Phlebotomy Best Practices Paediatric And Neonatal Blood Sampling

Paediatric And Neonatal Blood Sampling Who Guidelines On Drawing This chapter discusses aspects specific to paediatric and neonatal blood sampling (60, 61). anyone taking blood from children and neonates must be well trained and practiced in venepuncture techniques. a uniform sampling technique is important to reduce pain and psychological trauma. 6.1.1. Who library cataloguing in publication data who guidelines on drawing blood: best practices in phlebotomy. 1.bloodletting – standards. 2.phlebotomy – standards. 3.needlestick injuries – prevention and.

Phlebotomy Best Practices Paediatric And Neonatal Blood Sampling Capillary sampling from a finger, heel or (rarely) an ear lobe may be performed on patients of any age, for specific tests that require small quantities of blood. however, because the procedure is commonly used in paediatric patients, sections 7.1.1 and 7.1.2 focus particularly on paediatric capillary sampling. 7.1. Who guidelines on drawing blood: best practices in phlebotomy. geneva: world health organization; 2010. arterial blood sampling. 6. paediatric and neonatal blood. Aspects of phlebotomy 2. best practices in phlebotomy 3. blood sampling systems 4. venepuncture for blood donaton 5. arterial blood sampling 6. paediatric and neonatal blood sampling 7. capillary sampling part iii. implementation, evaluation and monitoring 8. implementing best phlebotomy practices 9. Phlebotomy uses large, hollow needles to remove blood specimens for lab testing or blood donation. each step in the process carries risks both for patients and health workers. patients may be bruised. health workers may receive needle stick injuries. both can become infected with bloodborne organisms such as hepatitis b, hiv, syphilis or malaria.

Paediatric And Neonatal Blood Sampling Who Guidelines On Drawing Aspects of phlebotomy 2. best practices in phlebotomy 3. blood sampling systems 4. venepuncture for blood donaton 5. arterial blood sampling 6. paediatric and neonatal blood sampling 7. capillary sampling part iii. implementation, evaluation and monitoring 8. implementing best phlebotomy practices 9. Phlebotomy uses large, hollow needles to remove blood specimens for lab testing or blood donation. each step in the process carries risks both for patients and health workers. patients may be bruised. health workers may receive needle stick injuries. both can become infected with bloodborne organisms such as hepatitis b, hiv, syphilis or malaria. 1.5 indications for blood sampling and blood collection; 1.6 structure of document; part ii. aspects of phlebotomy. 2. best practices in phlebotomy. 2.1 background information on best practices in phlebotomy; 2.2 practical guidance on best practices in phlebotomy; 2.3 illustrations for best practices in phlebotomy; 3. blood sampling systems. Annex c. devices available for drawing blood. annex d. managing occupational exposure to hepatitis b, hepatitis c and hiv. step 1 provide immediate first aid care to the exposure site. step 2 determine the risk associated with the exposure. step 3 evaluate the source of the potential exposure.
Level 3 Neonatal And Paediatric Phlebotomy Pro Phlebotomy Training 1.5 indications for blood sampling and blood collection; 1.6 structure of document; part ii. aspects of phlebotomy. 2. best practices in phlebotomy. 2.1 background information on best practices in phlebotomy; 2.2 practical guidance on best practices in phlebotomy; 2.3 illustrations for best practices in phlebotomy; 3. blood sampling systems. Annex c. devices available for drawing blood. annex d. managing occupational exposure to hepatitis b, hepatitis c and hiv. step 1 provide immediate first aid care to the exposure site. step 2 determine the risk associated with the exposure. step 3 evaluate the source of the potential exposure.
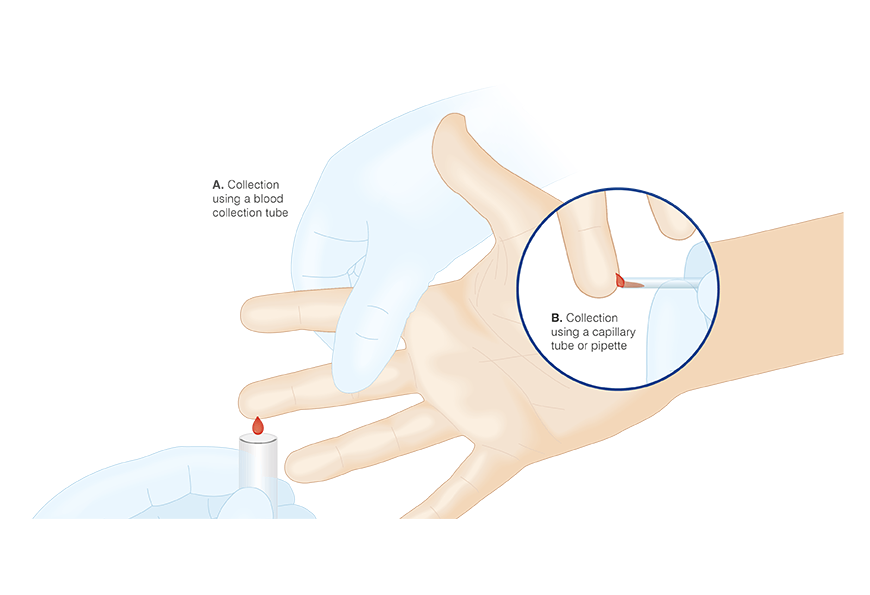
Adult Paediatric Sampling Essentials Owen Mumford

How To Collect Blood Sample Phlebotomy Techniques Youtube

Comments are closed.