Pythagorean Theorem Mathhelp Com

Pythagorean Theorem Mathhelp Com Youtube Need a custom math course? visit mathhelp.com.this lesson covers the pythagorean theorem, which states that the sum of the squares of the lengths. Students learn the pythagorean theorem, which states that the sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs of a right triangle is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse, or a^2 b^2 = c^2. students are then asked to find missing side lengths of right triangles using the pythagorean theorem. we help you determine the exact lessons.
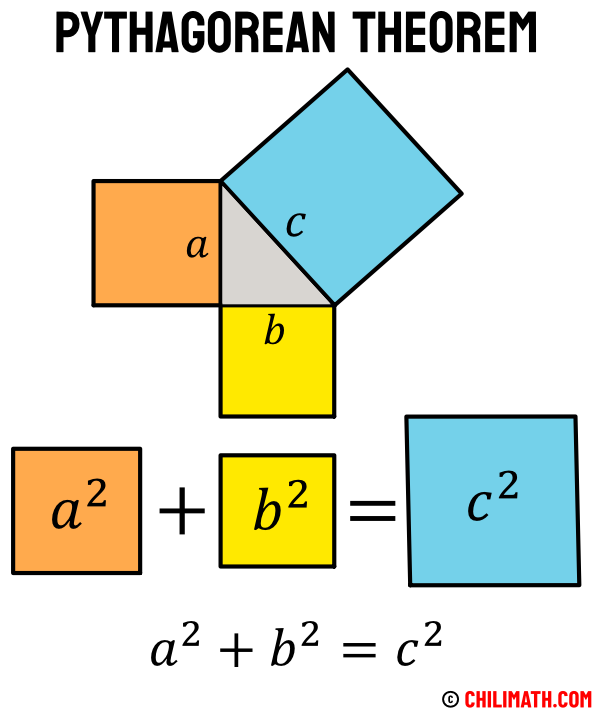
Pythagorean Theorem Definition Formula Examples Chilimath Want to practice the pythagorean theorem?go to: member.mathhelp.com courses middle and high school 48 chapter 7 lesson 3055in this lesson, students l. Need a custom math course? visit mathhelp.com.this lesson covers pythagorean theorem word problems. students use the pythagorean theorem to find. The pythagorean theorem is a rule that relates the two legs of a right triangle, having lengths a and b, to the length c of the hypotenuse by the following rule: a2 b2 = c2. this equation allows you to find the length of a side of a right triangle when they've given you the lengths for the other two sides, and, going in the other direction. Use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 6 and 8. x x is the hypotenuse because it is opposite the right angle. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). a2 b2 = c2 62 82 = x2 a 2 b 2 = c 2 6 2 8 2.

Exploring The Pythagorean Theorem Mathhelp Geometry Geometria Youtube The pythagorean theorem is a rule that relates the two legs of a right triangle, having lengths a and b, to the length c of the hypotenuse by the following rule: a2 b2 = c2. this equation allows you to find the length of a side of a right triangle when they've given you the lengths for the other two sides, and, going in the other direction. Use the pythagorean theorem to determine the length of x. step 1. identify the legs and the hypotenuse of the right triangle. the legs have length 6 and 8. x x is the hypotenuse because it is opposite the right angle. step 2. substitute values into the formula (remember 'c' is the hypotenuse). a2 b2 = c2 62 82 = x2 a 2 b 2 = c 2 6 2 8 2. Interior angle Δθ = θ 1 −θ 2. the pythagorean theorem is a special case of the more general theorem relating the lengths of sides in any triangle, the law of cosines, which states that where is the angle between sides and . [45] when is radians or 90°, then , and the formula reduces to the usual pythagorean theorem. The sum of the smaller squares (orange and yellow) is equal to the largest square (blue). the pythagorean theorem relates the three sides in a right triangle. to be specific, relating the two legs and the hypotenuse, the longest side. the pythagorean theorem can be summarized in a short and compact equation as shown below.
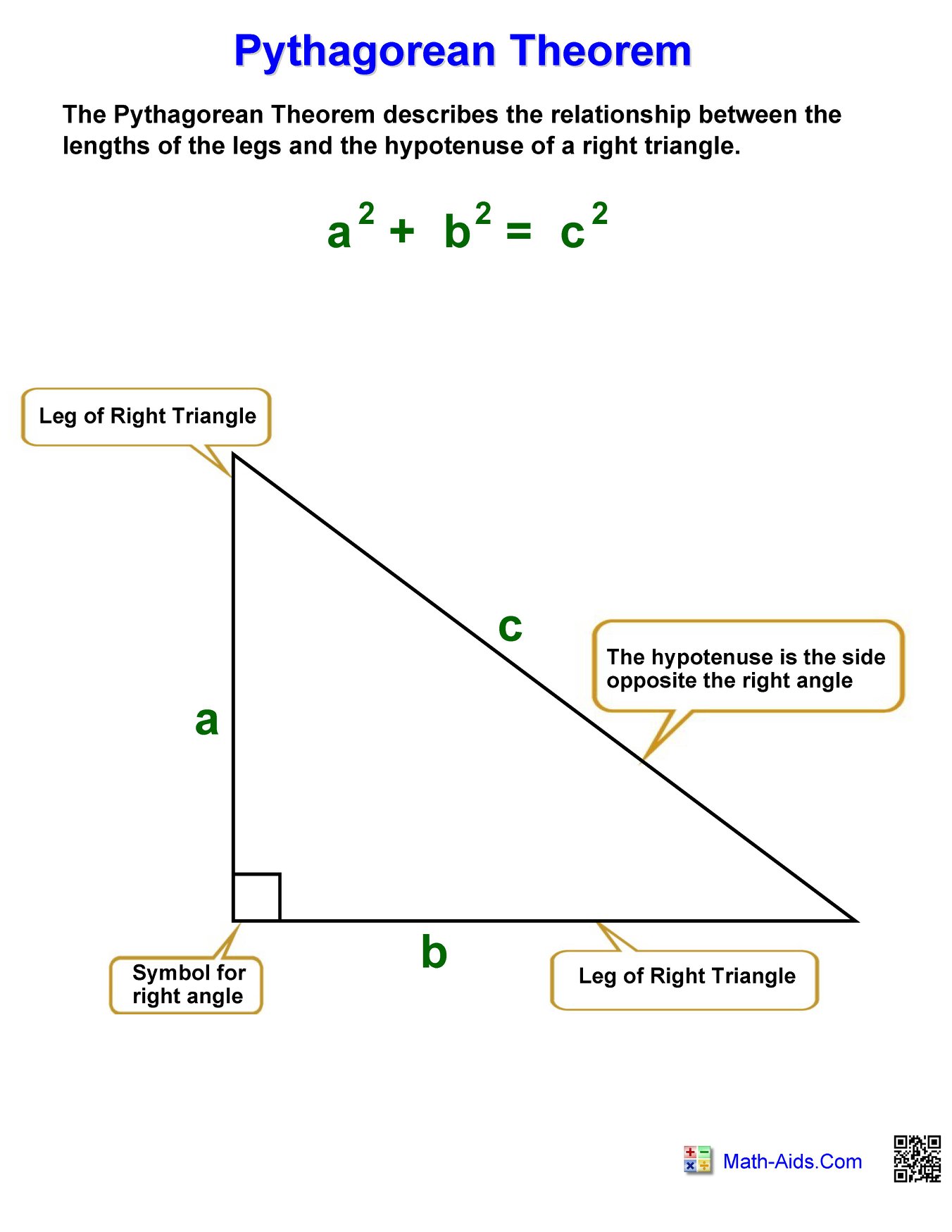
Pythagorean Theorem Chart Hoeden At Home Interior angle Δθ = θ 1 −θ 2. the pythagorean theorem is a special case of the more general theorem relating the lengths of sides in any triangle, the law of cosines, which states that where is the angle between sides and . [45] when is radians or 90°, then , and the formula reduces to the usual pythagorean theorem. The sum of the smaller squares (orange and yellow) is equal to the largest square (blue). the pythagorean theorem relates the three sides in a right triangle. to be specific, relating the two legs and the hypotenuse, the longest side. the pythagorean theorem can be summarized in a short and compact equation as shown below.
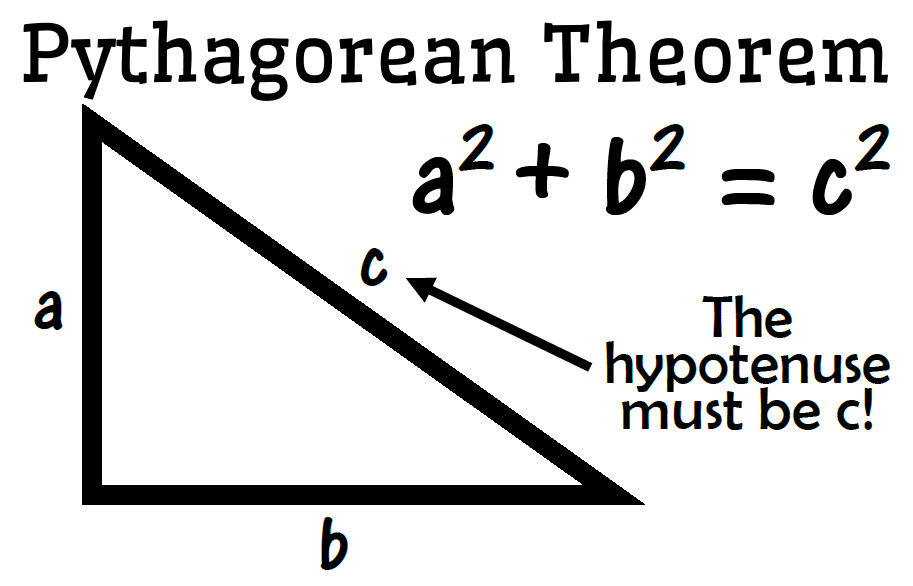
Pythagorean Theorem Poster Math Love

Comments are closed.