Pdf Local Structure Of Amorphous Carbon Investigated By X Ray Total

Pdf Local Structure Of Amorphous Carbon Investigated By X Ray Total X ray total scattering measurement is the most suitable analysis to evaluate the local structure in matter, and it can be applied to many fields: crystalline materials 32 , glasses 33 , amorphous. Amorphous carbon is a promising candidate as an energy storage material. in this paper, we performed an x ray total scattering measurement, rmc modeling, and persistent homology analysis for.

Figure 3 From Amorphous Carbon Nanowires Investigated By Near Edge X Amorphous carbon is a promising candidate as an energy storage material. in this paper, we performed an x ray total scattering measurement, rmc modeling, and persistent homology analysis for amorphous carbon samples fabricated at two different heat treatment temperatures. according to the analysis o …. Using a combination of extended x ray absorption fine structure measurements, stochastic quenching (sq) calculations and voronoi tessellation analysis, the local atomic environments in thin films of amorphous sm \( {x}\) co \( {1 x}\) (\(x =\) 0.10, 0.22 and 0.35) are investigated and also compared with crystalline stoichiometric sm–co alloys of similar compositions. Amorphous carbon (a c) is a solid consisting of multiple types of bonding configurations that lack long range ordered structures and may exhibit deviations in interatomic distances and bond angles. Amorphous magnesium carbonate (amc) is formed as a precursor to crystalline magnesium carbonates and as a product of thermal decomposition of nesquehonite (nsq). in this study, the amcs formed during the crystallization and decomposition of nsq were investigated using x ray diraction (xrd) and atomic pair distribution function (pdf) methods.

2 The Structure Of An Amorphous Carbon Particle Adopted From Amorphous carbon (a c) is a solid consisting of multiple types of bonding configurations that lack long range ordered structures and may exhibit deviations in interatomic distances and bond angles. Amorphous magnesium carbonate (amc) is formed as a precursor to crystalline magnesium carbonates and as a product of thermal decomposition of nesquehonite (nsq). in this study, the amcs formed during the crystallization and decomposition of nsq were investigated using x ray diraction (xrd) and atomic pair distribution function (pdf) methods. The structure of a c:h films is complex, being comprised of an amorphous mixture of sp 2 and sp 3 hybridized carbon atoms combined with hydrogen atoms in the local structure . the chemical structure in terms of the coordination of carbon ( sp 2 and sp 3 hybridization) and hydrogen atoms is one of the most important factors governing the quality. Signals must be considered, especially considering the deviating structure of the top layer. for hydrogen free amorphous carbon films, the mass density is by. g cm3 strongly correlated with the sp3fraction s. q q (1.8 1.6 s) the mass density can be derived from the plasmon peak in the low energy eels.
Local Structure Of Amorphous Carbon Investigated By X Ray Total The structure of a c:h films is complex, being comprised of an amorphous mixture of sp 2 and sp 3 hybridized carbon atoms combined with hydrogen atoms in the local structure . the chemical structure in terms of the coordination of carbon ( sp 2 and sp 3 hybridization) and hydrogen atoms is one of the most important factors governing the quality. Signals must be considered, especially considering the deviating structure of the top layer. for hydrogen free amorphous carbon films, the mass density is by. g cm3 strongly correlated with the sp3fraction s. q q (1.8 1.6 s) the mass density can be derived from the plasmon peak in the low energy eels.

Figure 2 From Study Of Stacking Structure Of Amorphous Carbon By X Ray
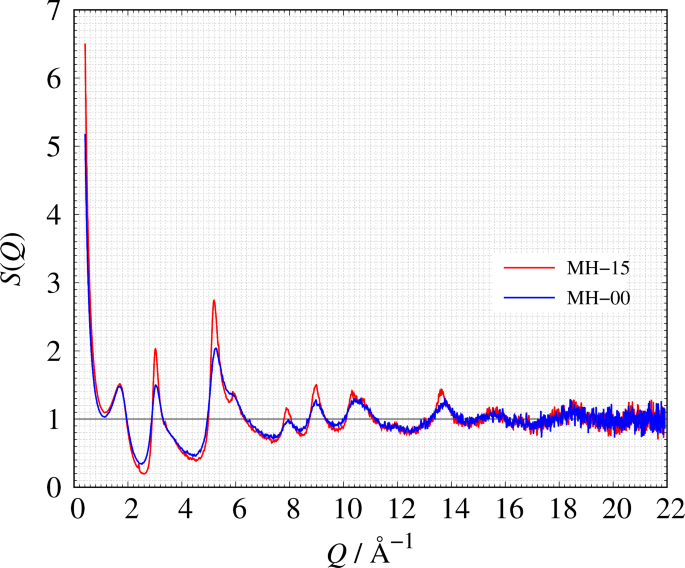
Local Structure Of Amorphous Carbon Investigated By X Ray Total

Comments are closed.