Orthodontic Wires Grouped According To Type And Cross Sectional

Orthodontic Wires Grouped According To Type And Cross Sectional Download table | orthodontic wires grouped according to type and cross sectional diameter (test at 37.0uc) a from publication: load deflection characteristics and force level of nickel titanium. The same operator calculated the values yielded by the three samples for each of the parameters considered (average plateau force, plateau length, and plateau slope) and for each type of wire tested. data pertaining to each type of wire, grouped according to cross sectional diameters, are summarized in table 2.

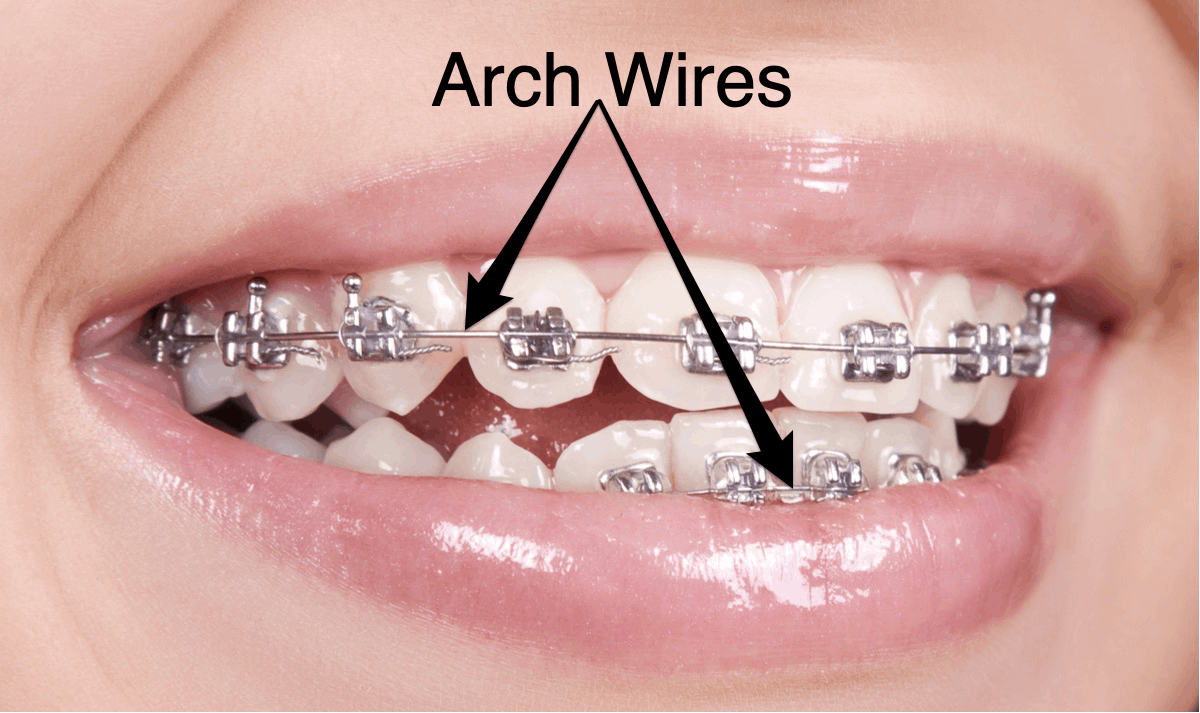
Orthodontic Wires Grouped According To Type And Cross Sectional Wires of the same cross section as well as less permanent deformation after deflection. since then, a number of studies have been conducted in an attempt to produce orthodontic wires with similar properties, a goal achieved only in 1986 with the introduction of the “japanese niti”. these alloys were produced by the gac com. Wires may have relatively simple or rather convoluted geometries. the most prominent wire in clinical orthodontic treatment is the "arch wire." marketed in just two, symmetrical, cross sectional sh pes, itssizes arenumerous, and arch wires are manufactured of a variety of metallic alloys andcompositions. the primary objective of this article. The most prominent wire in clinical orthodontic treatment is the “arch wire.”. marketed in just two, symmetrical, cross sectional shapes, its sizes are numerous, and arch wires are manufactured of a variety of metallic alloys and compositions. the primary objective of this article is to trace the history of arch wires over the past century. 1.4. orthodontic alloys. there are four major orthodontic alloys in current widespread use for orthodontic wires, brackets, and other appliances: stainless steel, cobalt (co)–chromium (cr), niti, and beta titanium. each of these alloys has advantageous factors for clinical selection, along with some concerns.

Orthodontic Wires Grouped According To Type And Cross Sectional The most prominent wire in clinical orthodontic treatment is the “arch wire.”. marketed in just two, symmetrical, cross sectional shapes, its sizes are numerous, and arch wires are manufactured of a variety of metallic alloys and compositions. the primary objective of this article is to trace the history of arch wires over the past century. 1.4. orthodontic alloys. there are four major orthodontic alloys in current widespread use for orthodontic wires, brackets, and other appliances: stainless steel, cobalt (co)–chromium (cr), niti, and beta titanium. each of these alloys has advantageous factors for clinical selection, along with some concerns. Background the aim of this study was the characterization of mechanical properties of representative types of orthodontic wires employing instrumented indentation testing (iit) according to iso 14577. methods segments were cut from ten wires. the first six are made of stainless steel (ss), two are made of ni ti, and the last two are made of titanium molybdenum alloys (tma). then, the martens. Orthodontic wires grouped according to type and cross sectional dimension (tested at 37°c). the average increase in plateau length, force and slope between m5 thermal copper niti and other.

Orthodontic Wires Grouped According To Type And Cross Sectional Background the aim of this study was the characterization of mechanical properties of representative types of orthodontic wires employing instrumented indentation testing (iit) according to iso 14577. methods segments were cut from ten wires. the first six are made of stainless steel (ss), two are made of ni ti, and the last two are made of titanium molybdenum alloys (tma). then, the martens. Orthodontic wires grouped according to type and cross sectional dimension (tested at 37°c). the average increase in plateau length, force and slope between m5 thermal copper niti and other.
Different Wire Sizes For Braces At Matthew Amundsen Blog

Comments are closed.