Platelet Structure And Function

Platelet Structure And Function Platelets. platelets are cell fragments and the smallest component of your blood. their primary job is to stop the bleeding if you’re injured. if a blood vessel is damaged, platelets cluster together to form a plug first and then a clot to stop the blood loss. common conditions involving platelets include thrombocytopenia and thrombocytosis. Learn about the structure, function, and regulation of platelets, the blood cells that participate in hemostasis and thrombosis. this article covers platelet membrane, granules, secretion, adhesion, aggregation, and coagulation.
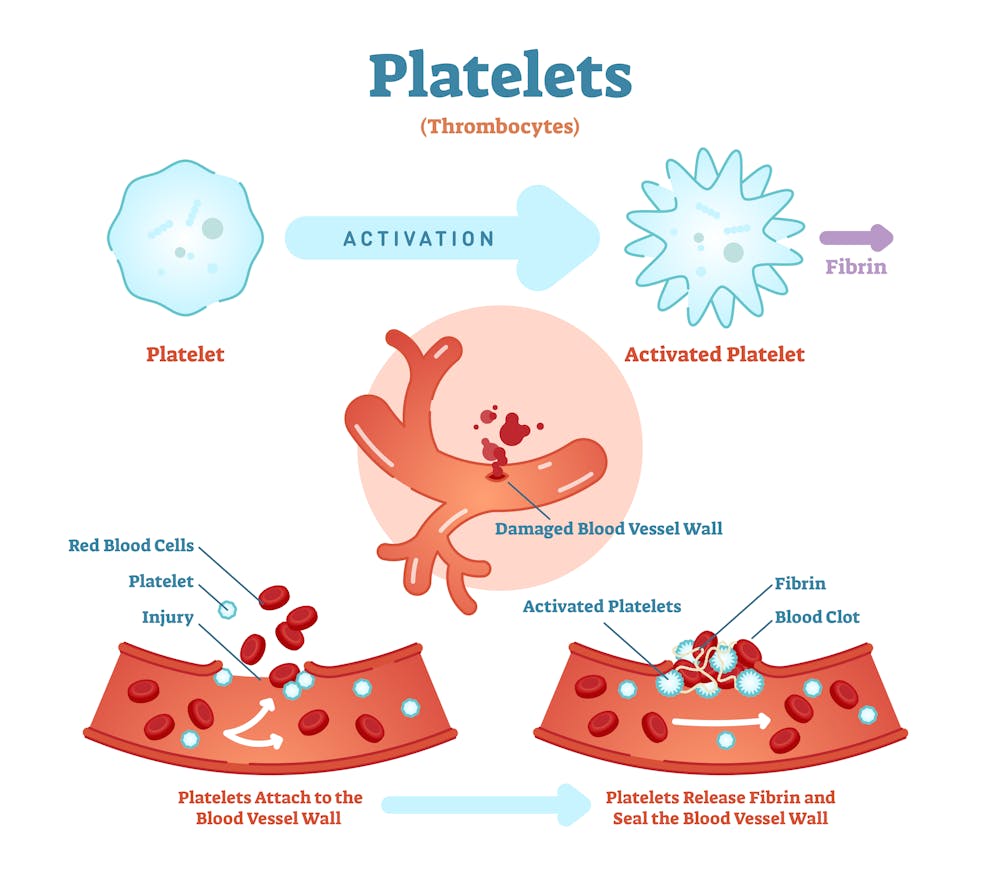
Platelets Structure Composition And Functions Overall Science Learn about platelets, anucleated cells that play a key role in hemostasis and immunity. find out how platelets are activated, what mediators they release, and what functions they perform in the body. Platelets are anucleate blood cells (2–4 μm in diameter) with multiple functions and a short lifespan, circulating in blood for 7–10 days in humans and for a shorter time in mice, after which. A normal platelet count is 150,000–450,000 platelets per microliter. a low platelet count can put you at risk for uncontrolled bleeding. it is also possible to have too many platelets in your blood. this leads to a potentially life threatening condition related to abnormal clotting. andrew brookes getty images. Megakaryocytes are large blood cells whose principal function is the production of platelets. when a megakaryocyte becomes mature, pseudomembrane blebs are extended and eventually break off of the membrane, forming platelets. platelets, once formed, have an average lifespan of 7 to 10 days, at which point they are removed from the bloodstream.

Ppt Platelet Structure Function Powerpoint Presentation Free A normal platelet count is 150,000–450,000 platelets per microliter. a low platelet count can put you at risk for uncontrolled bleeding. it is also possible to have too many platelets in your blood. this leads to a potentially life threatening condition related to abnormal clotting. andrew brookes getty images. Megakaryocytes are large blood cells whose principal function is the production of platelets. when a megakaryocyte becomes mature, pseudomembrane blebs are extended and eventually break off of the membrane, forming platelets. platelets, once formed, have an average lifespan of 7 to 10 days, at which point they are removed from the bloodstream. Platelet. platelets or thrombocytes (from ancient greek θρόμβος (thrómbos) 'clot' and κύτος (kútos) 'cell') are a blood component whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. [1] platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments. Definition. thrombocytes, also known as platelets, are specialized blood cells which function to controlling blood clotting. function. thrombocytes form clots in response to tears in blood vessels by triggering the release of a series of coagulation factors. learn more about the different components of blood in the following study unit:.
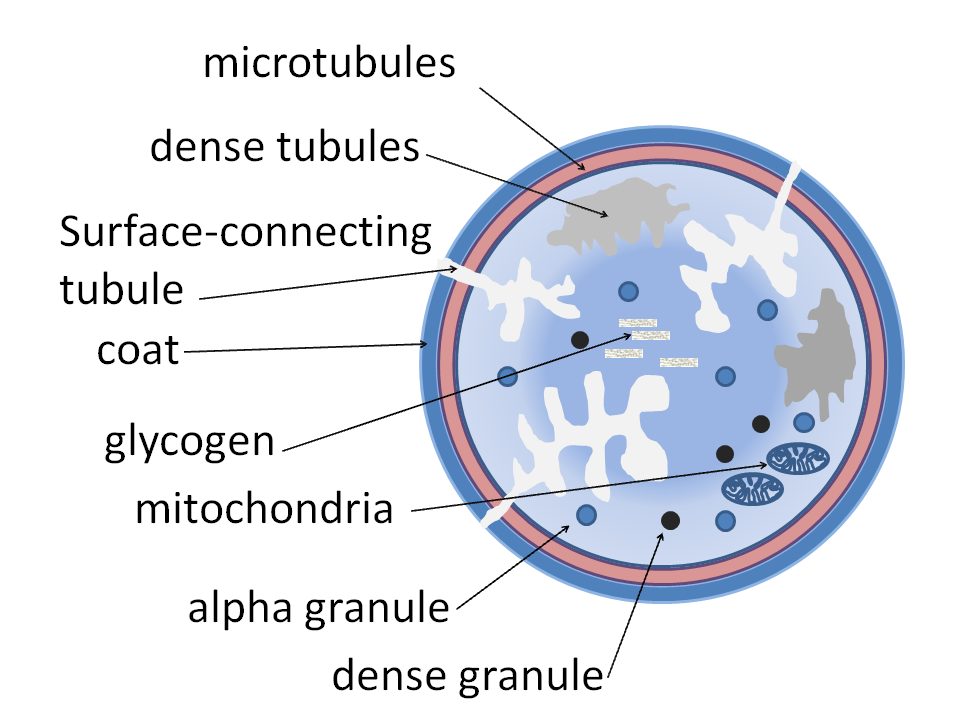
File Platelet Structure Png Wikipedia Platelet. platelets or thrombocytes (from ancient greek θρόμβος (thrómbos) 'clot' and κύτος (kútos) 'cell') are a blood component whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby initiating a blood clot. [1] platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments. Definition. thrombocytes, also known as platelets, are specialized blood cells which function to controlling blood clotting. function. thrombocytes form clots in response to tears in blood vessels by triggering the release of a series of coagulation factors. learn more about the different components of blood in the following study unit:.

Comments are closed.