Petrous Ridge Of Temporal Bone

Petrous Temporal Bone Outer surface. [clarification needed] the petrous part of the temporal bone is pyramid shaped and is wedged in at the base of the skull between the sphenoid and occipital bones. directed medially, forward, and a little upward, it presents a base, an apex, three surfaces, and three angles, and houses in its interior the components of the inner ear. Learn about the anatomy, radiographic features and related pathology of the petrous part of the temporal bone, also known as the petrous temporal bone. the petrous temporal bone forms the part of skull base between the sphenoid and occipital bones and has a pyramidal shape with an apex and a base.

Cranial Bones Continued Petrous Part Of Temporal Bone Diagram Quizlet Pneumatization of the petrous temporal bone apices is an anatomical variant that may be bilateral or asymmetrical. it is important not to confuse it with a pathological lesion especially on mri. benign lesions such as cholesterol granuloma and cholesteatoma are more likely to occur in a pneumatized petrous apex. also, it can be a site for csf. 1 2. synonyms: none. the temporal bones are a pair of bilateral, symmetrical bones that constitute a large portion of the lateral wall and base of the skull . they are highly irregular bones with extensive muscular attachments and articulations with surrounding bones. there are a number of openings and canals in the temporal bone through which. The middle ear is an air filled cavity within the petrous portion of the temporal bone that contains the ossicular chain and is bounded by the tympanic membrane laterally, the inner ear structures (surrounded by the otic capsule and the cochlear promontory) medially, the tegmen tympani superiorly, and the jugular wall (floor) inferiorly . The petrous ridge forms the upper edge of the petrous part of the temporal bone. it divides the middle cranial fossa, which is at the front, from the posterior cranial fossa located behind. along this border runs a groove that houses the superior petrosal sinus. this sinus links the transverse venous sinus to the cavernous sinus. additionally, the tentorium cerebelli, a dural covering that.
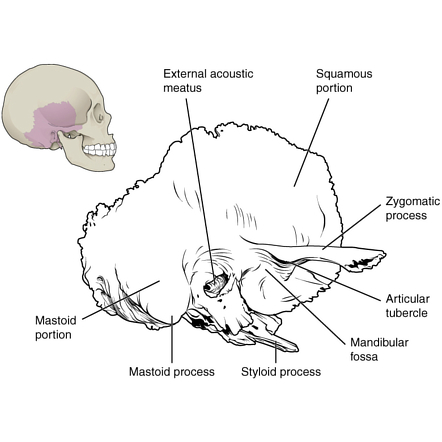
Temporal Bone Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org The middle ear is an air filled cavity within the petrous portion of the temporal bone that contains the ossicular chain and is bounded by the tympanic membrane laterally, the inner ear structures (surrounded by the otic capsule and the cochlear promontory) medially, the tegmen tympani superiorly, and the jugular wall (floor) inferiorly . The petrous ridge forms the upper edge of the petrous part of the temporal bone. it divides the middle cranial fossa, which is at the front, from the posterior cranial fossa located behind. along this border runs a groove that houses the superior petrosal sinus. this sinus links the transverse venous sinus to the cavernous sinus. additionally, the tentorium cerebelli, a dural covering that. Function. the temporal bone provides structural support for the skull, while protecting the cerebrum of the brain and surrounding membranes. in addition, this bone surrounds the middle and inner portions of the ear. the lower portion of the temporal bone connects with the mandible or jawbone to allow the mouth to open and close. The petrous part of the temporal bone is a pyramidal shaped ridge, with its wider base near the squamosal and mastoid portions of the bone and its smaller apex located anteromedially. it forms the posterior and anterior portions of the middle and posterior cranial fossae, respectively.

Petrous Part Of The Temporal Bone Wikidoc Function. the temporal bone provides structural support for the skull, while protecting the cerebrum of the brain and surrounding membranes. in addition, this bone surrounds the middle and inner portions of the ear. the lower portion of the temporal bone connects with the mandible or jawbone to allow the mouth to open and close. The petrous part of the temporal bone is a pyramidal shaped ridge, with its wider base near the squamosal and mastoid portions of the bone and its smaller apex located anteromedially. it forms the posterior and anterior portions of the middle and posterior cranial fossae, respectively.

From Wikiwand Petrous Part Of The Temporal Bones Sphenoid Bone

Boned Human Skull Petrous Part Of Temporal Bone

Comments are closed.