Precalculus 903 Cis Theta

Precalculus 903 Cis Theta Cis: in the context of polar form of complex numbers, the term 'cis' is a shorthand notation that combines the trigonometric functions of cosine and sine. it is used to represent a complex number in polar form, providing a compact and efficient way to express both the magnitude and the angle of the complex number. Cis (θ) the function is a shorthand way of writing the equivalent expression : by definition: cos i sin {\displaystyle \text {cis} (\theta)=\cos (\theta) i\sin (\theta)} this form simplifies complex arithmetic and allows for the study of complex analysis, as well as reduces the workload in writing the expressions.
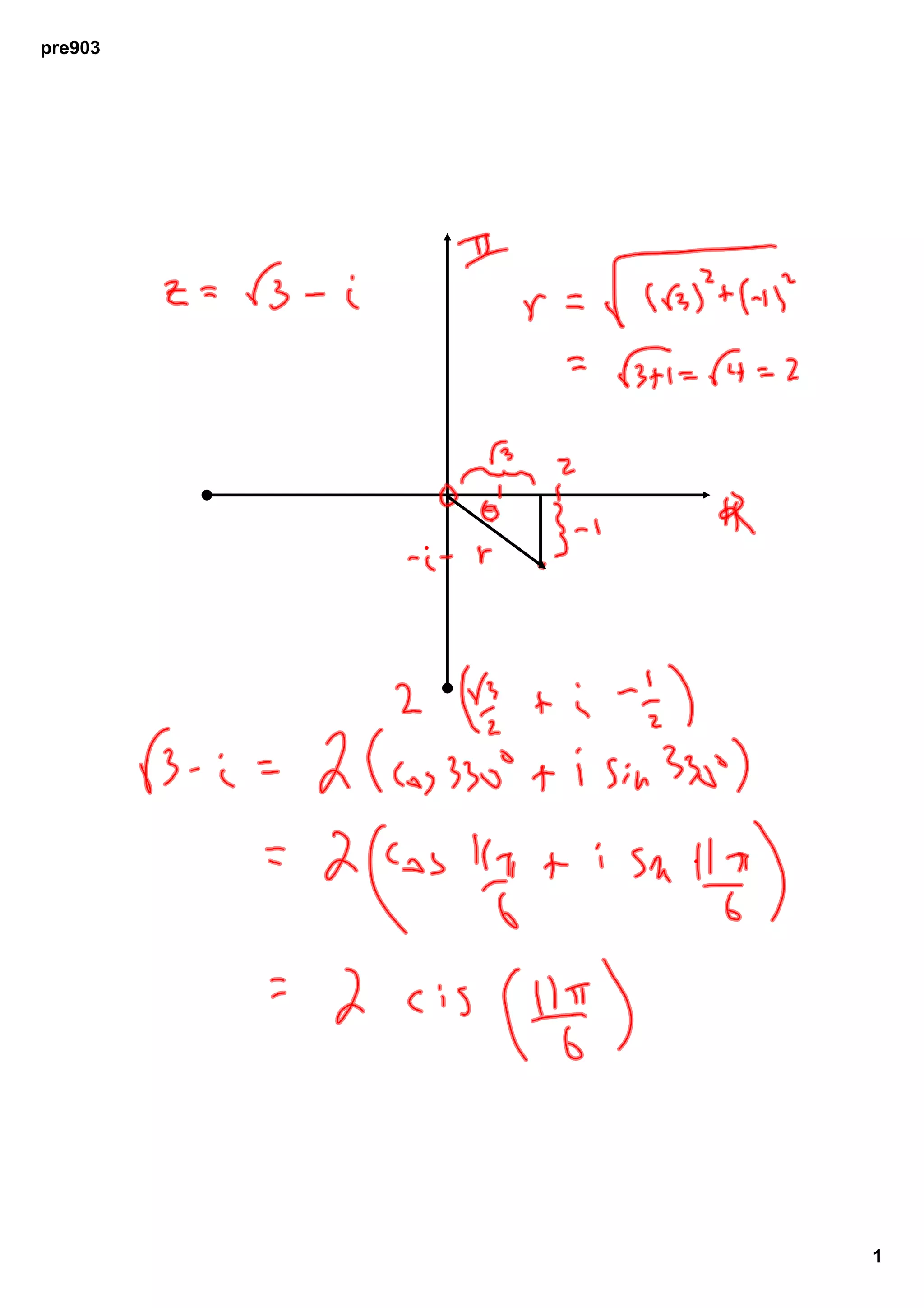
Precalculus 903 Cis Theta Pdf The document discusses a proposed policy change to increase the minimum wage in a mid sized city from $7.25 to $15 per hour over 3 years. it notes this would boost incomes for many low wage workers but some small businesses argue it may force them to cut jobs or raise prices. Cis (mathematics) cis is a mathematical notation defined by cis x = cos x i sin x, [nb 1] where cos is the cosine function, i is the imaginary unit and sin is the sine function. x is the argument of the complex number (angle between line to point and x axis in polar form). the notation is less commonly used in mathematics than euler's formula. Sin(π 2 − θ) = cos(π 2 − [π 2 − θ]) = cos(θ), which says, in words, that the ‘co’sine of an angle is the sine of its ‘co’mplement. now that these identities have been established for cosine and sine, the remaining circular functions follow suit. the remaining proofs are left as exercises. theorem 10.14. The polar form of a complex number expresses a number in terms of an angle [latex]\theta [ latex] and its distance from the origin [latex]r [ latex]. given a complex number in rectangular form expressed as [latex]z=x yi [ latex], we use the same conversion formulas as we do to write the number in trigonometric form:.

Precalculus 903 Cis Theta Sin(π 2 − θ) = cos(π 2 − [π 2 − θ]) = cos(θ), which says, in words, that the ‘co’sine of an angle is the sine of its ‘co’mplement. now that these identities have been established for cosine and sine, the remaining circular functions follow suit. the remaining proofs are left as exercises. theorem 10.14. The polar form of a complex number expresses a number in terms of an angle [latex]\theta [ latex] and its distance from the origin [latex]r [ latex]. given a complex number in rectangular form expressed as [latex]z=x yi [ latex], we use the same conversion formulas as we do to write the number in trigonometric form:. The first step toward working with a complex number in polar form is to find the absolute value. the absolute value of a complex number is the same as its magnitude, or [latex]\lvert z \rvert [ latex]. it measures the distance from the origin to a point in the plane. for example, the graph of [latex]z=2 4i [ latex], in figure 2, shows [latex. The origins of cis(θ) cis (θ) there is a abbreviation used in high school mathematics that is almost never seen outside of it: cis(θ) = cos(θ) i sin(θ) cis (θ) = cos (θ) i sin (θ), where cis stands for c osine i s ine. as soon as students get into university euler's formula eiθ = cos(θ) i sin(θ) e i θ = cos (θ) i sin (θ.

Comments are closed.