Oxygenation Fluid Balance Respiratory Medicine Lecturio

Oxygenation Fluid Balance Respiratory Medicine Lecturio Youtube Sign up here and try our free content: lectur.io freecontentyt if you’re an medical educator or faculty member, visit: lectur.io medytb2u t. Respiratory failure is a syndrome that develops when the respiratory system is unable to maintain oxygenation and or ventilation. respiratory failure may be acute or chronic and is classified as hypoxemic, hypercapnic, or a combination of the two. a number of etiologies exist, including diseases of the lungs, cardiovascular, and nervous system.
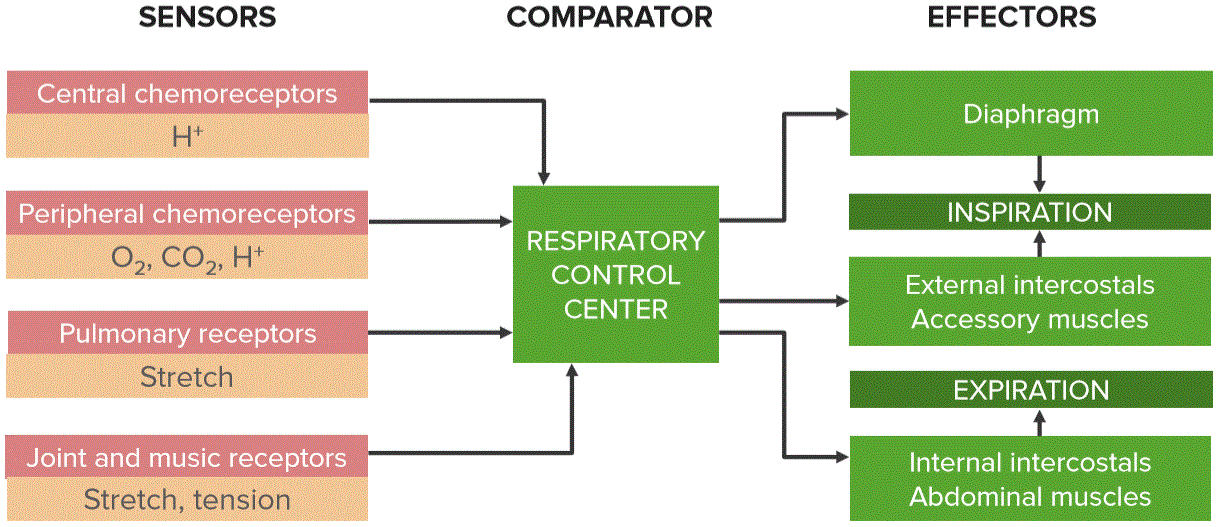
Respiratory Physiology Lecturio Online Medical Library Acid base balance. the ph of the blood is tightly regulated within the range 7.35–7.45 to ensure proper physiologic functions. large amounts of acid are generated each day through normal processes (aerobic anaerobic respiration respiration the act of breathing with the lungs, consisting of inhalation, or the taking into the lungs of the. Definition. respiratory acidosis is the process that results in an accumulation of carbon dioxide (co 2) due to abnormal gas exchange in the lungs. in primary respiratory acidosis, the arterial blood gas will show: ph ph the quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. acid base balance. < 7.35. The exchange of gases, primarily o 2 and co 2, is the purpose of the respiratory system. the removal of co 2 during expiration also helps to regulate the body’s acid base balance. acid base balance is measured by ph level. the body is sensitive to alterations in ph, and there is a narrow range of normal for ph: 7.35 to 7.45. The regulation of body fluid balance is a key concern in health and disease and comprises three concepts. the first concept pertains to the relationship between total body water (tbw) and total effective solute and is expressed in terms of the tonicity of the body fluids. disturbances in tonicity are the main factor responsible for changes in.

Respiratory System Physiology Nursing Video Lecturio The exchange of gases, primarily o 2 and co 2, is the purpose of the respiratory system. the removal of co 2 during expiration also helps to regulate the body’s acid base balance. acid base balance is measured by ph level. the body is sensitive to alterations in ph, and there is a narrow range of normal for ph: 7.35 to 7.45. The regulation of body fluid balance is a key concern in health and disease and comprises three concepts. the first concept pertains to the relationship between total body water (tbw) and total effective solute and is expressed in terms of the tonicity of the body fluids. disturbances in tonicity are the main factor responsible for changes in. Oxygenation. supine position dependent alveoli are in the back (dorsal). the heart and mediastinum add increased pressure to the lungs, which can collapse the dorsal alveoli. the added pressure in this position can increase the risk of atelectasis. dependent alveoli are in the front (ventral). fluid can shift from back to front. The combination of ecmo and crrt can effectively improve fluid balance and electrolyte disturbances. a systematic review showed that in ecmo survivors receiving crrt, the overall fluid balance was lower than that in non crrt survivors . in our study, the use of crrt was not statistically significantly associated with 28 day mortality (hr, 0.482.

Comments are closed.