Recognizing Features Of Ild On Hrct Radiology Rounds
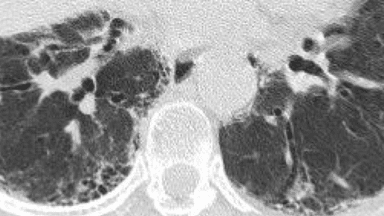
Recognizing Features Of Ild On Hrct Radiology Rounds This highlighted region of this image demonstrates traction bronchiectasis, resulting from fibrotic tissue “pulling” on the bronchi. recognizing and differentiating between features of ild on hrct. identification of comorbid conditions on hrct. distinguishing honeycombing and paraseptal emphysema. take the interactive quiz to test yourself. Next, we will review the common features of ild as seen on hrct. note that the characteristics associated with fibrotic lung disease include traction bronchiectasis, ground glass opacity, honeycombing, and reticulation. distinguishing honeycombing and paraseptal emphysema. select a feature of ild to learn more, or continue to the next section.
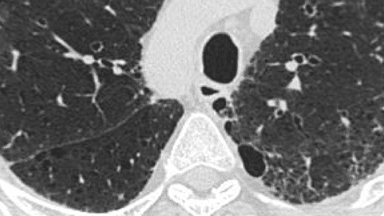
Recognizing Features Of Ild On Hrct Radiology Rounds Evaluating the features of an hrct scan. when evaluating a series of hrct scans, it is important to take note of both the dominant pattern or patterns and their distribution within the lungs. honeycombing, reticulation, traction bronchiectasis, and volume loss are hallmark features of fibrosis, 5,8 but scans from patients with fibrotic lung. 4.1. the hrct technique. in the era of multi detector row ct machines, a brief reminder of the hrct technique is pertinent. the two technical features that differentiate hrct imaging from conventional ct are, first, the narrow x ray beam collimation that significantly improves spatial resolution and, second, the use of a dedicated reconstruction algorithm []. Abstract. until today, computed tomography (ct) is the most important and valuable radiological modality to detect, analyze, and diagnose diffuse interstitial lung diseases (dild), based on the unsurpassed morphological detail provided by high resolution ct technique. in the past decade, there has been a shift from an isolated histopathological. A common understanding among all parties of the terms used to describe hrct features observed in ild can also help improve the effectiveness of mdd. when ipf is considered in the differential diagnosis, the radiologist should advise whether a uip pattern is present and, if so, their level of confidence, based on evaluation of image quality and.
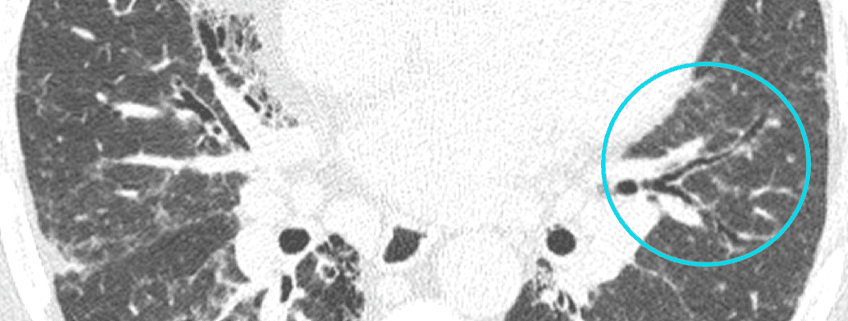
Recognizing Features Of Ild On Hrct Radiology Rounds Abstract. until today, computed tomography (ct) is the most important and valuable radiological modality to detect, analyze, and diagnose diffuse interstitial lung diseases (dild), based on the unsurpassed morphological detail provided by high resolution ct technique. in the past decade, there has been a shift from an isolated histopathological. A common understanding among all parties of the terms used to describe hrct features observed in ild can also help improve the effectiveness of mdd. when ipf is considered in the differential diagnosis, the radiologist should advise whether a uip pattern is present and, if so, their level of confidence, based on evaluation of image quality and. Ct findings common hrct findings of fibrosing disease include reticular opacities, ground glass opacities, traction bronchiolectasis, and honeycombing, the proportion and distribution of which vary. 10, 11 traction bronchiolectasis is an important finding for the diagnosis of fibrosing ild and often overlaps with reticular or ground glass opacities in patients with fibrosing lung disease. Rb ild is a clinicopathologic entity characterized by symptomatic interstitial lung disease associated with pathologic lesions of respiratory bronchiolitis [1, 11, 12]. highresolution ct features of rb ild include centrilobular ground glass opacities, thickening of central and peripheral airways with associated centrilobular emphysema and air.

Comments are closed.