Proven Ultra Widefield Retinal Imaging

Ultra Widefield Retinal Imaging Noosa Optical Noosa Junction Abstract. the development of ultra widefield retinal imaging has accelerated our understanding of common retinal diseases. as we continue to validate the diagnostic and prognostic significance of pathology in the retinal periphery, the ability to visualize and evaluate these features in an efficient and patient friendly manner will become more. In 2019, the international widefield imaging study group defined widefield imaging as a field of view of approximately 60 to 100 degrees, capturing the mid periphery of the retina up to the posterior edge of the vortex vein ampulla. 1 it defined ultra widefield imaging as an image of the far periphery of the retina, including the anterior edge of the vortex vein ampulla and beyond. 1 this.

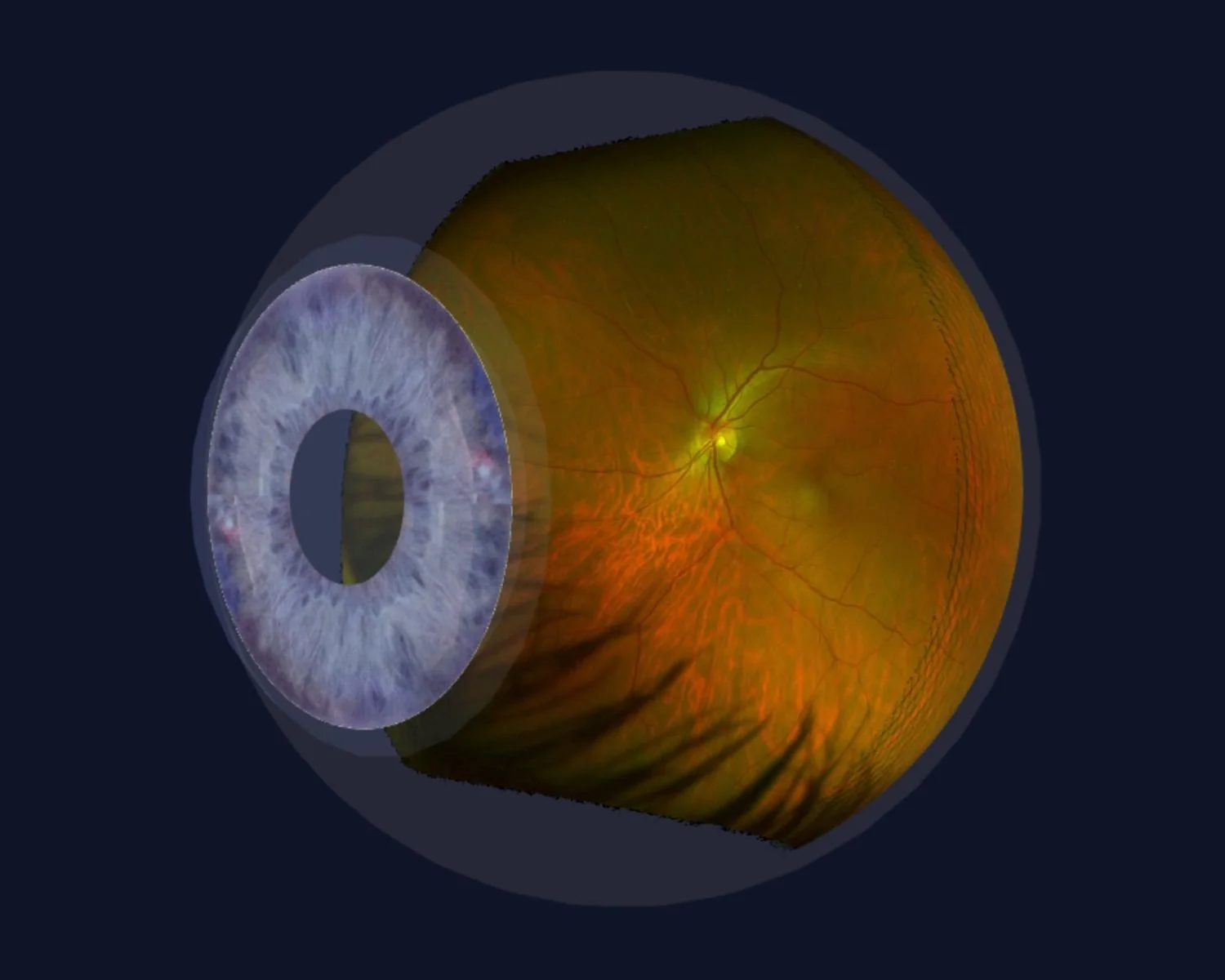
Ultra Widefield Retinal Imaging Local Eyes Optometrists Mackay Ultra widefield (uwf) imaging has changed the way ophthalmologists evaluate a patient’s fundus, and its use has led to a better understanding of the role that peripheral pathology can play in retinal diseases. uwf imaging modalities provide several options for posterior segment documentation and evaluation, including color and red free images. Recommendations from the international widefield imaging study group. purpose: to summarize the results of a consensus meeting aimed at defining terminology for wide field imaging across all retinal imaging methods and to provide recommendations for the nomenclature used to describe related images. Photographic imaging of the fundus has evolved significantly over the past century. the first fundus camera was developed by the carl zeiss company in 1926, providing a 20° and later 30° view of the posterior pole. 1 early widefield imaging, capturing more than the standard 30° view, was performed using a traditional camera; the use of a fixation lamp and mirror then allowed for the. This was followed by the portable retcam system in 1997 by bert massie. 8 the term ultra widefield subsequently was used to describe the capture of a single retinal image of 200° of the retina by the optos fundus imaging system. 9 although the retcam and optos cameras initially were adapted for pediatric use, the desire for a more complete.

Optos Ultra Widefield Retinal Imaging System Mivision Photographic imaging of the fundus has evolved significantly over the past century. the first fundus camera was developed by the carl zeiss company in 1926, providing a 20° and later 30° view of the posterior pole. 1 early widefield imaging, capturing more than the standard 30° view, was performed using a traditional camera; the use of a fixation lamp and mirror then allowed for the. This was followed by the portable retcam system in 1997 by bert massie. 8 the term ultra widefield subsequently was used to describe the capture of a single retinal image of 200° of the retina by the optos fundus imaging system. 9 although the retcam and optos cameras initially were adapted for pediatric use, the desire for a more complete. Traditional colour fundus photography (cfp) typically images 30–60° of the retina, but new imaging devices allow for ultra widefield (uwf) retinal images with a field of view of 100–200. Based on anatomical landmarks, the definition of these two terms were formalized by a consensus group of retinal imaging experts. [3] widefield image was defined as a single capture, fovea centered image, which captures retinal features beyond the posterior pole, but posterior to the vortex vein ampulla, in all four quadrants.
.jpg)
Optomap Ultra Widefield Retinal Imaging Traditional colour fundus photography (cfp) typically images 30–60° of the retina, but new imaging devices allow for ultra widefield (uwf) retinal images with a field of view of 100–200. Based on anatomical landmarks, the definition of these two terms were formalized by a consensus group of retinal imaging experts. [3] widefield image was defined as a single capture, fovea centered image, which captures retinal features beyond the posterior pole, but posterior to the vortex vein ampulla, in all four quadrants.

Comments are closed.