Parkinson S Disease Nurse Key
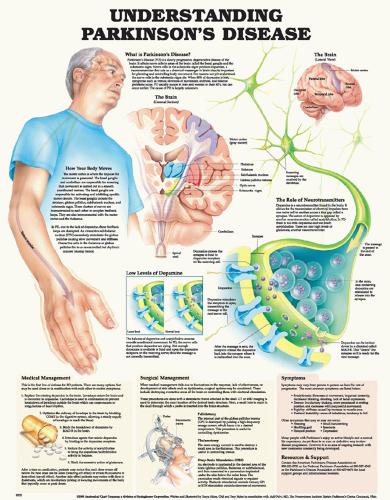
Parkinson S Disease Nurse Key Parkinson’s disease (pd) is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after alzheimer’s disease (ad). pd is characterized by a loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the basal ganglia. the major signs and symptoms include tremors. (at rest), rigidity, bradykinesia, and gait and balance disorders. The following are the nursing priorities for patients with parkinson’s disease: recognize and assess signs and symptoms of parkinson’s disease. monitor disease progression and assess motor and non motor symptoms. administer prescribed medications to manage symptoms, such as dopaminergic medications or anticholinergics.
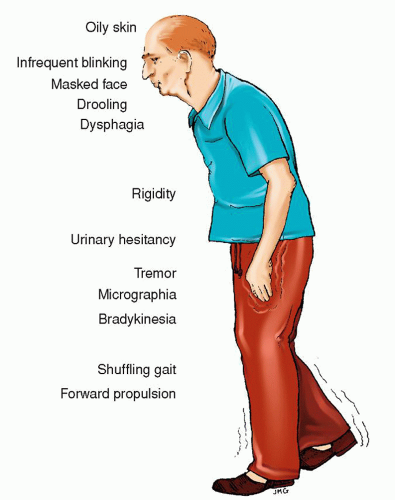
Parkinson S Disease Nurse Key Parkinson’s disease (pd) is a degenerative condition caused by the loss of dopamine, which disrupts the suppression of excitatory impulses and causes the extrapyramidal system to malfunction. it is a chronic, disabling condition that worsens over time. falls, poor self care, dysfunctional body systems, and depression can result from debilitation. The diagnosis of parkinson disease is clinical, and key disease features are bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremor. parkinson disease treatment in hospitals and nursing facilities: avoiding pitfalls. Recognize essential nursing care implications in different settings for people with parkinson’s. identify key non motor symptoms to determine relevant care management strategies. implement optimal communication strategies to use within intra and inter professional care teams to provide realistic expectations for people with parkinson’s and. Background: parkinson's disease nurse specialists (pdns) play an important role in the care for patients with parkinson's disease (pd) and their caregivers. until now, there were no nursing guidelines in pd, and interventions were based solely on daily clinical practice because there is no evidence to support the merits of nursing interventions.
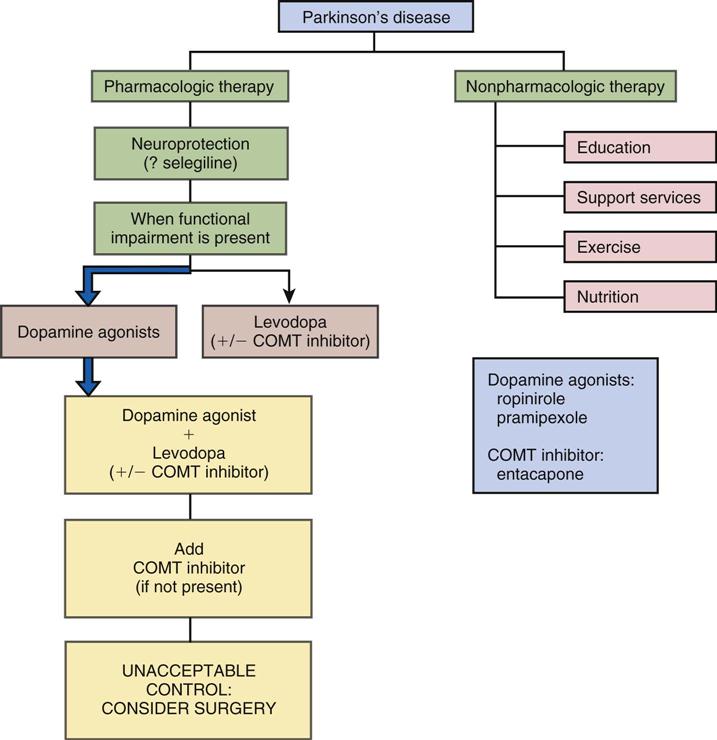
15 Drugs Used For Parkinson S Disease Nurse Key Recognize essential nursing care implications in different settings for people with parkinson’s. identify key non motor symptoms to determine relevant care management strategies. implement optimal communication strategies to use within intra and inter professional care teams to provide realistic expectations for people with parkinson’s and. Background: parkinson's disease nurse specialists (pdns) play an important role in the care for patients with parkinson's disease (pd) and their caregivers. until now, there were no nursing guidelines in pd, and interventions were based solely on daily clinical practice because there is no evidence to support the merits of nursing interventions. 10.3. deep brain stimulation, levodopa–carbidopa intestinal gel and best medical treatment for advanced parkinson’s disease. 10.4. deep brain stimulation compared with best medical treatment for earlier parkinson’s disease. 11. managing and monitoring impulse control disorder as an adverse effect of dopaminergic treatment. Parkinson disease (pd) is a slowly progressive, degenerative disease of the brain. it affects nerve cells in the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce dopamine, an important neurotransmitter that acts as a chemical messenger in brain circuits to plan and control body movement.

Parkinson S Disease Nursing Process 10.3. deep brain stimulation, levodopa–carbidopa intestinal gel and best medical treatment for advanced parkinson’s disease. 10.4. deep brain stimulation compared with best medical treatment for earlier parkinson’s disease. 11. managing and monitoring impulse control disorder as an adverse effect of dopaminergic treatment. Parkinson disease (pd) is a slowly progressive, degenerative disease of the brain. it affects nerve cells in the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra. nerve cells in the substantia nigra produce dopamine, an important neurotransmitter that acts as a chemical messenger in brain circuits to plan and control body movement.

Comments are closed.