Osce Essentials Ecg Interpretation Part 2 Rate Rhythm And Axis

Osce Essentials Ecg Interpretation Part 2 Rate Rhythm And Axis Axis got you twisted? join us for a concise look at how to systematically interpret an ecg in an osce! determine the rate, rhythm and axis while sounding lik. The standard ecg paper speed is 25 mm sec and therefore: 1 mm (1 ‘small square’) = 0.04 seconds. 5 mm (1 ‘large square’) = 0.2 seconds. on the vertical axis,10 mm (10 ‘small squares’) is equal to 1 mv when standard calibration is used. please refer to the ecg tracing below to familiarize yourself with the waves of the ecg and how.

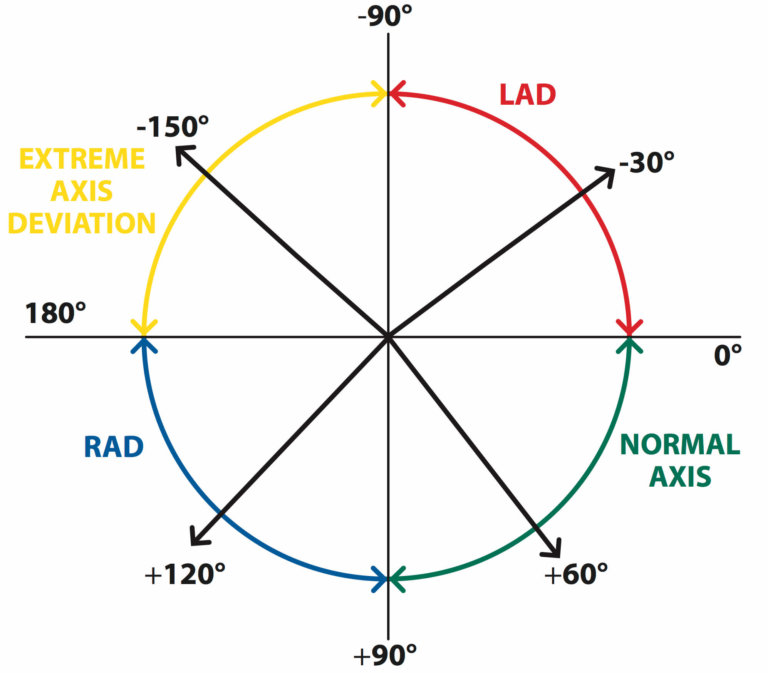
The Basics Of Ecg Interpretation Part 2 Rate Rhythm And Axis Use rhythm strip. rate: calculate by dividing 300 by number of large squares between r peaks or, if irregular, total r waves on ecg multiplied by 6 (ecg is 10 seconds long) sinus bradycardia <60 (physical fitness, hypothermia, hypothyroidism, sinoatrial node disease, β blockers digoxin). What are the values for proper calibration of ecg? speed: voltage: standard 12 lead ecg length: rhythm strip length: other leads length: scan p waves (positive in i, ii, avf and negative in avr. make sure there is a p before every qrs and qrs after every p). Confirm details. before beginning ecg interpretation, you should check the following details: confirm the name and date of birth of the patient matches the details on the ecg. check the date and time that the ecg was performed. check the calibration of the ecg (usually 25mm s and 10mm 1mv). Left axis deviation = qrs axis less than 30°. right axis deviation = qrs axis greater than 90°. extreme axis deviation = qrs axis between 90° and 180° (aka “northwest axis”). note that in paediatric ecg interpretation, the cardiac axis lies between 30 to 190 degrees at birth and moves leftward with age. cardiacaxis .
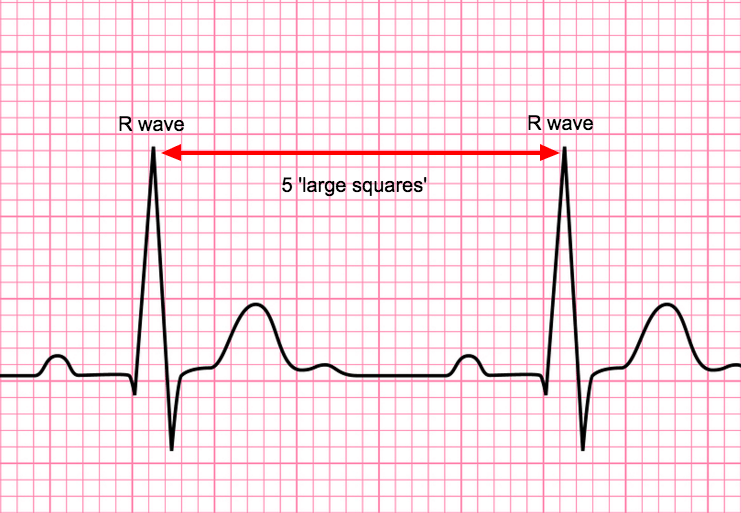
The Basics Of Ecg Interpretation Part 2 Rate Rhythm And Axis Confirm details. before beginning ecg interpretation, you should check the following details: confirm the name and date of birth of the patient matches the details on the ecg. check the date and time that the ecg was performed. check the calibration of the ecg (usually 25mm s and 10mm 1mv). Left axis deviation = qrs axis less than 30°. right axis deviation = qrs axis greater than 90°. extreme axis deviation = qrs axis between 90° and 180° (aka “northwest axis”). note that in paediatric ecg interpretation, the cardiac axis lies between 30 to 190 degrees at birth and moves leftward with age. cardiacaxis . 1. the basics. in this first video we walk you through every aspect of the basics of the ecg including: describe the parts of the ecg. rate, rhythm, axis. p wave, pr interval, qrs complex, st segment, t wave, qt interval. identify the features of a normal ecg. references and further reading. Normal heart rates in children. newborn: 110 – 150 bpm. 2 years: 85 – 125 bpm. 4 years: 75 – 115 bpm. 6 years : 60 – 100 bpm. other paper speeds: 50mm sec. doubling the standard rate will cause the ecg to appear drawn out or wider complex than 25mm sec paper speeds.
The Basics Of Ecg Interpretation Part 2 Rate Rhythm And Axis 1. the basics. in this first video we walk you through every aspect of the basics of the ecg including: describe the parts of the ecg. rate, rhythm, axis. p wave, pr interval, qrs complex, st segment, t wave, qt interval. identify the features of a normal ecg. references and further reading. Normal heart rates in children. newborn: 110 – 150 bpm. 2 years: 85 – 125 bpm. 4 years: 75 – 115 bpm. 6 years : 60 – 100 bpm. other paper speeds: 50mm sec. doubling the standard rate will cause the ecg to appear drawn out or wider complex than 25mm sec paper speeds.

Ecg Interpretation 2 Osce Station Oscehub

Comments are closed.