Radiator Convection Diagram

Convection Heat Through Radiator Inspection Gallery Internachi It's a closed cycle process that allows radiators to heat your home effectively.'. while the heat rises from your radiator in the form of air, the water inside becomes cooler and eventually returns to the boiler to be heated. this process is repeated as long as is needed and is typically regulated with a thermostat. Course: up class 11 physics > unit 6. lesson 4: heat transfer. thermal conduction, convection, and radiation. thermal conduction (basic) thermal conductivity rods connected at a junction.
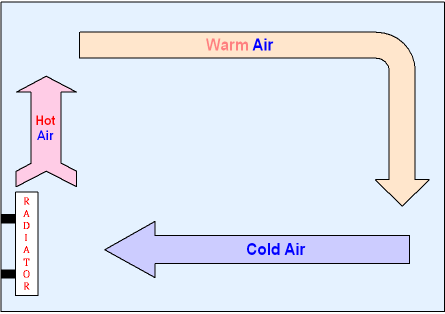
Gcse Physics How Convection Currents Transfer Heat Density Changes The colder air above it gets pushed along. to the right and then circulates as shown by the arrows. the arrows show how the convection currents move. in the room. finally the colder air circulates near to. repeats itself. the efficiency of convection can be. improved by placing shiny metal foil behind the radiator. A radiator is a device that transfers heat to a medium primarily through thermal radiation.in practice, the term radiator is often applied to any number of devices in which a fluid circulates through exposed pipes (often with fins or other means of increasing surface area), notwithstanding that such devices tend to transfer heat mainly by convection and might logically be called convectors. A more complicated example is the cooling system of a typical car, in which a pump moves coolant through the radiator and engine to cool the engine and a fan blows air to cool the radiator. in free or natural convection, the flow is driven by buoyant forces: hot fluid rises and cold fluid sinks because density decreases as temperature increases. A convection current from a radiator; radiation. absorbing radiation; heat the boiling tube at the top with a bunsen burner as shown in the diagram. record your observations.
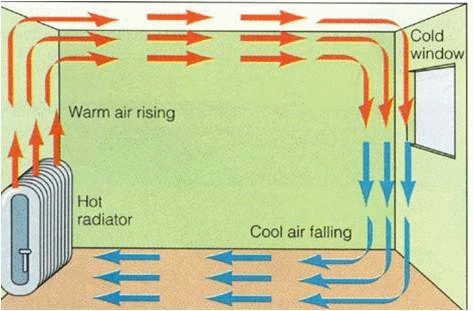
Convection A more complicated example is the cooling system of a typical car, in which a pump moves coolant through the radiator and engine to cool the engine and a fan blows air to cool the radiator. in free or natural convection, the flow is driven by buoyant forces: hot fluid rises and cold fluid sinks because density decreases as temperature increases. A convection current from a radiator; radiation. absorbing radiation; heat the boiling tube at the top with a bunsen burner as shown in the diagram. record your observations. A radiator works by heating the air around it. this hot air then rises and is replaced by colder air. this cycle continues and creates a convection current, which keeps your entire room warm. what are the 2 valves on a radiator? the two valves on a radiator are the flow valve, which controls the amount of hot water entering the radiator, and. In a radiator, convection occurs as hot air from the radiator rises, drawing in cooler air from the room which is then heated and rises in turn. this creates a circulation of hot and cool air that helps to evenly distribute the heat throughout the room. radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, and radiators emit heat in.
Structural Diagram Of Radiation And Convection Coupled Heat Transfer A radiator works by heating the air around it. this hot air then rises and is replaced by colder air. this cycle continues and creates a convection current, which keeps your entire room warm. what are the 2 valves on a radiator? the two valves on a radiator are the flow valve, which controls the amount of hot water entering the radiator, and. In a radiator, convection occurs as hot air from the radiator rises, drawing in cooler air from the room which is then heated and rises in turn. this creates a circulation of hot and cool air that helps to evenly distribute the heat throughout the room. radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, and radiators emit heat in.

Atmospheric Pressure And Temperature Air Pollution Brian Williams

Air Convection From Radiator Illustration Stock Image C050 7511

Comments are closed.