Permutation Combination Formulas
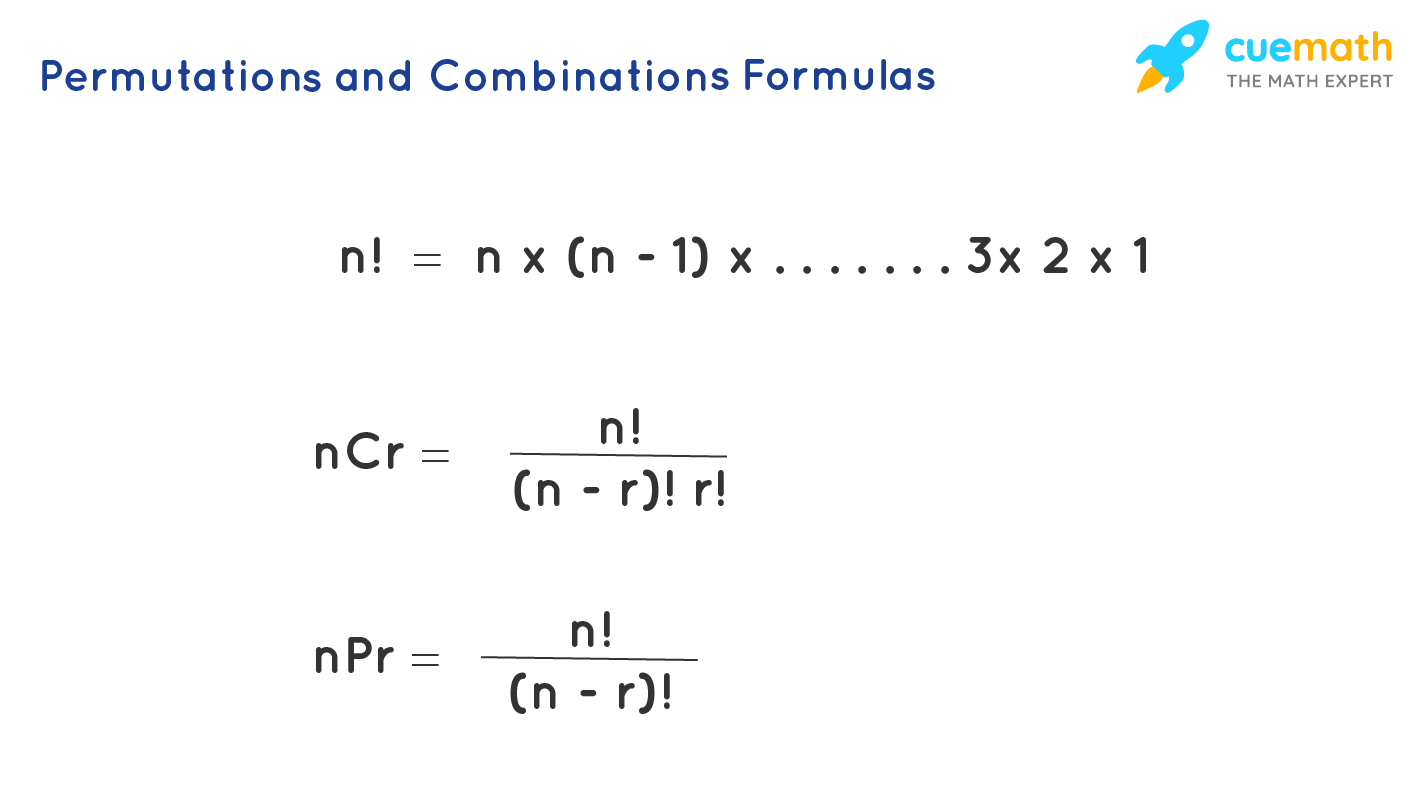
Permutation And Combination Definition Formulas Derivation Examples Learn the difference between combinations and permutations, and how to calculate them with formulas and examples. find out how to use factorial function, repetition, and notation for different types of combinations and permutations. Combinations are used when the same kind of things are to. be sorted. permutation of two things out of three given things. a, b, c is ab, ba, bc, cb, ac, ca. the combination of two things from three given things. a, b, c is ab, bc, ca. formula for permuation is: n pr = n! (n – r)!.
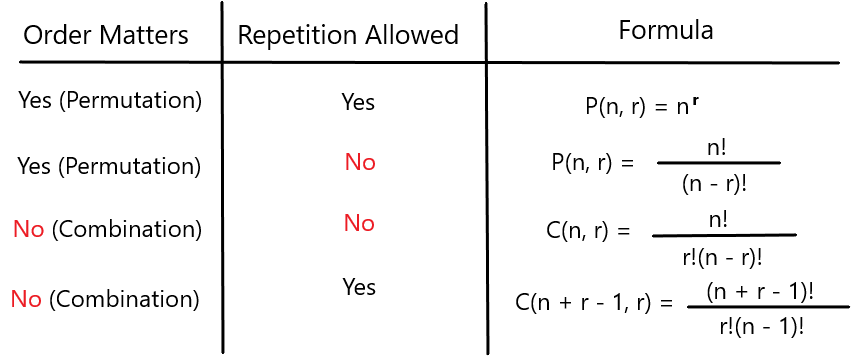
Permutation And Combination The Difference Explained With Formula Examples Use the multiplication principle. there are 10 possible cars to finish first. once a car has finished first, there are nine cars to finish second. after the second car is finished, any of the eight remaining cars can finish third. 10 x 9 x 8 = 720. this is a permutation of 10 items taking three at a time. using the permutation formula:. Learn the difference between permutation and combination, how to calculate them using formulas, and see real life examples and solved problems. find video lessons, practice questions, and faqs on this maths topic. The formula of n! is used in the formulas of permutation and combination. what are the examples of permutation and combination? the examples of permutations are for different arrangements such as seating arrangements, formation of different passwords from the given set of digits and alphabets, arrangement of books on a shelf, flower arrangements. In mathematics, permutation refers to the arrangement of all the members of a set in some order or sequence, while combination does not regard the order as a parameter. it is just a way of selecting items from a set or collection. permutation formula: a permutation is the arrangements of r things from a set of n things without replacement.
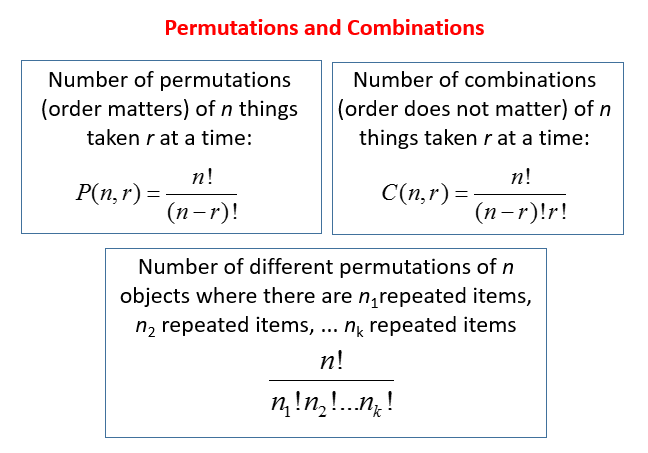
Permutations P N R Video Lessons Examples Solutions The formula of n! is used in the formulas of permutation and combination. what are the examples of permutation and combination? the examples of permutations are for different arrangements such as seating arrangements, formation of different passwords from the given set of digits and alphabets, arrangement of books on a shelf, flower arrangements. In mathematics, permutation refers to the arrangement of all the members of a set in some order or sequence, while combination does not regard the order as a parameter. it is just a way of selecting items from a set or collection. permutation formula: a permutation is the arrangements of r things from a set of n things without replacement. Using permutations to compute probabilities. recall that we can use permutations to count how many ways there are to put a number of items from a list in order. if we’re looking at an experiment whose sample space looks like an ordered list, then permutations can help us to find the right probabilities. example 7.23. Formulas for permutation and combination. there are several formulas associated with the concepts of permutation and combination. the two fundamental formulas are: permutation formula. a permutation involves the selection of 'r' items from a set of 'n' items, where the order of selection matters and replacement is not allowed. n p r = (n!) (n r)!.
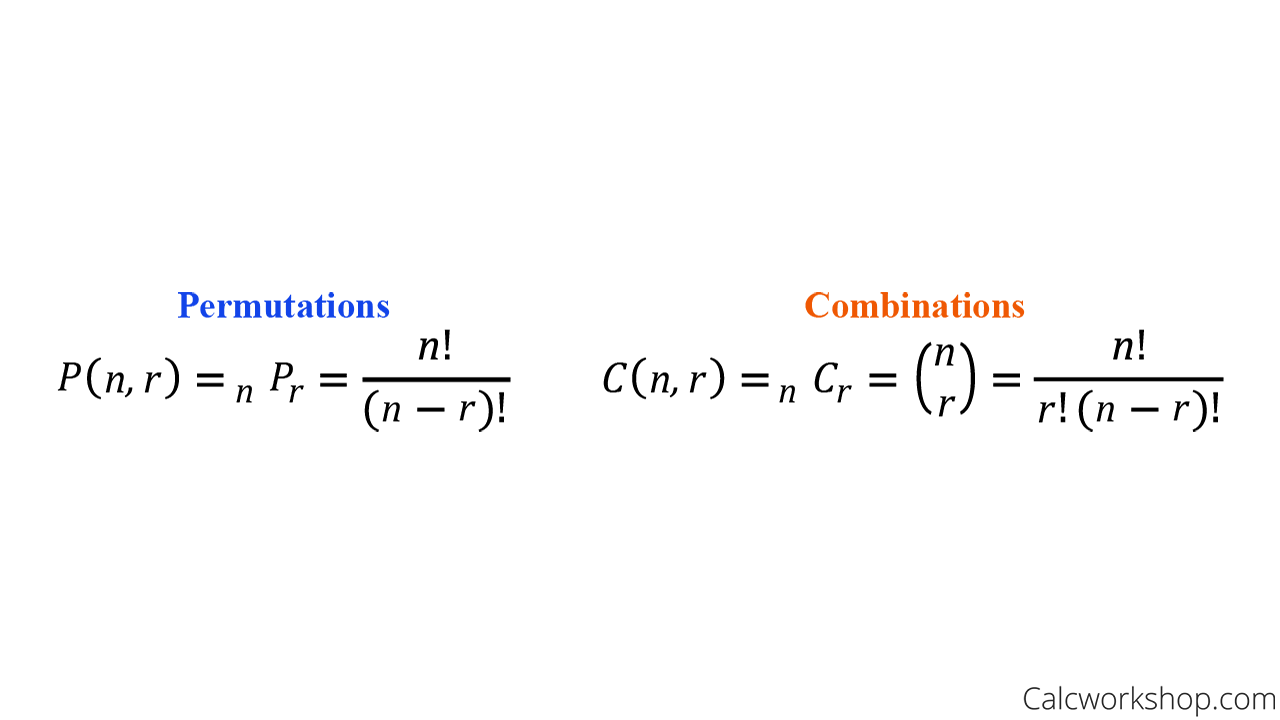
What Are Permutations And Combinations 15 Powerful Examples Using permutations to compute probabilities. recall that we can use permutations to count how many ways there are to put a number of items from a list in order. if we’re looking at an experiment whose sample space looks like an ordered list, then permutations can help us to find the right probabilities. example 7.23. Formulas for permutation and combination. there are several formulas associated with the concepts of permutation and combination. the two fundamental formulas are: permutation formula. a permutation involves the selection of 'r' items from a set of 'n' items, where the order of selection matters and replacement is not allowed. n p r = (n!) (n r)!.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/comb-5716dd163df78c3fa2e68194.jpg)
How Combinations And Permutations Differ

Comments are closed.