Noise Induced Hearing Loss Hearing Loss Association Of America
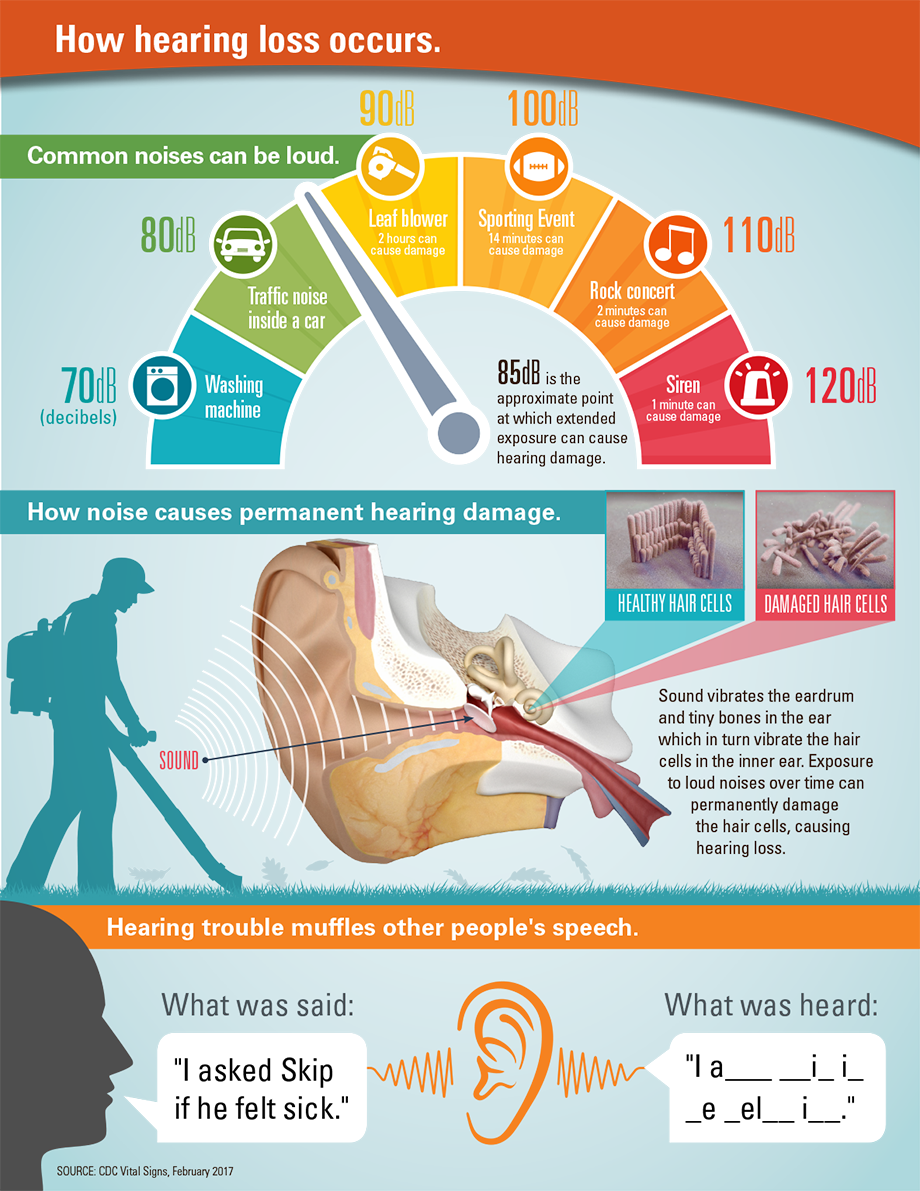
Noise Induced Hearing Loss Hearing Loss Association Of America Noise induced hearing loss (nihl) is an increasingly common condition caused by exposure to loud sounds or sudden intense noises. it can affect people of all ages and may be temporary or permanent. nihl occurs when the delicate sensory hair cells in the inner ear are damaged by noise. the effects of noise exposure are cumulative, meaning the. Hearing loss is a growing public health crisis affecting millions. young people especially are being diagnosed with noise induced hearing loss at increasing rates. we’re all at risk, no matter our age, and hlaa is working to share important messages of prevention with all americans. noise induced hearing loss is irreversible and mostly.

Noise Induced Hearing Loss Nihl Hearing Loss From Loud Noise Mild: hearing loss of 26 to 40 decibels. you may miss sounds such as people whispering, the hum of a refrigerator or a babbling brook. moderate: hearing loss of 41 to 60 decibels. you might have trouble hearing the television, falling rain, phone calls or group conversations. severe: hearing loss of 61 to 80 decibels. However, long or repeated exposure to sounds at or above 85 dba can cause hearing loss. the louder the sound, the shorter the amount of time it takes for nihl to happen. here are the average decibel ratings of some familiar sounds: normal conversation. 60 70 dba. movie theater. 74 104 dba. motorcyles and dirt bikes. 80 110 dba. Noise induced hearing loss. approximately 40 million american adults may have hearing loss resulting from noise exposure. 1 noise induced hearing loss is caused by damage to the hair cells found in the inner ear. hair cells are small sensory cells that convert the sounds we hear (sound energy) into electrical signals that travel to the brain. A. morgan selleck, md, hamid r. djalilian, md, and isaac d. erbele, md, hearing committee members. approximately 23 million americans aged 20 and older suffer from noise induced hearing loss (nihl). 1 nihl is the most significant preventable cause of hearing loss in the united states. 2 nihl has traditionally been defined as occurring at 3, 4.

What Is Noise Induced Hearing Loss Hearing Direct Us Noise induced hearing loss. approximately 40 million american adults may have hearing loss resulting from noise exposure. 1 noise induced hearing loss is caused by damage to the hair cells found in the inner ear. hair cells are small sensory cells that convert the sounds we hear (sound energy) into electrical signals that travel to the brain. A. morgan selleck, md, hamid r. djalilian, md, and isaac d. erbele, md, hearing committee members. approximately 23 million americans aged 20 and older suffer from noise induced hearing loss (nihl). 1 nihl is the most significant preventable cause of hearing loss in the united states. 2 nihl has traditionally been defined as occurring at 3, 4. Noise induced hearing loss can have a significant negative impact on your quality of life. you may have difficulty following conversation or communicating with friends and family. this can ultimately lead to an avoidance of social situations. fortunately, noise induced hearing loss can often be successfully managed with hearing aids or implants. Noise induced hearing loss (nihl) may be acute or chronic. acute noise exposure, or acoustic trauma, may, depending on the intensity of the exposure, result in reversible or irreversible hearing loss from explosions, loud music, and other short duration, high amplitude sounds. chronic noise exposure, on the other hand, can cause various.

Noise Induced Hearing Loss Everything You Need To Know Triton Hearing Noise induced hearing loss can have a significant negative impact on your quality of life. you may have difficulty following conversation or communicating with friends and family. this can ultimately lead to an avoidance of social situations. fortunately, noise induced hearing loss can often be successfully managed with hearing aids or implants. Noise induced hearing loss (nihl) may be acute or chronic. acute noise exposure, or acoustic trauma, may, depending on the intensity of the exposure, result in reversible or irreversible hearing loss from explosions, loud music, and other short duration, high amplitude sounds. chronic noise exposure, on the other hand, can cause various.

Comments are closed.