Our Star Sun Central Galaxy
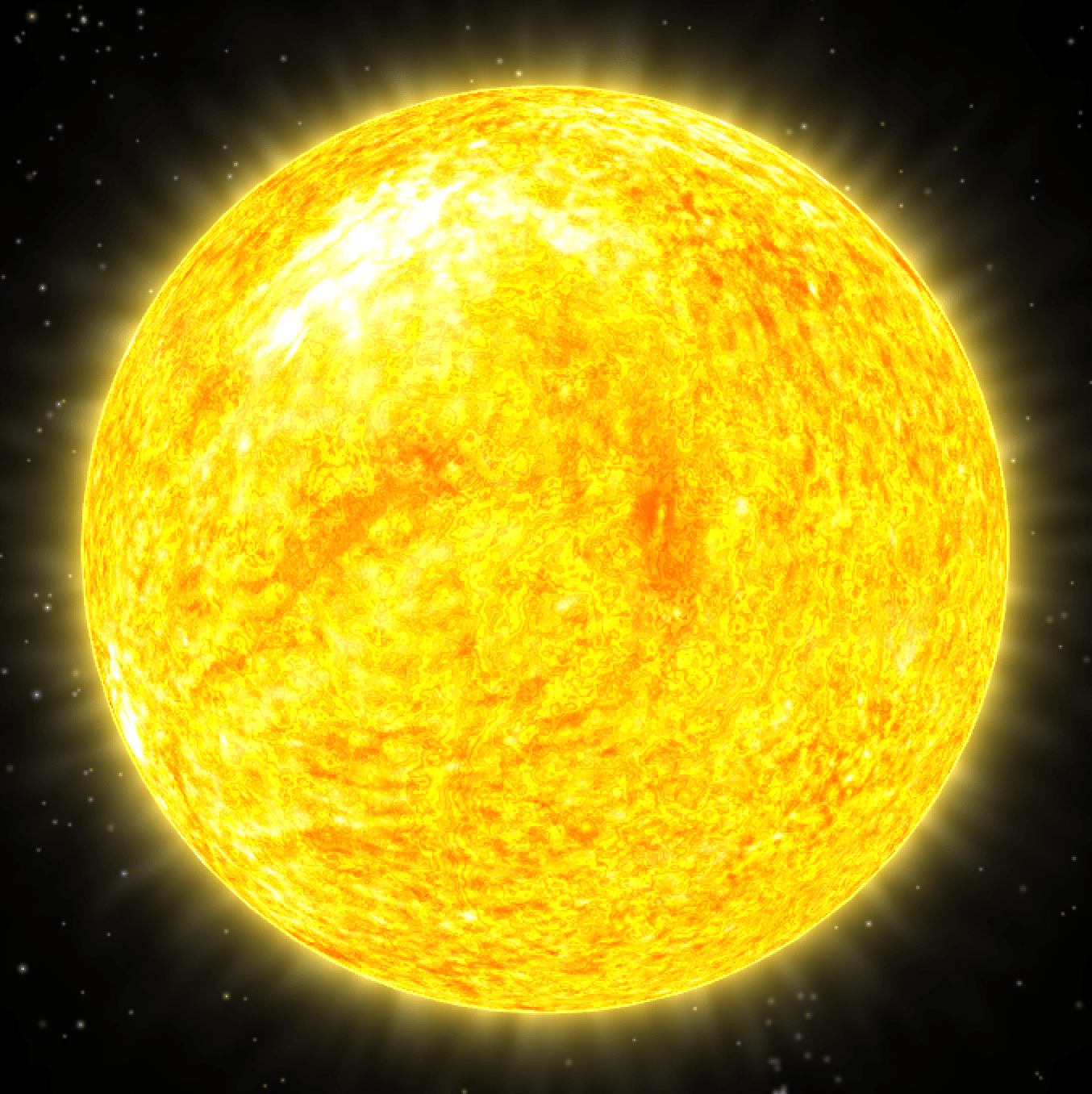
Our Star Sun Central Galaxy The death of sun. sun is now in a very stable variable star, with small changes in luminosity over a period of 11 years. but sun will eventually get unstable and too bright to support life. in a billion years, sun will already get so luminous that earth will get pushed out of the habitable zone. The closest star to our sun is about four light years away; in the center of the galaxy, stars are only 0.4–0.04 light years apart. in the inner 10,000 light year region of the milky way, the galaxy’s spiral arm structure has broken down and transformed into a “bulge” of stars. at its heart—and the dominant force in that area of the.

Our Star Sun Central Galaxy Lower level. our sun is an ordinary star, just one among hundreds of billions of stars in the milky way galaxy. as the only star we can observe in detail, it provides a basis for our understanding of all stars. the sun is composed almost entirely of hydrogen and helium gas. multimillion degree temperatures in its dense core sustain nuclear. About the episode: the sun is our closest star. billions of years ago, it shaped the formation of our home planet and the beginning of life on earth. today, it provides the heat and energy that powers our civilization, but it can also disrupt our technology and spacecraft through explosive outbursts of radiation. The sun is the star at the center of the solar system. it is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. The front of this lithograph features images of the sun, a coronal mass ejection, and sunspots from nasa’s soho and trace missions. the back of the lithograph has general information, significant dates and interesting facts about the sun. our star — the sun lithograph [266kb pdf file] view high resolution [1.3mb pdf file] this lithograph is.

Our Star Sun Central Galaxy The sun is the star at the center of the solar system. it is a massive, nearly perfect sphere of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core, radiating the energy from its surface mainly as visible light and infrared radiation with 10% at ultraviolet energies. The front of this lithograph features images of the sun, a coronal mass ejection, and sunspots from nasa’s soho and trace missions. the back of the lithograph has general information, significant dates and interesting facts about the sun. our star — the sun lithograph [266kb pdf file] view high resolution [1.3mb pdf file] this lithograph is. It’s not the most common type: much smaller red dwarfs make up about 75% of all the stars in our galaxy. it’s also a singleton, whereas almost half of sun like stars, are part of a stellar group. regardless whether the sun is typical, it’s certainly stable: as a main sequence g 2 star in the prime of its life cycle, the sun’s consistent. The connection and interactions between the sun and earth drive the seasons, ocean currents, weather, climate, radiation belts and auroras. though it is special to us, there are billions of stars like our sun scattered across the milky way galaxy. the sun has many names in many cultures. the latin word for sun is “sol,” which is the main.

Comments are closed.