Neurology Motor Pathways

Accessphysiotherapy Motor Pathways Pathways Neurology Teaching The test will help the clinician to determine whether or not the lesion is occurring in the upper motor neuron versus the lower motor neuron. as is the case with every clinical examination, the practitioner must obtain informed consent before commencing the test. this examination focuses on the upper and lower limbs. The dorsal column system (sometimes referred to as the dorsal column–medial lemniscus) and the spinothalamic tract are two major pathways that bring sensory information to the brain (figure 14.5.1). the sensory pathways in each of these systems are composed of three successive neurons.

Neurology Motor Pathways Youtube Extrapyramidal tracts – these tracts originate in the brain stem, carrying motor fibres to the spinal cord. they are responsible for the involuntary and automatic control of all musculature, such as muscle tone, balance, posture and locomotion. there are no synapses within the descending pathways. The ascending and descending tracts are the first two articles, which cover the anatomy of the sensory and motor pathways of the central nervous system respectively. there are also articles on the visual pathways and auditory pathways to help you understand the intricacies of these important senses. the ascending tracts refer to the neural. Because the second order neurons are insignificant, we use only a two order system for the descending (motor) tracts. this way, the first neuron in the pathway (the upper motor neuron) arises in the cerebral cortex or brainstem, descends along the spinal cord and synapses in the anterior gray horn. the second neuron in the pathway (lower motor. While the term “motor neuron” evokes the idea that there is only one type of neuron that conducts movement, this is far from the truth. in fact, within the classification of a “motor neuron,” there lies both upper and lower motor neurons, which are entirely different in terms of their origins, synapse points, pathways, neurotransmitters, and lesion characteristics. overall, motor.
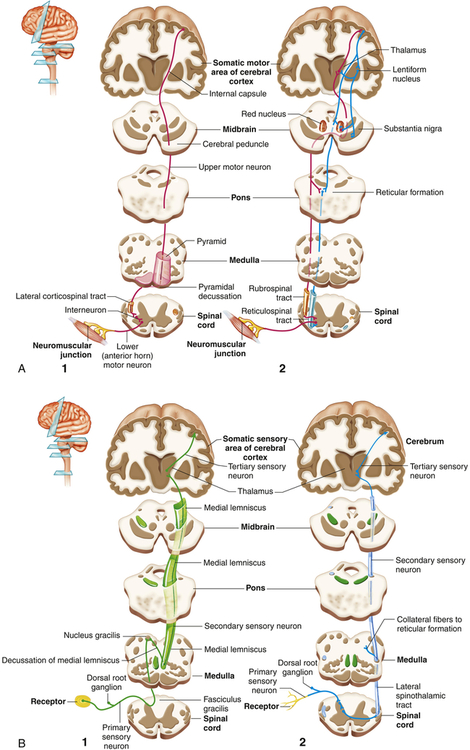
Structure And Function Of The Neurologic System Basicmedical Key Because the second order neurons are insignificant, we use only a two order system for the descending (motor) tracts. this way, the first neuron in the pathway (the upper motor neuron) arises in the cerebral cortex or brainstem, descends along the spinal cord and synapses in the anterior gray horn. the second neuron in the pathway (lower motor. While the term “motor neuron” evokes the idea that there is only one type of neuron that conducts movement, this is far from the truth. in fact, within the classification of a “motor neuron,” there lies both upper and lower motor neurons, which are entirely different in terms of their origins, synapse points, pathways, neurotransmitters, and lesion characteristics. overall, motor. The most important motor pathways of the cns. corticospinal and corticonuclear tract (tractus corticospinalis et corticonuclearis) the pyramidal tract provides voluntary control of muscular movements. it consists of two distinct pathways, the corticonuclear tract and the corticospinal tract. the corticospinal tract carries motor signals from. List the components of the basic processing stream for the motor system; describe the pathway of descending motor commands from the cortex to the skeletal muscles; compare different descending pathways, both by structure and function; explain the initiation of movement from the neurological connections.

Comments are closed.