Ppt Chapter 3 Supply Demand Powerpoint Presentation Free Download

Ppt Chapter 3 Supply And Demand Powerpoint Presentation Free 3. introduction to demand • demand is the desire, willingness, and ability to buy a good or service. – supply can refer to one individual consumer or to the total demand of all consumers in the market (market demand). demand function shows how the quantity demanded of a good is dependent on its determinants. demand curve is the graphical presentation of the demand schedule. Presentation on theme: "chapter 3 demand and supply"— presentation transcript: ch.3 outline 3.1: demand, supply, and equilibrium in markets for goods and services 3.2: shifts in demand and supply for goods and services 3.3: changes in equilibrium price and quantity: the four step process 3.4: price ceilings and price floors 3.5: demand.
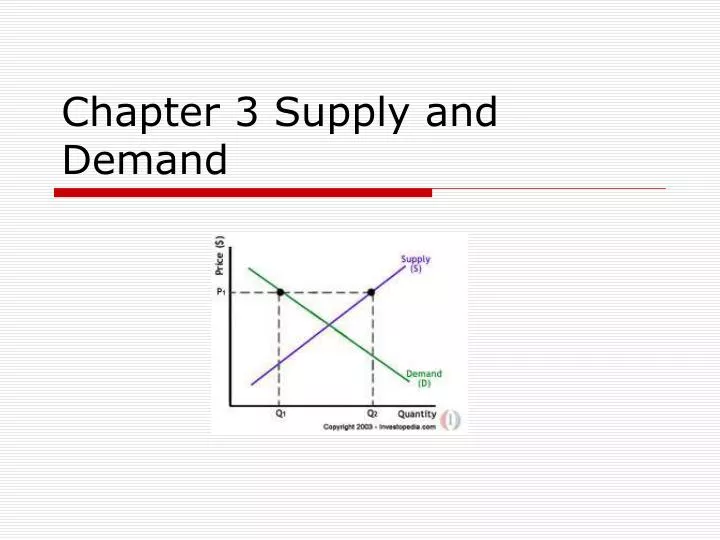
Ppt Chapter 3 Supply And Demand Powerpoint Presentation Free This document discusses key concepts related to demand and supply, including: 1) demand and supply schedules show the relationship between price and quantity at different price levels. demand and supply curves graph this relationship. 2) a change in a non price factor like income causes a shift of the demand or supply curve, while a price. The law of demand and law of supply state that quantity demanded increases with lower prices and quantity supplied increases with higher prices, respectively. market equilibrium occurs when quantity demanded equals quantity supplied at the equilibrium price. changes in demand or supply curves result in new equilibrium prices and quantities. Presentation transcript. chapter 3demand, supply and relative prices • demand and supply determine relative prices. • the word “price” means relative price. price is an opportunity cost. • if we predict a price will fall, we mean its price will fall relative to the average price of other goods and services. Anges between peo. place.ii. supply and demand. emandthe buying side of the market.there is a negative relationship between the quan. ty demanded of a good and its price.the relationship reflects optimizi. d. sprice (p)dquantity (q) pplythe selling side of the market.there is a positive relationship between the quan.

Ppt Chapter 3 Demand And Supply Powerpoint Presentation Free Presentation transcript. chapter 3demand, supply and relative prices • demand and supply determine relative prices. • the word “price” means relative price. price is an opportunity cost. • if we predict a price will fall, we mean its price will fall relative to the average price of other goods and services. Anges between peo. place.ii. supply and demand. emandthe buying side of the market.there is a negative relationship between the quan. ty demanded of a good and its price.the relationship reflects optimizi. d. sprice (p)dquantity (q) pplythe selling side of the market.there is a positive relationship between the quan. Download presentation. presentation on theme: "1 chapter 3 demand, supply and market equilibrium."—. presentation transcript: 1 1 chapter 3 demand, supply and market equilibrium. 2 markets an institution or mechanism that brings together buyers and sellers of particular goods and services. this chapter focuses on competitive markets. Presentation transcript. chapter 3: demand and supply. barter vs. monetary economy • barter – goods are traded directly for other goods • problems: • requires double coincidence of wants • large number of trading ratios: n (n 1) 2 (high information costs) • monetary economy has lower transaction and information costs.

Ppt Chapter 3 Supply And Demand Powerpoint Presentation Free Download presentation. presentation on theme: "1 chapter 3 demand, supply and market equilibrium."—. presentation transcript: 1 1 chapter 3 demand, supply and market equilibrium. 2 markets an institution or mechanism that brings together buyers and sellers of particular goods and services. this chapter focuses on competitive markets. Presentation transcript. chapter 3: demand and supply. barter vs. monetary economy • barter – goods are traded directly for other goods • problems: • requires double coincidence of wants • large number of trading ratios: n (n 1) 2 (high information costs) • monetary economy has lower transaction and information costs.

Comments are closed.