Numerical Modelling Glossary

Numerical Modelling Glossary Refs: plummer and phillips 2003. 3 dimensional (3d). a kind of spatially distributed model using the whole domain with the ice flow calculated for different depths through the ice column. numerical models are one of two fundamental kinds: flowline models and spatially distributed models. The world. a well chosen model facilitates the grasp of a new phenomenon and can be an effective heuristic tool in the search for explanations. numerical modeling is an activity distinct from computation. the endless printouts of numbers generated by computers are meaningless outside a system of knowledge and rationality that stems from human.
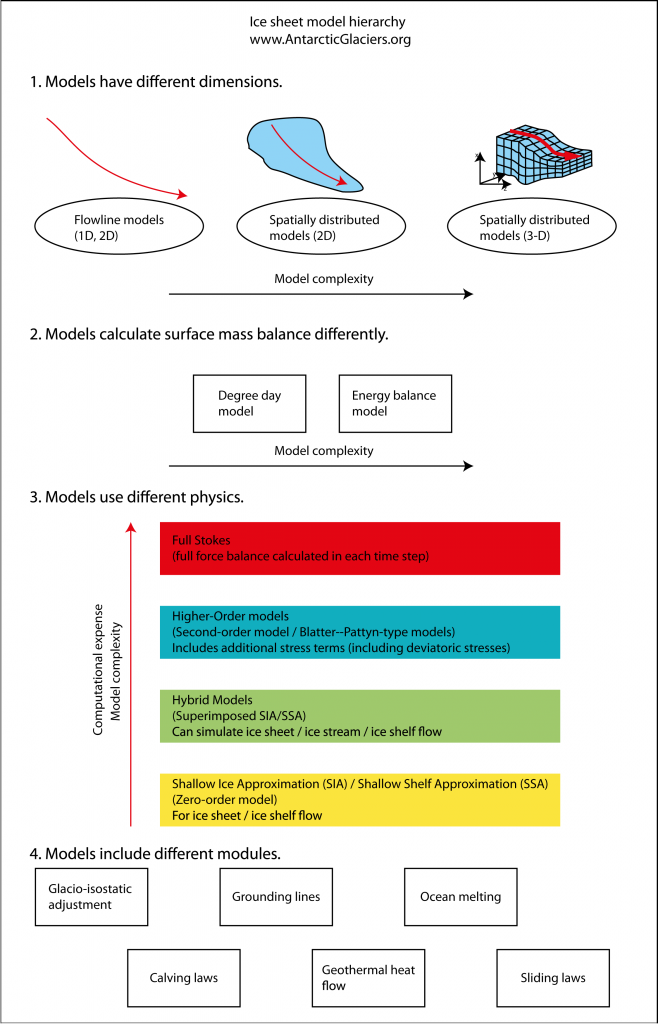
Numerical Modelling Glossary Models are therefore usually verified (the model physics tested against good models or good analytical solutions) (e.g., 3 5) and validated (run against a period for which observations are available, and tested against these observations) (e.g., 6). model inputs and outputs. numerical glacier and ice sheet models need input data. Numerical ice sheet models. degree day models: modelling glacier melt; glacier response to climate change; mountain glacier models; ice sheet modelling; a introduction to the hierarchy of ice sheet models; numerical glacier modelling glossary; southern annular mode; global ocean circulation; uk climate change arcgis stories; glacier processes. Numerical modeling refers to the process of using mathematical equations and algorithms to simulate and predict real world phenomena or systems. it involves representing complex physical, biological, or engineering problems as a set of mathematical equations and then solving these equations using computational methods. Geodynamic modelling provides a powerful tool to investigate processes in the earth’s crust, mantle and core. to ensure high quality modelling studies, fair external interpretation, and sensible use of published work, a basic understanding of numerical modelling is necessary. the earth's interior spans massive scales, both in time and space.

Numerical Modelling Glossary Numerical modeling refers to the process of using mathematical equations and algorithms to simulate and predict real world phenomena or systems. it involves representing complex physical, biological, or engineering problems as a set of mathematical equations and then solving these equations using computational methods. Geodynamic modelling provides a powerful tool to investigate processes in the earth’s crust, mantle and core. to ensure high quality modelling studies, fair external interpretation, and sensible use of published work, a basic understanding of numerical modelling is necessary. the earth's interior spans massive scales, both in time and space. In geology, numerical modeling is a widely applied technique to tackle complex geological problems by computational simulation of geological scenarios. numerical modeling uses mathematical models to describe the physical conditions of geological scenarios using numbers and equations. [2] nevertheless, some of their equations are difficult to. Basic concepts. numerical modeling involves selecting an appropriate set of equations to simulate the behavior of the coastal system under study and then solving the equations using suitable numerical techniques. other elements of numerical modeling are verification, validation, and calibration (see figure n35 for a description of the main.

Comments are closed.