guns at 11:44 am. email this blogthis! share to twitter share to facebook share to pinterest. no. A theoretical cross section of a maar–diatreme volcano (a) and a tuff cone (b).on “a” the left side of the diagram shows the most likely volcanic edifice cross section developed on a “hard substrate” country rock environment, while on the right side of the diagram the typical features expected in the cross section of a maar–diatreme formed over “soft substrate” are shown. The sizes and shapes of typical shield, composite, and cinder cone volcanoes are compared in figure 4.3.1, although, to be fair, mauna loa is the largest shield volcano on earth; all others are smaller. mauna loa rises from the surrounding flat sea floor, and its diameter is in the order of 200 km. Seismic and outcrop examples of large (>5 km 3 ) composite volcanos. this type of volcanic landform typically constitutes a single cone shaped body with a central vent located at or near the.

Comments are closed.