Pdb 101 Diabetes Mellitus Diabetes Mellitus Monitoring Diagnosis

Pdb 101 Global Health Diabetes Mellitus Monitoring Diagnosis The diagnosis of diabetes requires fasting glucose levels greater than 126 mg dl on two occasions. blood is drawn from the vein following overnight fasting (for fasting blood glucose levels) or at any random moment during the day (to measure random glucose levels). there may be some bruising, infection, and soreness at the site of puncture for. Blurry vision. slow healing of cuts bruises. weight loss. tingling, pain, or numbness in the hands feet. in more advanced stages of diabetes, the following symptoms and diabetes complications may also be seen. fainting and or dizziness (possibly due to sudden drops in blood glucose levels due to poor management or increased medication).

Pdb 101 Global Health Diabetes Mellitus Monitoring Diagnosis Complications resulting from large vessel damage may lead to cardiomyopathy, stroke, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoporosis, and the degenerative process of aging (singh et al., 2014). the major concern amongst these complications is myocardial infarction (heart attack). at present, it appears that blood glucose control does not significantly. This topic will review the clinical presentation, diagnosis, and initial evaluation of diabetes in nonpregnant adults. screening for and prevention of diabetes, the etiologic classification of diabetes mellitus, the treatment of diabetes, as well as diabetes during pregnancy are discussed separately. (see "screening for type 2 diabetes mellitus".). Gestational diabetes mellitus (gdm), which resembles type 2 diabetes more than type 1, develops during approximately 17% (ranging from 5% to 30%, depending on the screening method, diagnostic criteria used, and maternal age) of pregnancies, usually remits after delivery, and is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes later in. The national academy of clinical biochemistry (nacb) issued its “guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus” in 2002 . these recommendations were reviewed and updated with an evidence based approach, especially in key areas in which new evidence has emerged since the 2002.
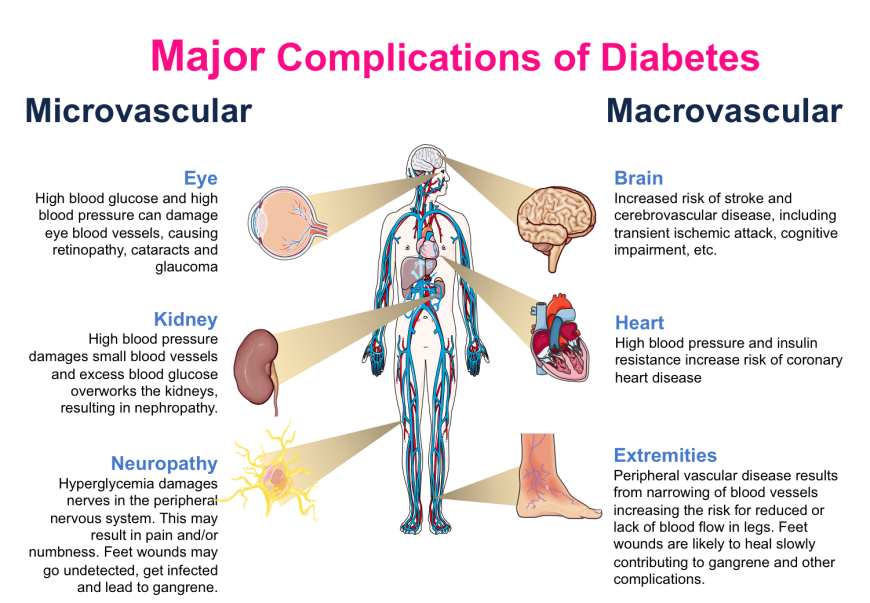
Pdb 101 Global Health Diabetes Mellitus Monitoring Complications Gestational diabetes mellitus (gdm), which resembles type 2 diabetes more than type 1, develops during approximately 17% (ranging from 5% to 30%, depending on the screening method, diagnostic criteria used, and maternal age) of pregnancies, usually remits after delivery, and is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes later in. The national academy of clinical biochemistry (nacb) issued its “guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus” in 2002 . these recommendations were reviewed and updated with an evidence based approach, especially in key areas in which new evidence has emerged since the 2002. Definition and description of diabetes mellitus. diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. the chronic hyperglycemia of diabetes is associated with long term damage, dysfunction, and failure of different organs, especially the eyes, kidneys. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder that affect many lives globally. diabetes can be caused by the absense or improper function of insulin. diabetes is classified into various types based on its causes. this timeline lists key events in the discovery of diabetes and its main treatment options.

Pdb 101 Global Health Diabetes Mellitus Monitoring Complications Definition and description of diabetes mellitus. diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both. the chronic hyperglycemia of diabetes is associated with long term damage, dysfunction, and failure of different organs, especially the eyes, kidneys. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder that affect many lives globally. diabetes can be caused by the absense or improper function of insulin. diabetes is classified into various types based on its causes. this timeline lists key events in the discovery of diabetes and its main treatment options.
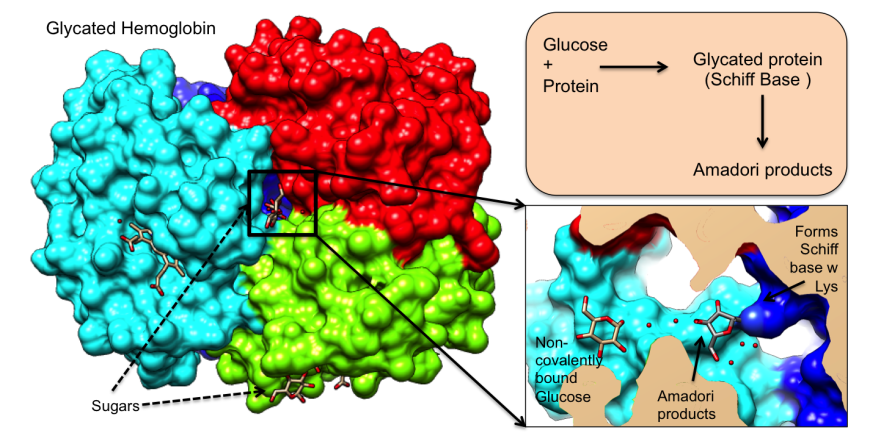
Pdb 101 Global Health Diabetes Mellitus Monitoring Diagnosis

Comments are closed.