Predicted Vs Actual Plot
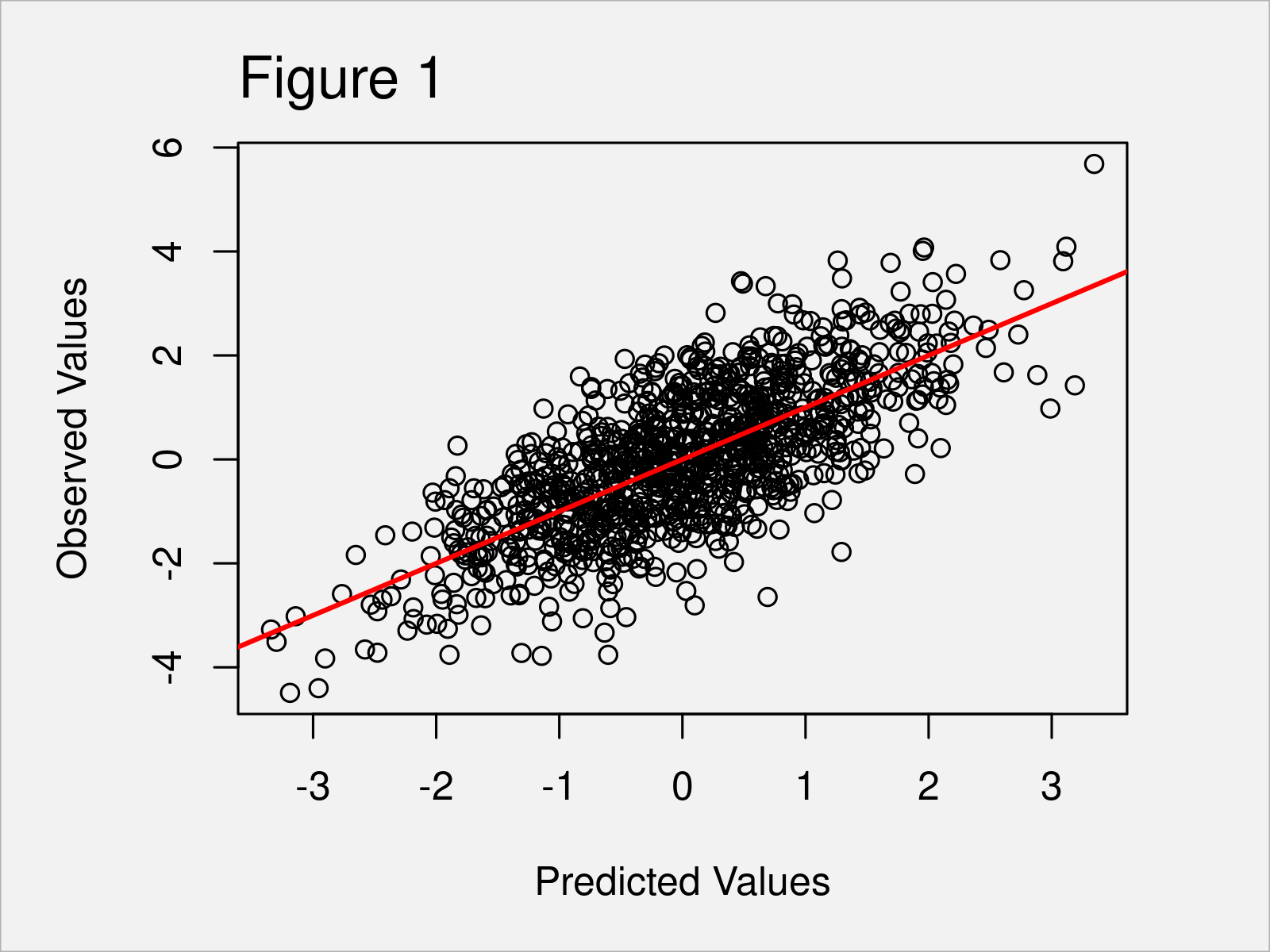
Plot Predicted Vs Actual Values In R Example Draw Fitted Observed Scatter plots of actual vs predicted are one of the richest form of data visualization. you can tell pretty much everything from it. ideally, all your points should be close to a regressed diagonal line. so, if the actual is 5, your predicted should be reasonably close to 5 to. if the actual is 30, your predicted should also be reasonably close. As shown in figure 1, we have created a base r scatterplot that shows predicted vs. actual values. the red line illustrates the slope of our values. example 2: draw predicted vs. observed using ggplot2 package. in this example, i’ll demonstrate how to use the ggplot2 package to draw an xy plot of predicted vs. actual values.
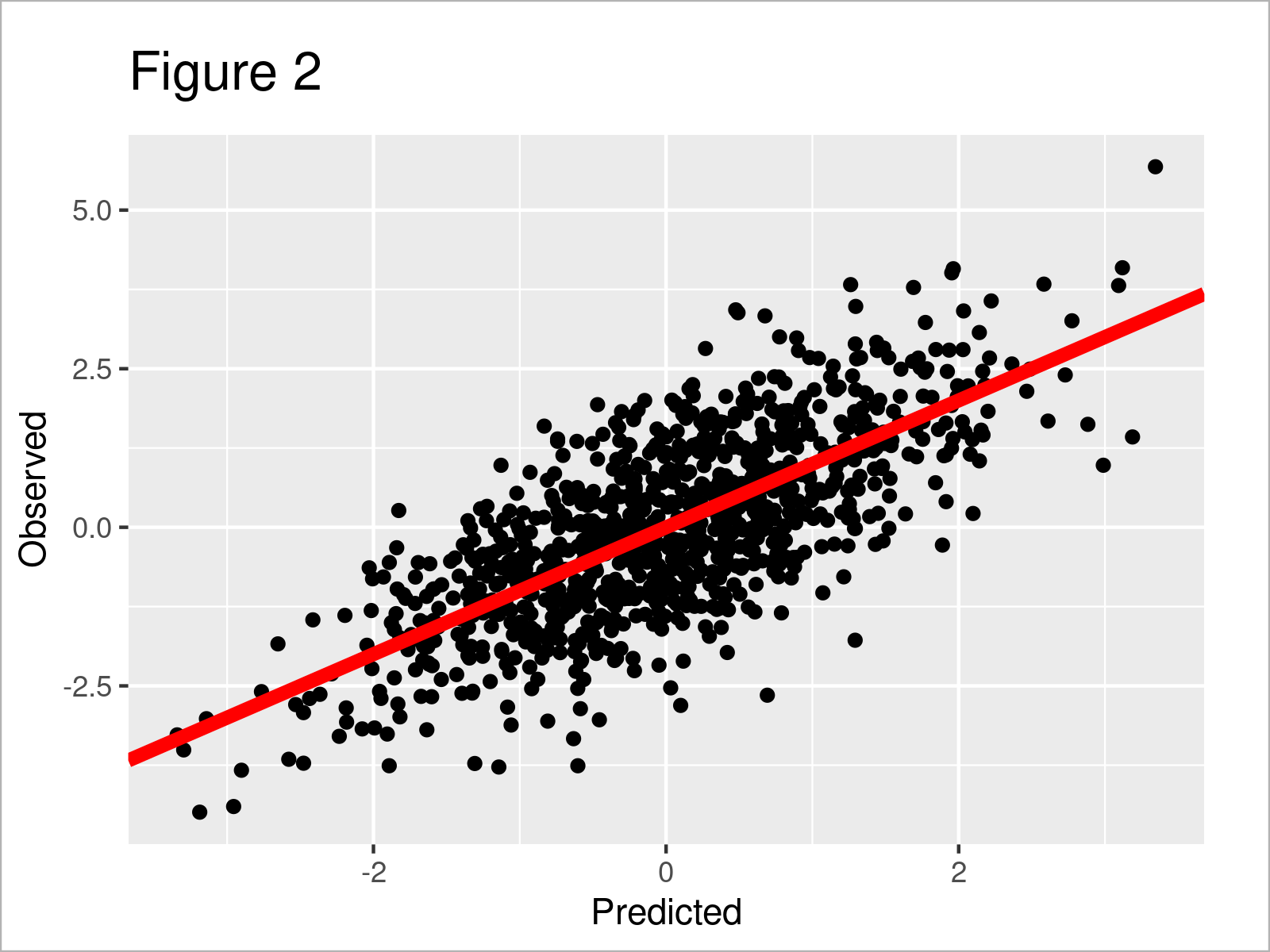
Plot Predicted Vs Actual Values In R Example Draw Fitted Observed This tutorial provides examples of how to create this type of plot in base r and ggplot2. example 1: plot of predicted vs. actual values in base r. the following code shows how to fit a multiple linear regression model in r and then create a plot of predicted vs. actual values:. I will like to make a plot of my machine learning model's predicted value vs the actual value. i made a prediction using random forest algorithm and will like to visualize the plot of true values and predicted values. i used the below code, but the plot isn't showing clearly the relationship between the predicted and actual values. Cross val predict returns an array of the same size of y where each entry is a prediction obtained by cross validation. since cv=10, it means that we trained 10 models and each model was used to predict on one of the 10 folds. we can now use the predictionerrordisplay to visualize the prediction errors. on the left axis, we plot the observed. Actual vs predicted graph for linear regression from scatter plots of actual vs predicted you can tell how well the model is performing. for ideal model, the points should be closer to a diagonal.

How To Create Predicted Vs Actual Plot Using Abline Plot And Cross val predict returns an array of the same size of y where each entry is a prediction obtained by cross validation. since cv=10, it means that we trained 10 models and each model was used to predict on one of the 10 folds. we can now use the predictionerrordisplay to visualize the prediction errors. on the left axis, we plot the observed. Actual vs predicted graph for linear regression from scatter plots of actual vs predicted you can tell how well the model is performing. for ideal model, the points should be closer to a diagonal. Comparing predicted results vs. actual results. i have a dataframe that spans across 6 years (2015 2020), with ~500 companies and several fundamental stats (e.g. sales, # employees, roa). i used a span of 5 years (2015 2019) to predict the roa for each company in 2020, in order to compare the predicted roa (2020) and the actual roa (2020). Simple actual vs predicted plot¶ this example shows you the simplest way to compare the predicted output vs. the actual output. a good model will have most of the scatter dots near the diagonal black line.

The Scatter Plot Between The Actual And Predicted Values According To A Comparing predicted results vs. actual results. i have a dataframe that spans across 6 years (2015 2020), with ~500 companies and several fundamental stats (e.g. sales, # employees, roa). i used a span of 5 years (2015 2019) to predict the roa for each company in 2020, in order to compare the predicted roa (2020) and the actual roa (2020). Simple actual vs predicted plot¶ this example shows you the simplest way to compare the predicted output vs. the actual output. a good model will have most of the scatter dots near the diagonal black line.

A Plot Of Predicted Vs Actual Download Scientific Diagram

Comments are closed.