Primary Somatosensory Cortex Homunculus

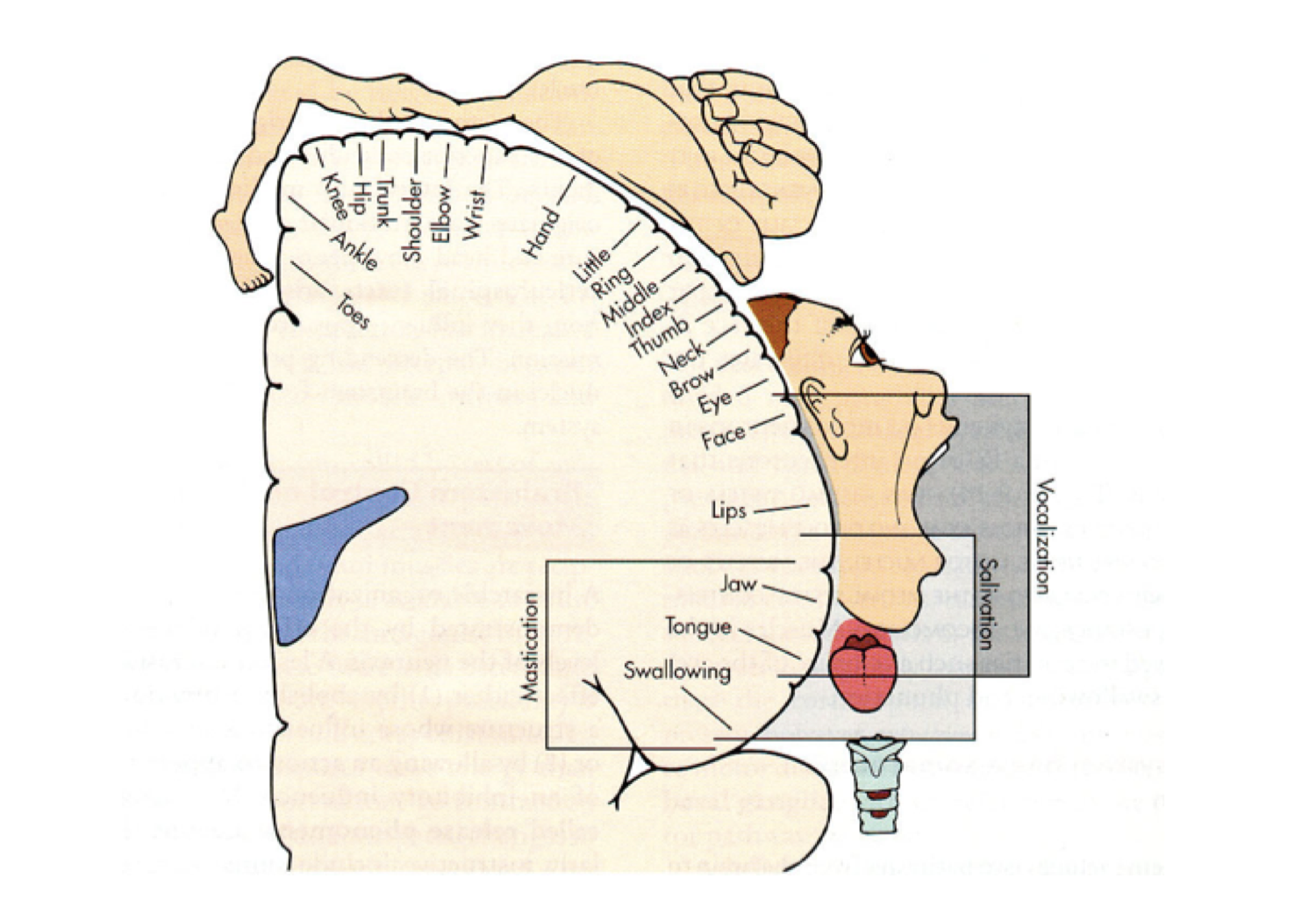
Primary Somatosensory Cortex Homunculus Primary somatosensory cortex lateral view, cortical homunculus and cortical homunculus, primary somatosensory cortex). the primary somatosensory cortex is found just behind the central sulcus. it receives sensory information from the ventral posterolateral nucleus (vpl) of the thalamus via the internal capsule and corona radiata. Homunculus: the idea of the cortical homunculus was created by wilder penfield and serves as a rough map of the receptive fields for regions of primary somatosensory cortex. the resulting image is a grotesquely disfigured human with disproportionately huge hands, lips, and face in comparison to the rest of the body.

Primary Somatosensory Cortex Homunculus A 2 d model of cortical sensory homunculus. a cortical homunculus (from latin homunculus 'little man, miniature human' [1] [2]) is a distorted representation of the human body, based on a neurological "map" of the areas and portions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor functions, and or sensory functions, for different parts of the body. Dysfunction. the somatosensory cortex is a region of the brain located in the parietal lobe and lies behind the primary motor cortex of the frontal lobe. it is responsible for processing sensory information from the body. the cortex interprets tactile stimuli, such as touch, temperature, pain, and proprioception (awareness of body position). Penfield’s description of the ‘homunculus’, a ‘grotesque creature’ with large lips and hands and small trunk and legs depicting the representation of body parts within the primary somatosensory cortex (s1), is one of the most prominent contributions to the neurosciences. since then, numerous studies have identified additional body. The primary somatosensory cortex exhibits a somatotopic organization, often illustrated as a sensory homunculus. this is a distorted representation of the human body, based on the neurological “map” of the areas and proportions of the brain dedicated to processing motor functions or sensory input for different parts of the body.
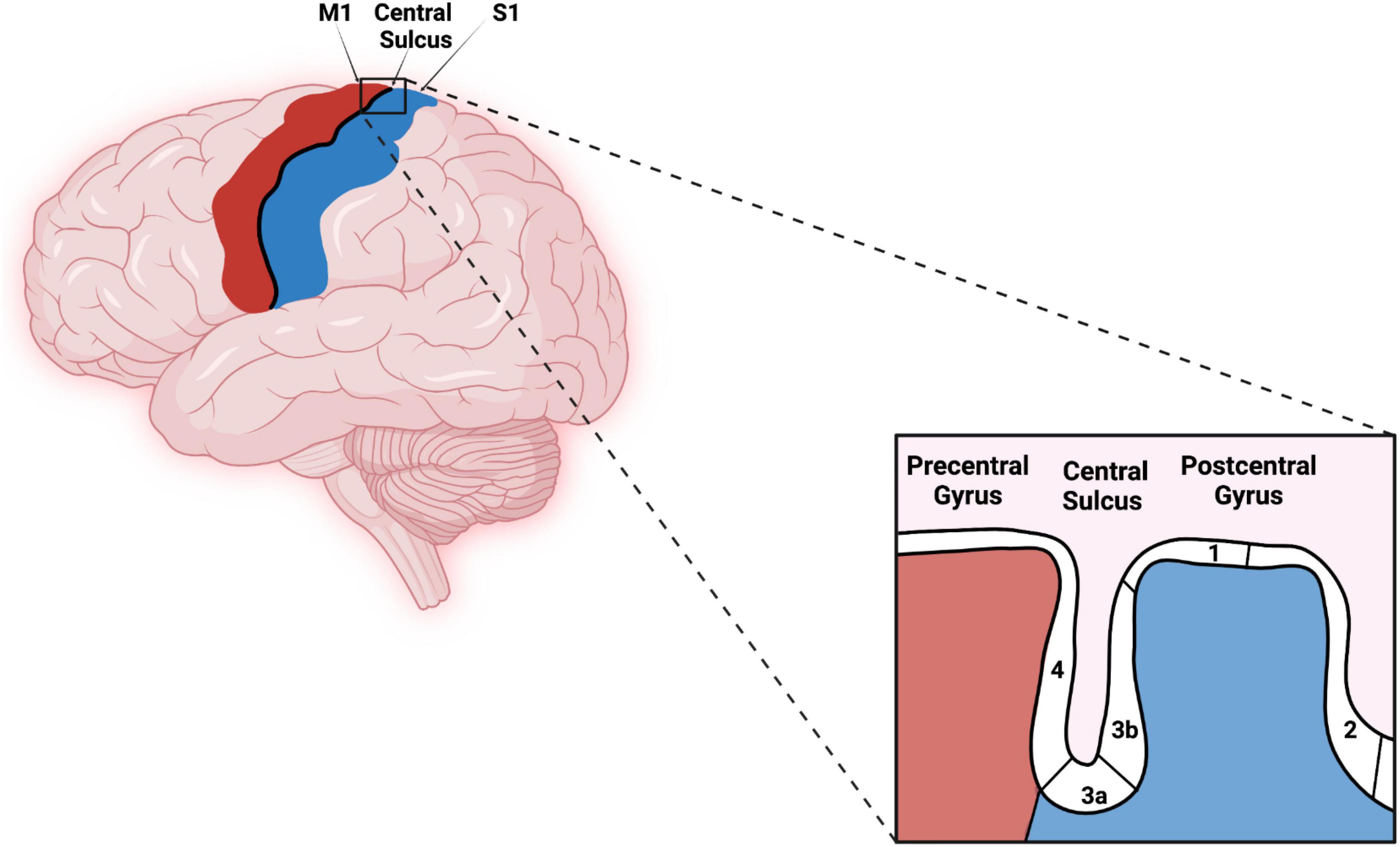
Primary Somatosensory Cortex Homunculus Penfield’s description of the ‘homunculus’, a ‘grotesque creature’ with large lips and hands and small trunk and legs depicting the representation of body parts within the primary somatosensory cortex (s1), is one of the most prominent contributions to the neurosciences. since then, numerous studies have identified additional body. The primary somatosensory cortex exhibits a somatotopic organization, often illustrated as a sensory homunculus. this is a distorted representation of the human body, based on the neurological “map” of the areas and proportions of the brain dedicated to processing motor functions or sensory input for different parts of the body. The primary somatosensory cortex (s1) plays a critical role in processing afferent somatosensory input and contributes to the integration of sensory and motor signals necessary for skilled movement. neuroimaging and neurostimulation approaches provide unique opportunities to non invasively study s1 structure and function including connectivity. The primary somatosensory cortex (si) is located in the anterior part of the parietal lobe, where it constitutes the postcentral gyrus. it consists of brodmann areas 1, 2, 3a, and 3b (figure 2 (a)). areas 3b and 1 receive cutaneous tactile input, areas 3a and 2 proprioceptive input.
Primary Somatosensory Cortex Homunculus The primary somatosensory cortex (s1) plays a critical role in processing afferent somatosensory input and contributes to the integration of sensory and motor signals necessary for skilled movement. neuroimaging and neurostimulation approaches provide unique opportunities to non invasively study s1 structure and function including connectivity. The primary somatosensory cortex (si) is located in the anterior part of the parietal lobe, where it constitutes the postcentral gyrus. it consists of brodmann areas 1, 2, 3a, and 3b (figure 2 (a)). areas 3b and 1 receive cutaneous tactile input, areas 3a and 2 proprioceptive input.

Homunculus Description History Models Importance Britannica

Comments are closed.