Pdf Uncovering Mechanisms Of Brain Inflammation In Alzheimer S
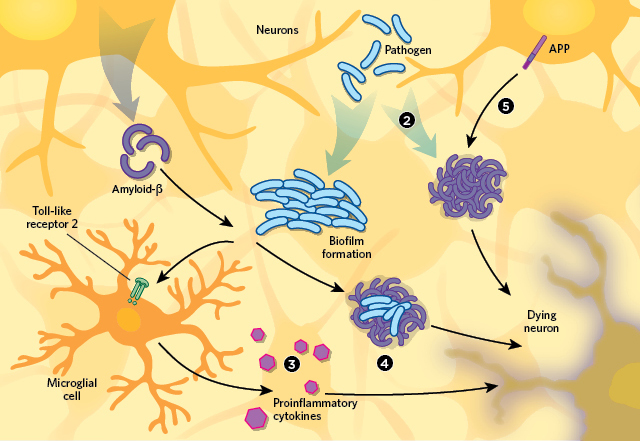
Infographic Brain Infection And Alzheimer S Disease Pathology The A chronic state of unresolved inflammation in alzheimer's disease (ad) is intrinsically involved with the remodeling of brain lipids. this review highlights the effect of carrying the apolipoprotein e ε4 allele (apoe4) on various brain cell types in promoting an unresolved inflammatory state. among …. Lipid droplets: a hallmark of ad pathology. in addition to amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, a hallmark of ad pathology identified in brain autopsies includes lipid‐based aggregations within both glial and neuronal cells, frequently referenced in alois alzheimer's writings as “adipose saccules,” also known as “lipoid granules” or droplets. 15 , 16 lipid droplets coordinate.

Neuroinflammation In Alzheimer S Disease The Lancet Neurology Abstract. alzheimer's disease (ad) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that is characterized by cognitive decline and the presence of two core pathologies, amyloid β plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. over the last decade, the presence of a sustained immune response in the brain has emerged as a third core pathology in ad. To better understand the impact of systemic inflammation on ad pathology, researcher looked into the effect of systemic inflammation on the removal or the deposition of aβ plaques in the brain (42). studies in tg2576 (43), pdapp (44), appswe (45), app ps1 (40, 46) and appnl g f (47) mice show an increase in aβ deposition upon lps induced. Micro and astroglial changes in alzheimer´s disease brain and app ps1 mice (a) cd11b positive microglia (blue) within a aβ deposit (brown) in the parietal cortex of a human ad brain section (bar = 50 μm). (b) activated, iba1 positive microglia (green) at a aβ plaque site (red) in a section of a app ps1 transgenic mouse (bar = 50 μm). The blood–brain barrier and ad. the vascular blood–brain barrier (bbb), which serves as the brain’s primary interface with the outside world, is vital to maintaining brain homeostasis, it regulates the entry and exit of biological substances and is essential for shielding the brain parenchyma from blood borne pathogens or exogenous substances into the central nervous system (takechi et.

Neuroinflammatory Cytokine Signaling And Alzheimer S Disease Nejm Micro and astroglial changes in alzheimer´s disease brain and app ps1 mice (a) cd11b positive microglia (blue) within a aβ deposit (brown) in the parietal cortex of a human ad brain section (bar = 50 μm). (b) activated, iba1 positive microglia (green) at a aβ plaque site (red) in a section of a app ps1 transgenic mouse (bar = 50 μm). The blood–brain barrier and ad. the vascular blood–brain barrier (bbb), which serves as the brain’s primary interface with the outside world, is vital to maintaining brain homeostasis, it regulates the entry and exit of biological substances and is essential for shielding the brain parenchyma from blood borne pathogens or exogenous substances into the central nervous system (takechi et. To uncover molecular changes underlying blood brain barrier dysfunction in alzheimer’s disease, we performed single nucleus rna sequencing in 24 alzheimer’s disease and control brains and. Alzheimer’s disease (ad), the most common form of dementia, is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid β (aβ) and hyperphosphorylated tau protein aggregates. importantly, aβ and tau species are able to activate astrocytes and microglia, which release several proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor α (tnf α) and interleukin 1β (il 1β), together with reactive.
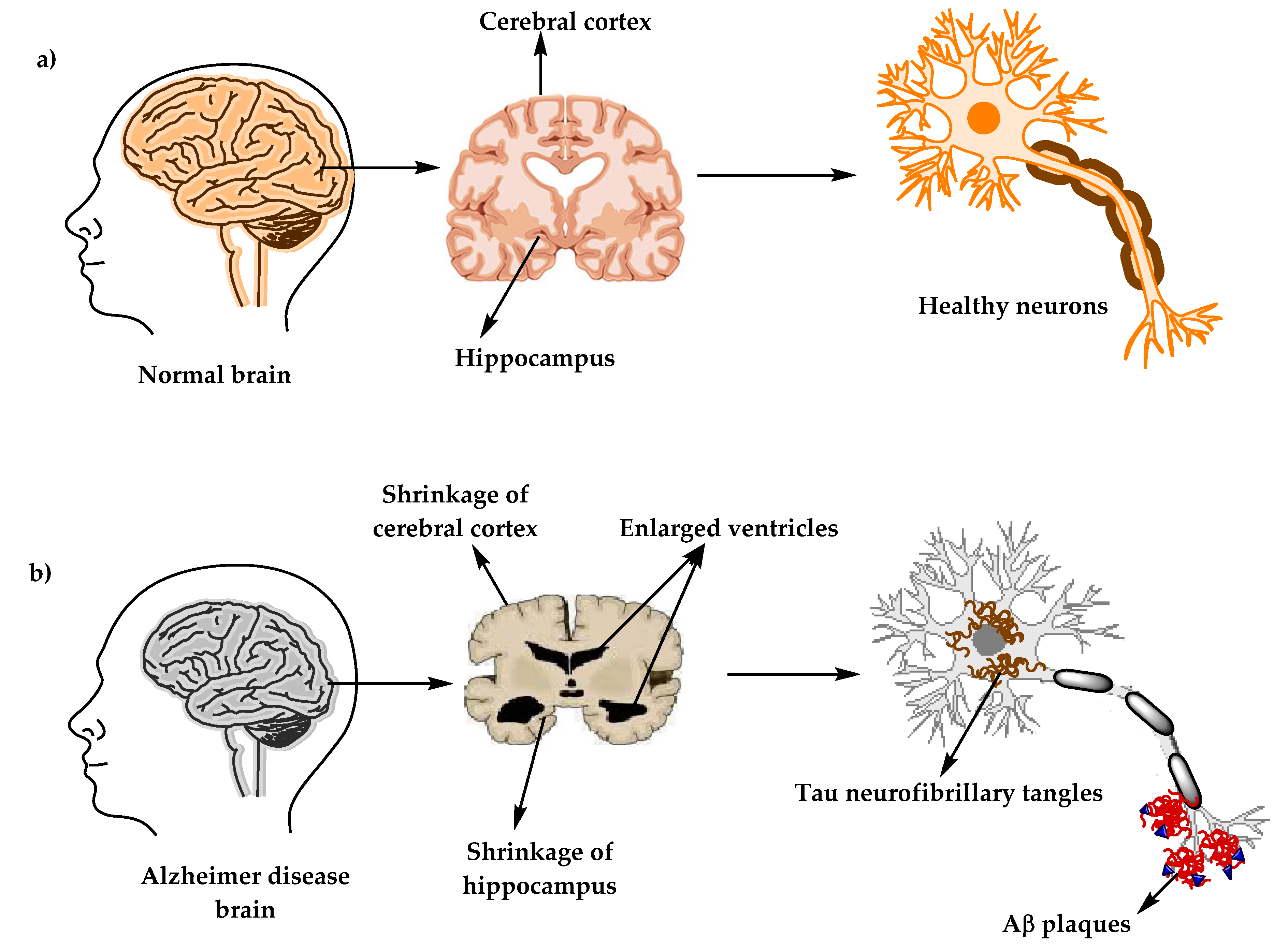
Molecules Free Full Text Comprehensive Review On Alzheimer S To uncover molecular changes underlying blood brain barrier dysfunction in alzheimer’s disease, we performed single nucleus rna sequencing in 24 alzheimer’s disease and control brains and. Alzheimer’s disease (ad), the most common form of dementia, is characterized by the accumulation of amyloid β (aβ) and hyperphosphorylated tau protein aggregates. importantly, aβ and tau species are able to activate astrocytes and microglia, which release several proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor α (tnf α) and interleukin 1β (il 1β), together with reactive.
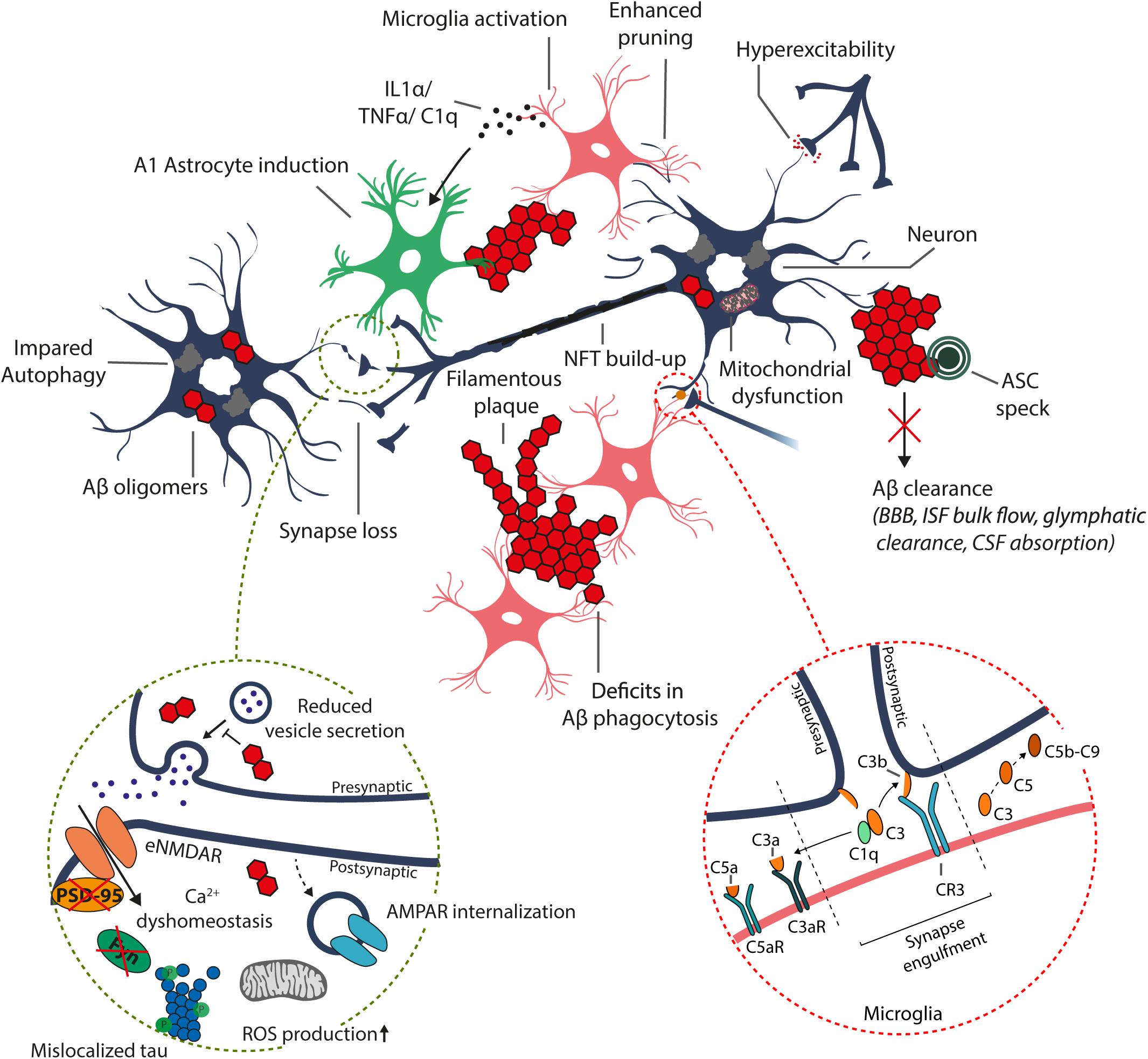
Frontiers Molecular Mechanisms Of Synaptotoxicity And

Implications Of Sleep Disturbance And Inflammation For Alzheimer S

Comments are closed.