Real Numbers Chart With Examples

Real Numbers What Are Real Numbers Definitions Examples Real numbers are closed under the arithmetic operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. in other words, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division of two real numbers, ‘m’ and ‘n’, always give a real number. for example, 2 5 = 7. 0.9 – 0.6 = 0.3. Some of the examples of real numbers are 23, 12, 6.99, 5 2, π, and so on. in this article, we are going to discuss the definition of real numbers, the properties of real numbers and the examples of real numbers with complete explanations. table of contents: definition; set of real numbers; chart; properties of real numbers. commutative.
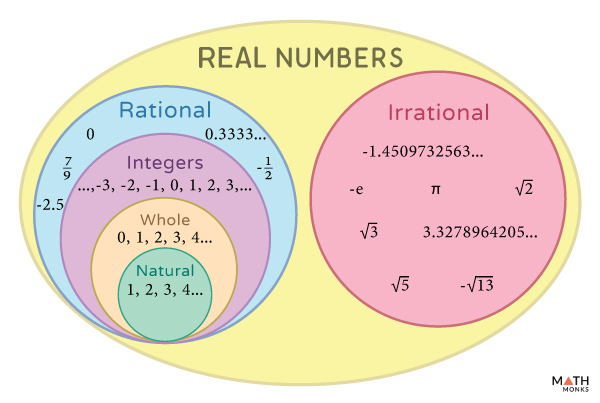
Real Numbers Definition Symbol Properties Chart Examples Integers include negative numbers, positive numbers, and zero. examples of real numbers: 1 2, 2 3, 0.5, √2. examples of integers: 4, 3, 0, 1, 2. the symbol that is used to denote real numbers is r. the symbol that is used to denote integers is z. every point on the number line shows a unique real number. Mathematicians also play with some special numbers that aren't real numbers. the real number line. the real number line is like a geometric line. a point is chosen on the line to be the "origin". points to the right are positive, and points to the left are negative. a distance is chosen to be "1", then whole numbers are marked off: {1,2,3. Properties of real numbers mathbitsnotebook (a1) a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuous number line. real numbers can be ordered. the symbol for the set of real numbers is , which is the letter r in the typeface "blackboard bold". the real numbers include: counting (natural) numbers () {1, 2, 3,. The following diagram shows the real number system and how real numbers can be classified. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on classifying real numbers. how to classify real numbers? classifying real numbers this video explains the different classifications of real numbers and has a number of examples.
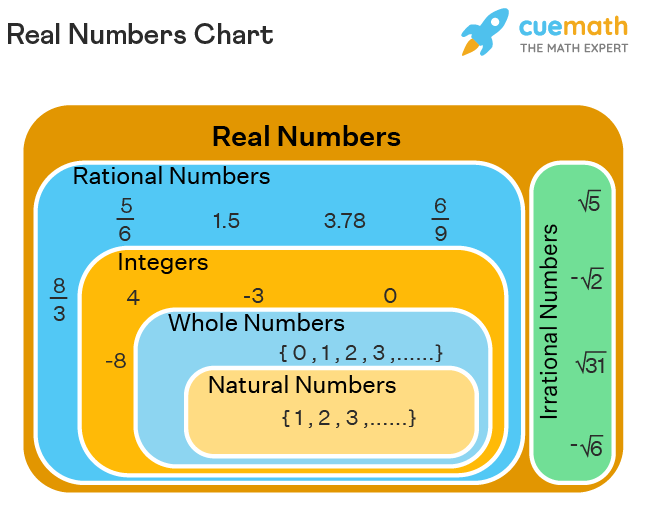
Real Numbers Definition Examples What Are Real Numbers Properties of real numbers mathbitsnotebook (a1) a real number is a value that represents a quantity along a continuous number line. real numbers can be ordered. the symbol for the set of real numbers is , which is the letter r in the typeface "blackboard bold". the real numbers include: counting (natural) numbers () {1, 2, 3,. The following diagram shows the real number system and how real numbers can be classified. scroll down the page for more examples and solutions on classifying real numbers. how to classify real numbers? classifying real numbers this video explains the different classifications of real numbers and has a number of examples. A real number is any number that can be placed on a number line or expressed as in infinite decimal expansion. in other words, a real number is any rational or irrational number, including positive and negative whole numbers, integers, decimals, fractions, and numbers such as pi (π) and euler’s number (e). in contrast, an imaginary number or. A rational number is a number of the form p q, p q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. q ≠ 0. a rational number can be written as the ratio of two integers. all signed fractions, such as 45, − 78, 134, − 203 4 5, − 7 8, 13 4, − 20 3 are rational numbers. each numerator and each denominator is an integer.
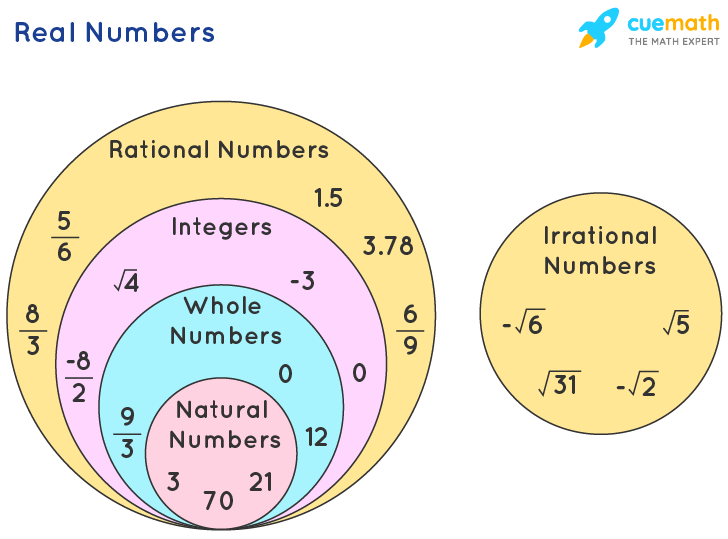
Representation Of Real Numbers On Number Line Steps Method Real A real number is any number that can be placed on a number line or expressed as in infinite decimal expansion. in other words, a real number is any rational or irrational number, including positive and negative whole numbers, integers, decimals, fractions, and numbers such as pi (π) and euler’s number (e). in contrast, an imaginary number or. A rational number is a number of the form p q, p q, where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. q ≠ 0. a rational number can be written as the ratio of two integers. all signed fractions, such as 45, − 78, 134, − 203 4 5, − 7 8, 13 4, − 20 3 are rational numbers. each numerator and each denominator is an integer.

Comments are closed.