Obesity And Metabolic Syndrome Clinical Medicine

Obesity And Metabolic Syndrome Clinical Sciences Osmosis Video Library Keywords: metabolic syndrome, exercise medicine, abdominal obesity, adiposopathy. background. metabolic syndrome is defined as a cluster of at least three out of five clinical risk factors: abdominal (visceral) obesity, hypertension, elevated serum triglycerides, low serum high density lipoprotein (hdl) and insulin resistance . Clinical medicine; emergency medicine (bmi, ≥25) or obesity in the clinical and upper body subcutaneous adipose tissue mass are consistent with the diagnosis of a metabolic syndrome. 24.
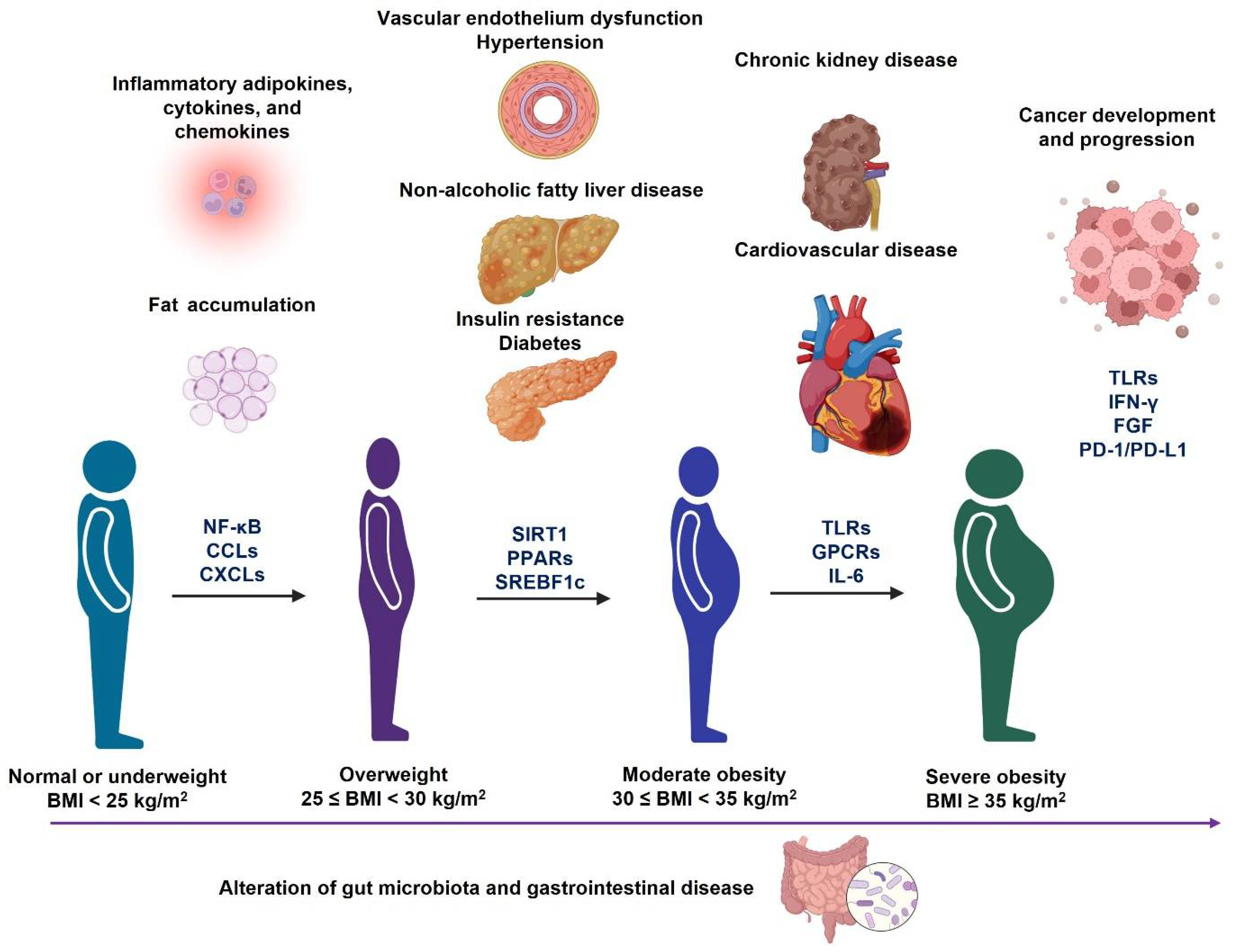
The Related Metabolic Diseases And Treatments Of Obesity Encyclopedia The clinical presentation of metabolic syndrome is variable and depends on the underlying atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. the common signs of metabolic syndrome include abdominal obesity with high body mass index and increased waist circumference, elevated blood pressure, and signs of insulin resistance. metabolic syndrome has serious. Obesity is an epidemic and a public health threat. medical weight management remains one of the options for the treatment of excess weight and recent advances have revolutionized how we treat, and more importantly how we will be treating obesity in the near future. metreleptin and setmelanotide are currently indicated for rare obesity syndromes, and 5 other medications (orlistat, phentermine. The predominant underlying risk factors for the syndrome appear to be abdominal obesity 2–4 and insulin resistance 5,6; other associated conditions can be physical inactivity, 3,7 aging, 8 and hormonal imbalance. 9 an atherogenic diet (eg, a diet rich in saturated fat and cholesterol) can enhance risk for developing cardiovascular disease in people with the syndrome, although this diet is. Obesity, which is the most common cause of insulin resistance in children, 4 is also associated with dyslipidemia, 5 type 2 diabetes, 6 and long term vascular complications. 7–9 in a sample of.

Obesity And Metabolic Syndrome Clinical Sciences Osmosis Video Library The predominant underlying risk factors for the syndrome appear to be abdominal obesity 2–4 and insulin resistance 5,6; other associated conditions can be physical inactivity, 3,7 aging, 8 and hormonal imbalance. 9 an atherogenic diet (eg, a diet rich in saturated fat and cholesterol) can enhance risk for developing cardiovascular disease in people with the syndrome, although this diet is. Obesity, which is the most common cause of insulin resistance in children, 4 is also associated with dyslipidemia, 5 type 2 diabetes, 6 and long term vascular complications. 7–9 in a sample of. This phenomenon poses serious health risks because obesity can progressively cause a wide range of diseases such metabolic syndrome, non alcoholic fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. 1 to resolve obesity, a negative energy balance, in which energy expenditure is greater than energy intake, must be encouraged. Abdominal obesity was recognized globally as a crucial clinical indicator for the early identification of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes 8,9, individuals with metabolic syndrome face a.

Obesity And Associated Metabolic Disorders Download Scientific Diagram This phenomenon poses serious health risks because obesity can progressively cause a wide range of diseases such metabolic syndrome, non alcoholic fatty liver disease, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. 1 to resolve obesity, a negative energy balance, in which energy expenditure is greater than energy intake, must be encouraged. Abdominal obesity was recognized globally as a crucial clinical indicator for the early identification of cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes 8,9, individuals with metabolic syndrome face a.

Comments are closed.