Perfect Competition Economics Help
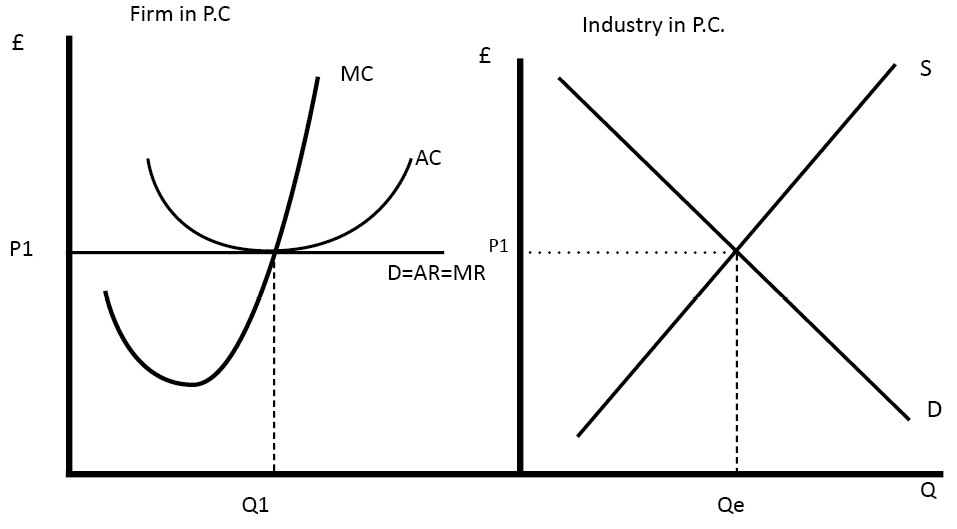
Profit Maximisation Economics Help Perfect competition is a market structure where many firms offer a homogeneous product. because there is freedom of entry and exit and perfect information, firms will make normal profits and prices will be kept low by competitive pressures. features of perfect competition. many firms. freedom of entry and exit; this will require low sunk costs. Diagram of perfect competition. the market price is set by the supply and demand of the industry (diagram on right) this sets the market equilibrium price of p1. individual firms (on the left) are price takers. their demand curve is perfectly elastic. a firm maximises profit at q1 where mc = mr.
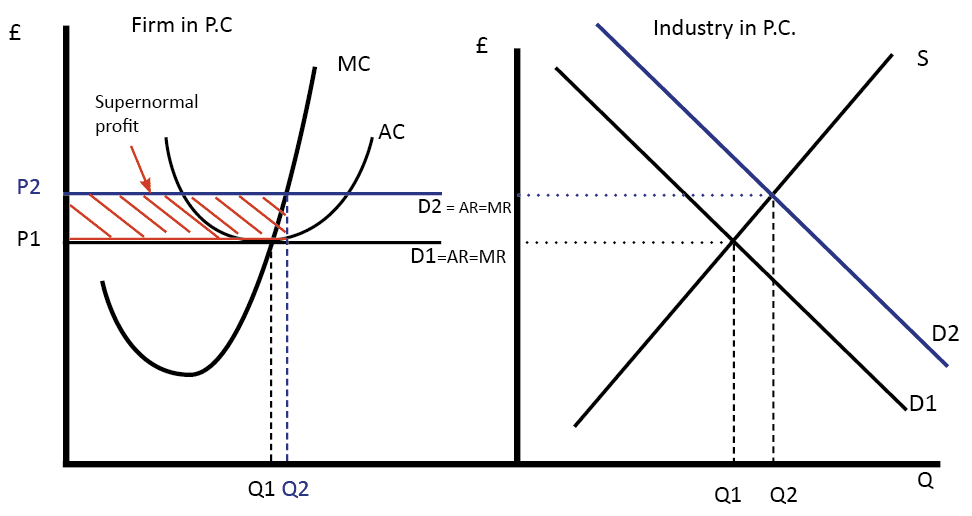
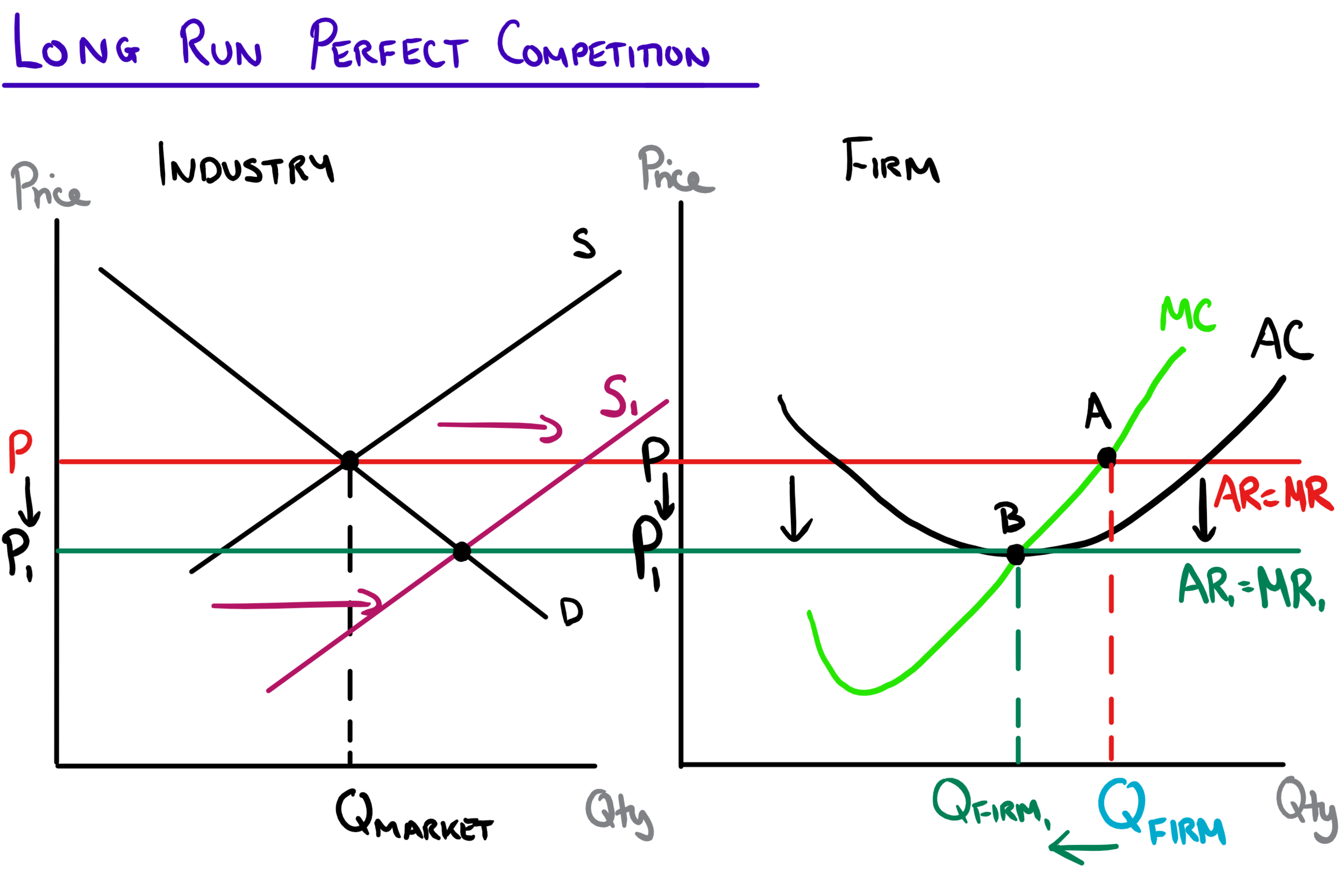
Diagram Of Perfect Competition Economics Help Perfect competition in the long run: in the long run, economic profit cannot be sustained. the arrival of new firms in the market causes the demand curve of each individual firm to shift downward, bringing down the price, the average revenue and marginal revenue curve. in the long run, the firm will make zero economic profit. Learn how perfect competition leads to allocative, productive and x efficiency in the long run, and the challenges and limitations of this market structure. see diagrams, definitions and examples of perfect competition and its outcomes. In this chapter, we focus on perfect competition. however, in other chapters we will examine other industry types: monopoly and monopolistic competition and oligopoly. this free textbook is an openstax resource written to increase student access to high quality, peer reviewed learning materials. Perfect competition is a model of the market based on the assumption that a large number of firms produce identical goods consumed by a large number of buyers. the model of perfect competition also assumes that it is easy for new firms to enter the market and for existing ones to leave. and finally, it assumes that buyers and sellers have.
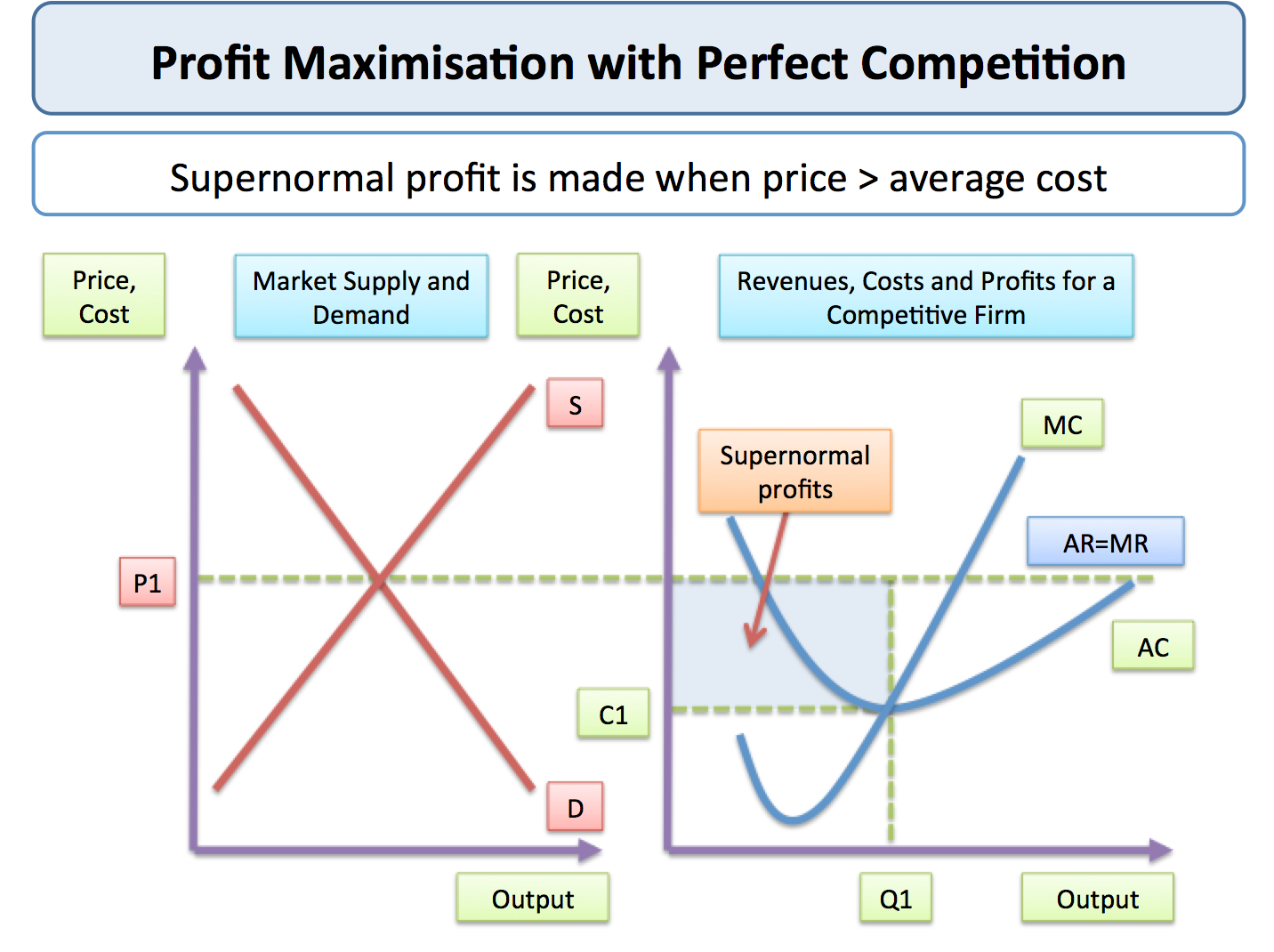
Perfect Competition Short Run Price And Output Economics Tutor2u In this chapter, we focus on perfect competition. however, in other chapters we will examine other industry types: monopoly and monopolistic competition and oligopoly. this free textbook is an openstax resource written to increase student access to high quality, peer reviewed learning materials. Perfect competition is a model of the market based on the assumption that a large number of firms produce identical goods consumed by a large number of buyers. the model of perfect competition also assumes that it is easy for new firms to enter the market and for existing ones to leave. and finally, it assumes that buyers and sellers have. Perfect competition is an idealized market structure in which equal and identical products are sold. imperfect competition can be found in monopolies and real life examples. it involves companies. This video provides an introductory overview of the main characteristics and assumptions of perfect competition, along with some examples. perfect competition video 1. activity 2: video the short run, the long run, and relevant diagrams. in perfect competition, there are different outcomes in both the short run and the long run.

Perfect Competition Economic Efficiency Tutor2u Economics Perfect competition is an idealized market structure in which equal and identical products are sold. imperfect competition can be found in monopolies and real life examples. it involves companies. This video provides an introductory overview of the main characteristics and assumptions of perfect competition, along with some examples. perfect competition video 1. activity 2: video the short run, the long run, and relevant diagrams. in perfect competition, there are different outcomes in both the short run and the long run.
Perfect Competition Mr Banks Economics Hub Resources Tutoring

Comments are closed.