Preposition Rules Javatpoint

Preposition Rules Javatpoint 10. use preposition "like" and "as" properly. 10 (a) avoid using 'like' when there is a verb involved. the preposition 'like,' which is equivalent to "similar to," must be accompanied by a noun, pronoun, or noun phrase as the preposition's object. the preposition 'like' must not be followed by a subject or verb. Preposition. " a preposition is a term or phrase preceding the nouns, pronouns, or noun phrases to indicate directions, timing, place, location, spatial relations, or introducing an item." terms like "in," "at," "on," "of," and "to" are instances of prepositions. moreover, it is important to note that in english language, prepositions are.
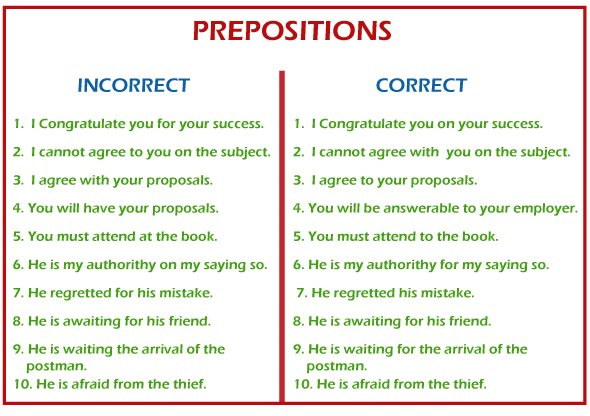
Preposition Rules Javatpoint 4. participle preposition. participle prepositions can be of two types present participles ( ing) and past participles ( ed and en), which are employed as prepositions rather than verbs. these are both participles and prepositions. participle prepositions usually end with a suffix such as ed en and ing. A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other parts of a sentence. it tells us where something is, when something happens, or how things are related. common prepositions include words like “in,” “on,” “at,” “under,” and “with.”. for example, in the sentence “the book is on the. For instance, royal inn is a good place to stay at. rule no. 4 and when an object is a relative pronoun ‘that’ in that case, the preposition comes at the end. for instance, this is an activity that i’m fond of. rule no. 5 in the formation of interrogative sentences preposition comes at the beginning of the sentence. Participle prepositions; prepositions in phrases; 1. prepositions that are simple. terms such as at, for, in, off, on, over, and beneath are examples of simple prepositions. such prepositions are commonly employed for describing the locations, timing, or places. here are a few preposition examples of common prepositions employed in statements:.
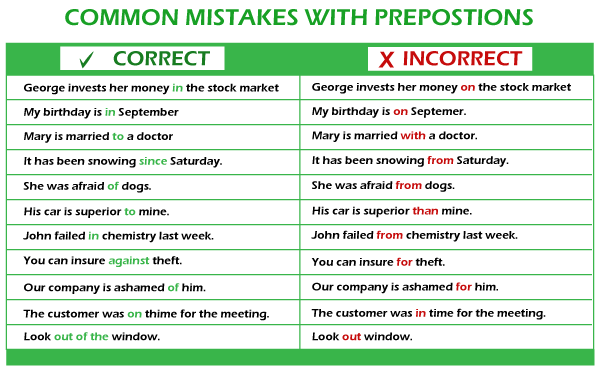
Preposition Rules Javatpoint For instance, royal inn is a good place to stay at. rule no. 4 and when an object is a relative pronoun ‘that’ in that case, the preposition comes at the end. for instance, this is an activity that i’m fond of. rule no. 5 in the formation of interrogative sentences preposition comes at the beginning of the sentence. Participle prepositions; prepositions in phrases; 1. prepositions that are simple. terms such as at, for, in, off, on, over, and beneath are examples of simple prepositions. such prepositions are commonly employed for describing the locations, timing, or places. here are a few preposition examples of common prepositions employed in statements:. Discrete mathematics propositional logic the rules of mathematical logic specify methods of reasoning mathematical statements. greek philosopher, aristotle, was the pioneer of logical reasoning. logical reasoning provides the theoretical base for many areas of mathematics and consequently computer science. it has many practical application. The following rules will help you understand and use prepositions correctly. 1. a preposition must have an object. all prepositions have objects. if a "preposition" does not have an object it is not a preposition—it's probably an adverb. a preposition always has an object. an adverb never has an object.
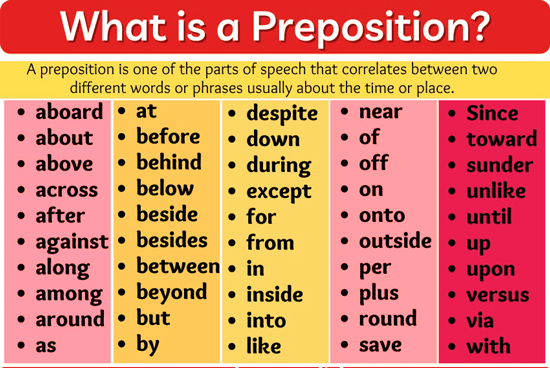
Preposition Javatpoint Discrete mathematics propositional logic the rules of mathematical logic specify methods of reasoning mathematical statements. greek philosopher, aristotle, was the pioneer of logical reasoning. logical reasoning provides the theoretical base for many areas of mathematics and consequently computer science. it has many practical application. The following rules will help you understand and use prepositions correctly. 1. a preposition must have an object. all prepositions have objects. if a "preposition" does not have an object it is not a preposition—it's probably an adverb. a preposition always has an object. an adverb never has an object.

Comments are closed.