Platelets Diagram Gcse

Structure Of The Platelet Royalty Free Vector Image Gcse; wjec; the circulatory system in humans – wjec platelets. the proper functioning of the circulatory system is essential for health. blood transports substances around the body to every cell. A series of reactions occur within the blood plasma: platelets release chemicals that cause soluble fibrinogen proteins to convert into insoluble fibrin. this forms an insoluble mesh across the wound. red blood cells become trapped, forming a clot. the clot eventually dries and develops into a scab. this process helps to prevent excessive blood.

Platelets Diagram Gcse Platelets are cell fragments produced by giant cells in the bone marrow close bone marrow soft tissue found inside bones that produces new blood cells platelets stop bleeding in two main ways:. Platelets are fragments (small parts of) cells which look very small in diagrams. platelets have cell surface proteins, which enable them to clump together and close up a broken blood vessel. platelets also have stored proteins, which they release to initiate a sequence of reactions called the clotting cascade. this causes something called. 🦊 in this gcse biology video, we look at how the platelets are tiny fragments in the blood, not true cells, numbering approximately 350 million per cubic ce. Platelets are small cell fragments that do not have a nucleus. 1 cell biology. 2 organisation. 3 infection & response. 4 bioenergetics. 5 homeostasis & response. 6 inheritance, variation & evolution. 7 ecology. affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home.
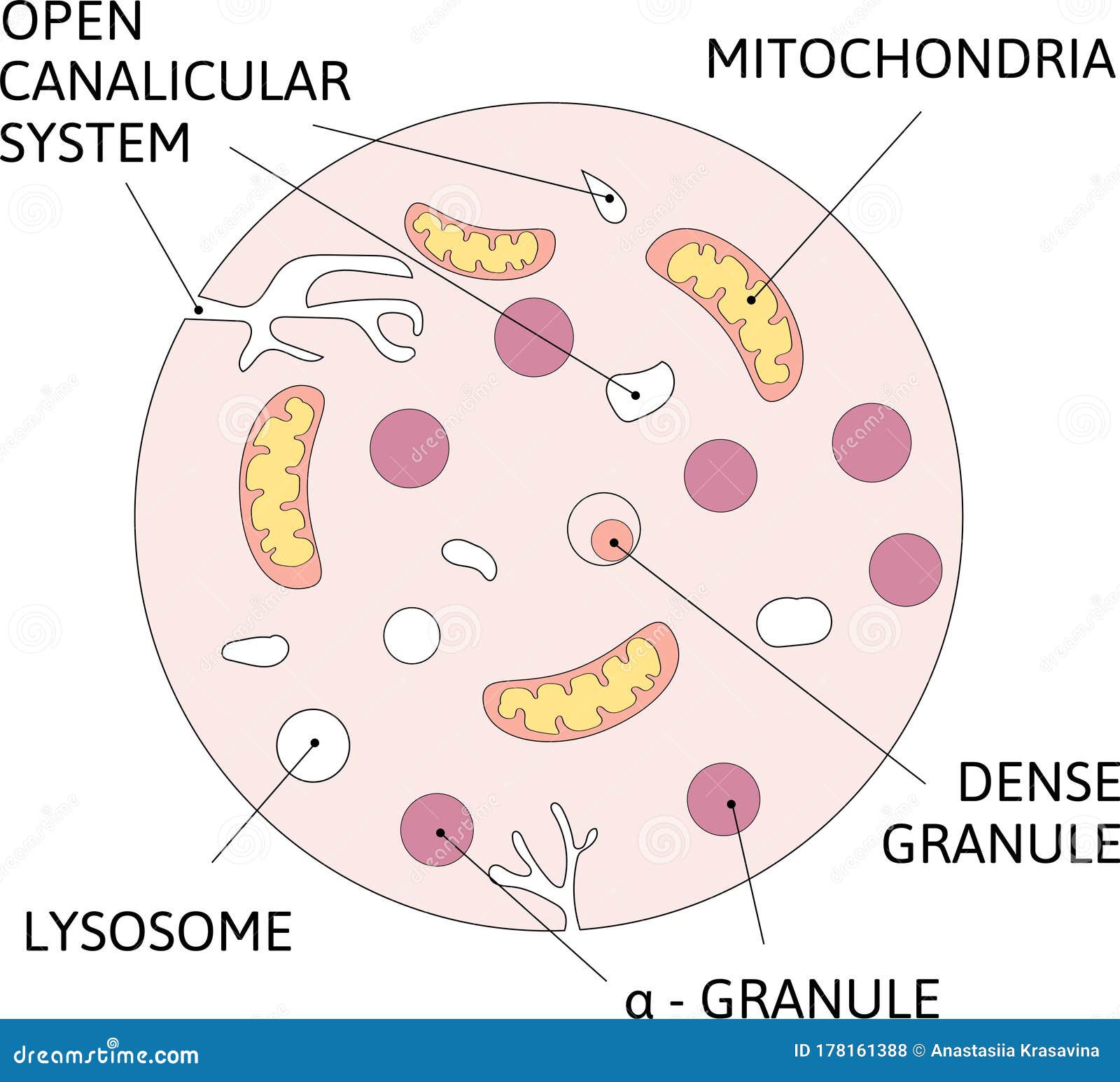
Schematic Diagram Of Platelet Contains Granules Dense Granules And 🦊 in this gcse biology video, we look at how the platelets are tiny fragments in the blood, not true cells, numbering approximately 350 million per cubic ce. Platelets are small cell fragments that do not have a nucleus. 1 cell biology. 2 organisation. 3 infection & response. 4 bioenergetics. 5 homeostasis & response. 6 inheritance, variation & evolution. 7 ecology. affordable 1:1 tutoring from the comfort of your home. Key points. there are four components or parts of the blood: red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma and platelets. blood carries things you need, like oxygen and glucose, and waste. Function. the key role of platelets is their participation in haemostasis through the formation of blood clots at the site of bleeding. there are three main stages in the formation of a blood clot: adhesion, activation and aggregation. adhesion. injury to the blood vessel wall exposes its underlying endothelium and collagen fibres.
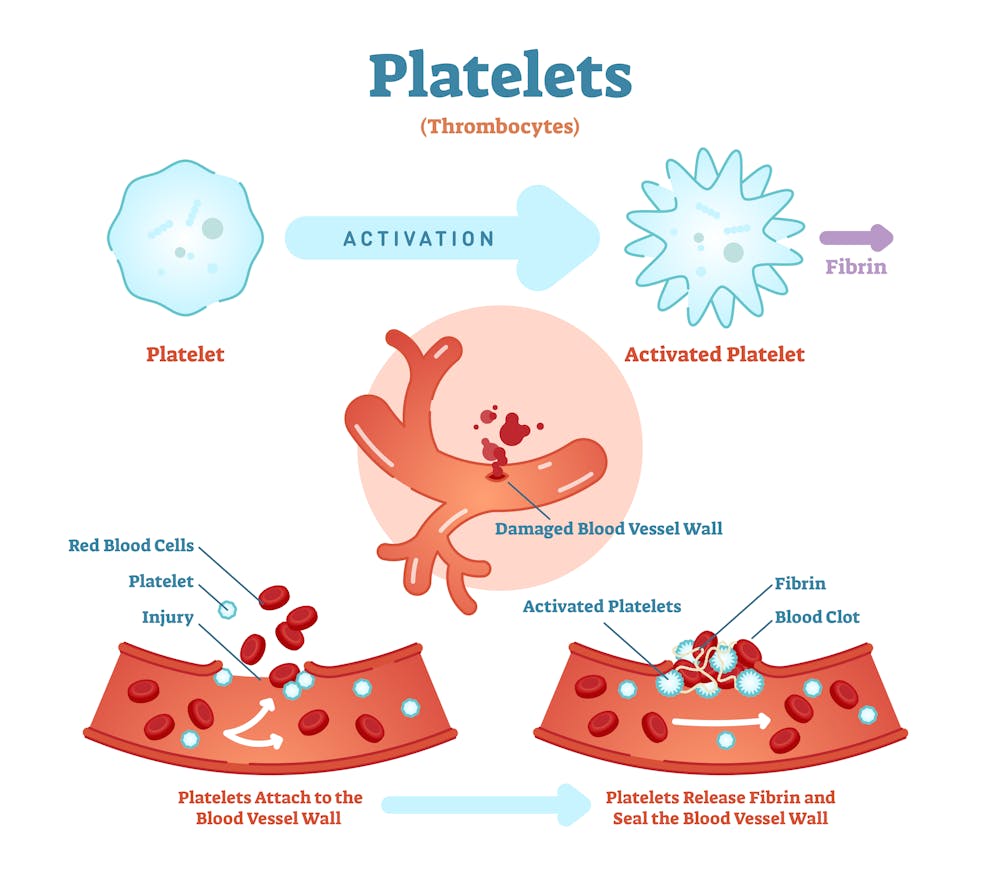
Platelets Structure Composition And Functions Overall Science Key points. there are four components or parts of the blood: red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma and platelets. blood carries things you need, like oxygen and glucose, and waste. Function. the key role of platelets is their participation in haemostasis through the formation of blood clots at the site of bleeding. there are three main stages in the formation of a blood clot: adhesion, activation and aggregation. adhesion. injury to the blood vessel wall exposes its underlying endothelium and collagen fibres.

Comments are closed.